您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇文章為大家展示了怎么在Java中實現哈希表,內容簡明扼要并且容易理解,絕對能使你眼前一亮,通過這篇文章的詳細介紹希望你能有所收獲。
public class HashBuck {
class Node {
public int key;
int value;
Node next;
Node(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
public int usedSize;
public Node[] array;
HashBuck() {
this.array = new Node[8];
this.usedSize = 0;
}
//JDk1.7及之前是頭插法
public void put1(int key, int value) {
int index = key % this.array.length;
Node node = new Node(key, value);
Node cur = array[index];
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key == key) {
cur.value = value;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
node.next = array[index];
array[index] = node;
this.usedSize++;
if (loadFactor() > 0.75) {
resize1();
}
}
public double loadFactor() {
return this.usedSize / this.array.length * 1.0;
}
}//JDK1.8是尾插法
public Node findLast(Node head) {
if (head == null) return head;
Node cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
public void put2(int key, int value) {
int index = key % this.array.length;
Node node = new Node(key, value);
Node cur = array[index];
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key == key) {
cur.value = value;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
Node last = findLast(array[index]);
if (last == null) {
array[index] = node;
this.usedSize++;
return;
}
last.next = node;
this.usedSize++;
if (loadFactor() > 0.75) {
resize2();
}
}public void resize1() {
Node[] newArray = new Node[this.array.length * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < this.array.length; i++) {
Node cur = array[i];
while (cur != null) {
int index = cur.key % newArray.length;
Node curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = newArray[index];
newArray[index] = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
}
this.array = newArray;
}
//resize尾插
public void resize2() {
Node[] newArray = new Node[this.array.length * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < this.array.length; i++) {
Node cur = array[i];
while (cur != null) {
int index = cur.key % newArray.length;
Node curNext = cur.next;
Node last = findLast(newArray[index]);
if (last == null) {
newArray[index] = cur;
break;
}
last.next = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
}
this.array = newArray;
}
public Node findLast(Node head) {
if (head == null) return head;
Node cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
} public int get(int key) {
int index = key % this.array.length;
Node cur = this.array[index];
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key == key) {
return cur.value;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return -1;
}class HashBuckTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashBuck hashBuck = new HashBuck();
//頭插
hashBuck.put1(9,451);
hashBuck.put1(17,455);
//尾插
//hashBuck.put2(9,451);
//hashBuck.put2(17,455);
hashBuck.put1(2,45);
hashBuck.put1(3,14);
hashBuck.put1(4,52);
hashBuck.put1(4,89);
System.out.println(hashBuck.get(1));
System.out.println("+=================");
}
}頭插
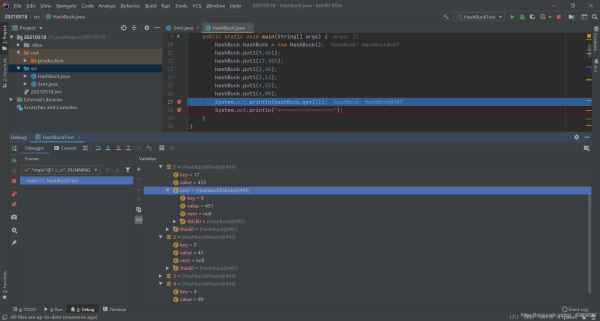
尾插
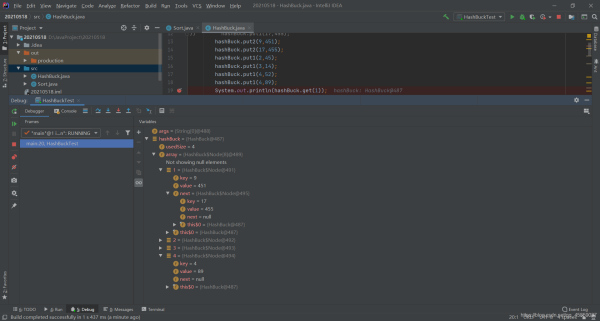
擴容
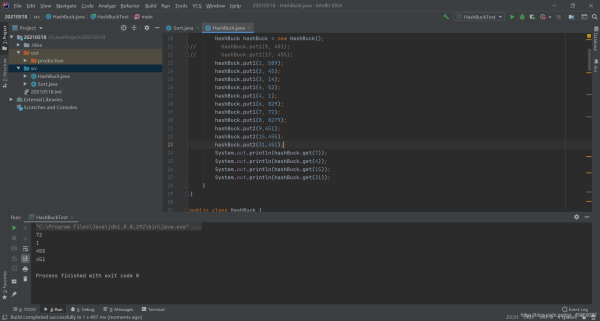
class HashBuckTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashBuck hashBuck = new HashBuck();
// hashBuck.put1(9, 451);
// hashBuck.put1(17, 455);
