您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章將為大家詳細講解有關python怎么進行基準測試,小編覺得挺實用的,因此分享給大家做個參考,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后可以有所收獲。
Python是一種跨平臺的、具有解釋性、編譯性、互動性和面向對象的腳本語言,其最初的設計是用于編寫自動化腳本,隨著版本的不斷更新和新功能的添加,常用于用于開發獨立的項目和大型項目。
基準測試屬于性能測試的一種,用于評估和衡量軟件的性能指標。我們可以在軟件開發的某個階段通過基準測試建立一個已知的性能水平,稱為"基準線"。當系統的軟硬件環境發生變化之后再進行一次基準測試以確定那些變化對性能的影響。 這是基準測試最常見的用途。
Donald Knuth在1974年出版的《Structured Programming with go to Statements》提到:
毫無疑問,對效率的片面追求會導致各種濫用。程序員會浪費大量的時間在非關鍵程序的速度上,實際上這些嘗試提升效率的行為反倒可能產生很大的負面影響,特別是當調試和維護的時候。我們不應該過度糾結于細節的優化,應該說約97%的場景:過早的優化是萬惡之源。
當然我們也不應該放棄對那關鍵3%的優化。一個好的程序員不會因為這個比例小就裹足不前,他們會明智地觀察和識別哪些是關鍵的代碼;但是僅當關鍵代碼已經被確認的前提下才會進行優化。對于很多程序員來說,判斷哪部分是關鍵的性能瓶頸,是很容易犯經驗上的錯誤的,因此一般應該借助測量工具來證明。
雖然經常被解讀為不需要關心性能,但是的少部分情況下(3%)應該觀察和識別關鍵代碼并進行優化。
python中提供了非常多的工具來進行基準測試。
為了使演示的例子稍微有趣,我們來隨機生成一個列表,并對列表中數字進行排序。
import random def random_list(start, end, length): """ 生成隨機列表 :param start: 隨機開始數 :param end: 隨機結束數 :param length: 列表長度 """ data_list = [] for i in range(length): data_list.append(random.randint(start, end)) return data_list def bubble_sort(arr): """ 冒泡排序: 對列表進行排序 :param arr 列表 """ n = len(arr) for i in range(n): for j in range(0, n - i - 1): if arr[j] > arr[j + 1]: arr[j], arr[j + 1] = arr[j + 1], arr[j] return arr if __name__ == '__main__': get_data_list = random_list(1, 99, 10) ret = bubble_sort(get_data_list) print(ret)
運行結果如下:
? python .\demo.py [8, 16, 22, 31, 42, 58, 66, 71, 73, 91]
timeit是python自帶的模塊,用來進行基準測試非常方便。
if __name__ == '__main__':
import timeit
get_data_list = random_list(1, 99, 10)
setup = "from __main__ import bubble_sort"
t = timeit.timeit(
stmt="bubble_sort({})".format(get_data_list),
setup=setup
)
print(t)運行結果:
? python .\demo.py 5.4201355
以測試bubble_sort()函數為例。timeit.timeit() 參數說明。
stmt:需要測試的函數或語句,字符串形式.
setup: 運行的環境,本例子中表示if __name__ == '__main__':.
number: 執行的次數,省缺則默認是1000000次。所以你會看到運行bubble_sort() 耗時 5秒多。
https://github.com/psf/pyperf
pyperf 的用法與timeit比較類似,但它提供了更豐富結果。(注:我完全是發現了這個庫才學習基準測試的)
if __name__ == '__main__':
get_data_list = random_list(1, 99, 10)
import pyperf
setup = "from __main__ import bubble_sort"
runner = pyperf.Runner()
runner.timeit(name="bubble sort",
stmt="bubble_sort({})".format(get_data_list),
setup=setup)運行結果:
? python .\demo.py -o bench.json ..................... bubble sort: Mean +- std dev: 5.63 us +- 0.31 us
測試結果會寫入bench.json 文件。可以使用pyperf stats命令分析測試結果。