hashBuck.put1(1, 589);
hashBuck.put1(2, 45);
hashBuck.put1(3, 14);
hashBuck.put1(4, 52);
hashBuck.put1(4, 1);
hashBuck.put1(6, 829);
hashBuck.put1(7, 72);
hashBuck.put1(8, 8279);
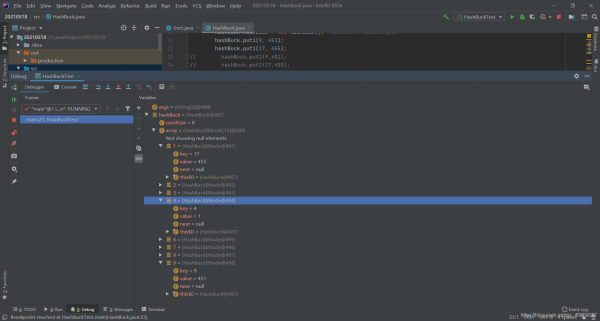
hashBuck.put2(9,451);
hashBuck.put2(15,455);
hashBuck.put2(31,451);
System.out.println(hashBuck.get(7));
System.out.println(hashBuck.get(4));
System.out.println(hashBuck.get(15));
System.out.println(hashBuck.get(31));
}
}
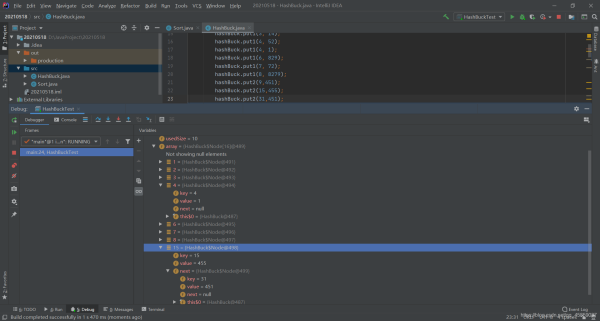
get
public class HashBuck2<K, V> {
static class Node<K, V> {
public K key;
public V val;
public Node<K, V> next;
public Node(K key, V val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
public Node<K, V>[] array;
public int usedSize;
public HashBuck2() {
this.array = (Node<K, V>[]) new Node[8];
}
public void put(K key, V val) {
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = hash % array.length;
Node<K, V> cur = array[index];
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key.equals(key)) {
cur.val = val;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
Node<K, V> node = new Node<>(key, val);
node.next = array[index];
array[index] = node;
this.usedSize++;
if (loadFactor() > 0.75) {
resize();
}
}
public V get(K key) {
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = hash % array.length;
Node<K, V> cur = array[index];
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.key.equals(key)) {
return cur.val;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
public void resize() {
Node[] newArray = new Node[this.array.length * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < this.array.length; i++) {
Node<K,V> cur = array[i];
while (cur != null) {
int hash = cur.key.hashCode();
int index = hash % array.length;
Node <K,V>curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = newArray[index];
newArray[index] = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
}
this.array = newArray;
}
public double loadFactor() {
return this.usedSize / this.array.length * 1.0;
}
}/**
* user:ypc;
* date:2021-05-20;
* time: 15:25;
*/
class Student{
public int id;
Student(int id){
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return id == student.id;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id);
}
}
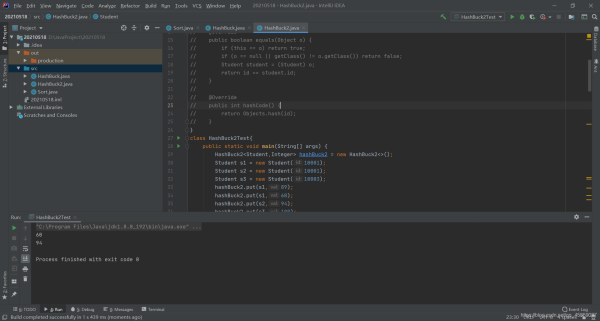
class HashBuck2Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashBuck2<Student,Integer> hashBuck2 = new HashBuck2<>();
Student s1 = new Student(10001);
Student s2 = new Student(10001);
Student s3 = new Student(10003);
hashBuck2.put(s1,89);
hashBuck2.put(s1,60);
hashBuck2.put(s2,94);
hashBuck2.put(s3,100);
System.out.println(hashBuck2.get(s1));
System.out.println(hashBuck2.get(s2));
}
}注意:
要用自定義類作為 HashMap 的 key 或者 HashSet 的值,必須覆寫 hashCode 和 equals 方 法,而且要做到 equals 相等的對象,hashCode 一定是一致的。
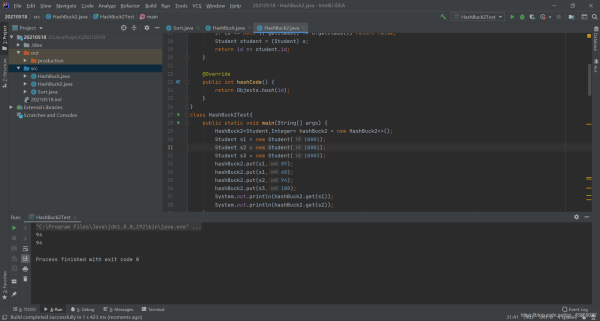
比如Student s1 和 s2 的id一樣,得到的卻是不同的value,所以要覆寫hashCode 和 equals 方 法,如果不覆寫,則使用的是Object類的hashCode 和 equals 方 法,比較的是地址。
重寫之后
1.SpringMVC,Spring Web MVC是一種基于Java的實現了Web MVC設計模式的請求驅動類型的輕量級Web框架。2.Shiro,Apache Shiro是Java的一個安全框架。3.Mybatis,MyBatis 是支持普通 SQL查詢,存儲過程和高級映射的優秀持久層框架。4.Dubbo,Dubbo是一個分布式服務框架。5.Maven,Maven是個項目管理和構建自動化工具。6.RabbitMQ,RabbitMQ是用Erlang實現的一個高并發高可靠AMQP消息隊列服務器。7.Ehcache,EhCache 是一個純Java的進程內緩存框架。
上述內容就是怎么在Java中實現哈希表,你們學到知識或技能了嗎?如果還想學到更多技能或者豐富自己的知識儲備,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。