? python -m pyperf stats bench.json Total duration: 15.9 sec Start date: 2021-04-02 00:17:18 End date: 2021-04-02 00:17:36 Raw value minimum: 162 ms Raw value maximum: 210 ms Number of calibration run: 1 Number of run with values: 20 Total number of run: 21 Number of warmup per run: 1 Number of value per run: 3 Loop iterations per value: 2^15 Total number of values: 60 Minimum: 4.94 us Median +- MAD: 5.63 us +- 0.12 us Mean +- std dev: 5.63 us +- 0.31 us Maximum: 6.41 us 0th percentile: 4.94 us (-12% of the mean) -- minimum 5th percentile: 5.10 us (-9% of the mean) 25th percentile: 5.52 us (-2% of the mean) -- Q1 50th percentile: 5.63 us (+0% of the mean) -- median 75th percentile: 5.81 us (+3% of the mean) -- Q3 95th percentile: 5.95 us (+6% of the mean) 100th percentile: 6.41 us (+14% of the mean) -- maximum Number of outlier (out of 5.07 us..6.25 us): 6
https://github.com/ionelmc/pytest-benchmark
pytest-benchmark是 pytest單元測試框架的一個插件。 單獨編寫單元測試用例:
from demo import bubble_sort def test_bubble_sort(benchmark): test_list = [5, 2, 4, 1, 3] result = benchmark(bubble_sort, test_list) assert result == [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
需要注意:
導入bubble_sort() 函數。
benchmark 作為鉤子函數使用,不需要導入包。前提是你需要安裝pytest和pytest-benchmark。
為了方便斷言,我們就把要排序的數固定下來了。
運行測試用例:
? pytest -q .\test_demo.py . [100%] ------------------------------------------------ benchmark: 1 tests ----------------------------------------------- Name (time in us) Min Max Mean StdDev Median IQR Outliers OPS (Kops/s) Rounds Iterations ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- test_bubble_sort 1.6000 483.2000 1.7647 2.6667 1.7000 0.0000 174;36496 566.6715 181819 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Legend: Outliers: 1 Standard Deviation from Mean; 1.5 IQR (InterQuartile Range) from 1st Quartile and 3rd Quartile. OPS: Operations Per Second, computed as 1 / Mean 1 passed in 1.98s
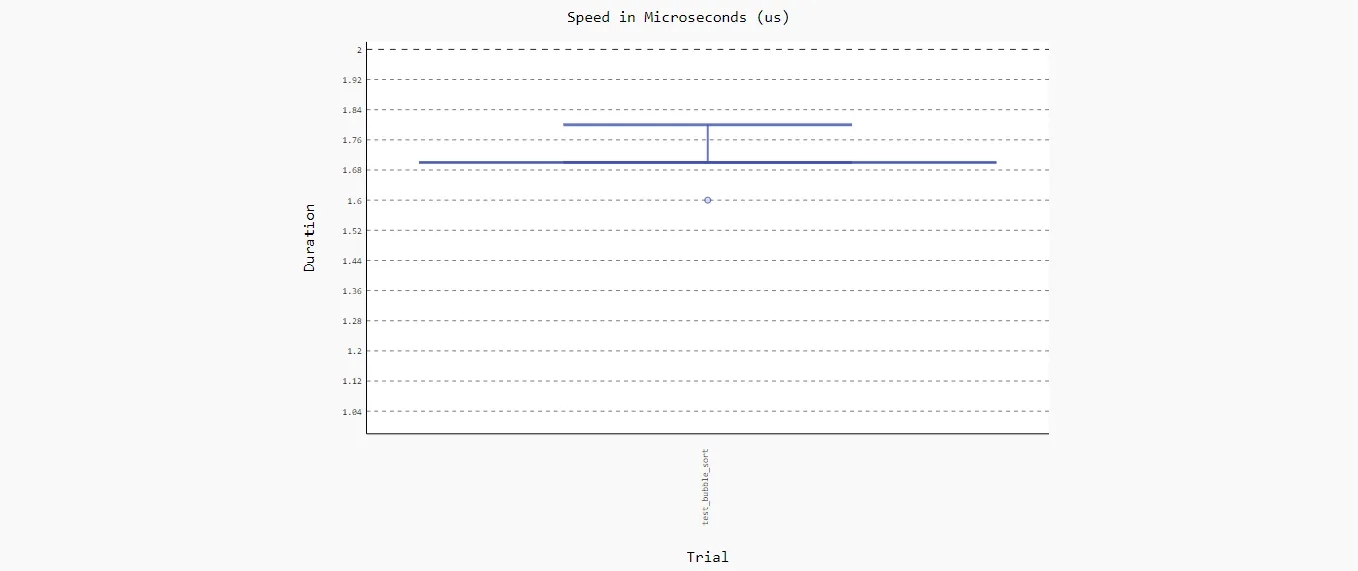
加上 --benchmark-histogram 參數,你會得到一張圖表
? pytest -q .\test_demo.py --benchmark-histogram . [100%] ------------------------------------------------ benchmark: 1 tests ----------------------------------------------- Name (time in us) Min Max Mean StdDev Median IQR Outliers OPS (Kops/s) Rounds Iterations ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- test_bubble_sort 1.6000 53.9000 1.7333 0.3685 1.7000 0.0000 1640;37296 576.9264 178572 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Generated histogram: D:\github\test-circle\article\code\benchmark_20210401_165958.svg
圖片如下:
關于“python怎么進行基準測試”這篇文章就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,使各位可以學到更多知識,如果覺得文章不錯,請把它分享出去讓更多的人看到。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。