您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇文章為大家展示了CSS中有哪些尺寸單位,內容簡明扼要并且容易理解,絕對能使你眼前一亮,通過這篇文章的詳細介紹希望你能有所收獲。
絕對單位
px: Pixel 像素
pt: Points 磅
pc: Picas 派卡
in: Inches 英寸
mm: Millimeter 毫米
cm: Centimeter 厘米
q: Quarter millimeters 1/4毫米
相對單位
%: 百分比
em: Element meter 根據文檔字體計算尺寸
rem: Root element meter 根據根文檔( body/html )字體計算尺寸
ex: 文檔字符“x”的高度
ch: 文檔數字“0”的的寬度
vh: View height 可視范圍高度
vw: View width 可視范圍寬度
vmin: View min 可視范圍的寬度或高度中較小的那個尺寸
vmax: View max 可視范圍的寬度或高度中較大的那個尺寸
運算
calc: 四則運算
實例:
h2 {
width: calc(100% - 10px + 2rem);
}單位比例
1in = 2.54cm = 25.4 mm = 101.6q = 72pt = 6pc = 96px
詳細
絕對單位
px - Pixel 像素
像素 px 相對于設備顯示器屏幕分辨率而言。
div { font-size: 12px }
p { text-indent: 24px }pt Points 磅
1 pt = 1/72 英寸
div { font-size: 10pt }
p { height: 100pt }pc Picas 派卡
十二點活字(印刷中使用的),相當于我國新四號鉛字的尺寸。
div { font-size: 10pc }
p { height: 10pc }in Inches 英寸
div { font-size: 10in }
p { height: 10in }mm Millimeter 毫米
div { font-size: 10mm }
p { height: 10mm }cm Centimeter 厘米
div { font-size: 10cm }
p { height: 10cm }q Quarter millimeters 1/4毫米
div { font-size: 20q }
p { height: 100q }相對單位
% 百分比
相對于父元素寬度
<body>
<div class="parent">
<div class="children"></div>
</div>
</body>
<style>
.parent { width: 100px }
.children { width: 66.6% }
/* children的寬度為 66.6px */
</style>em Element meter 根據文檔計算尺寸
相對于當前文檔對象內文本的字體尺寸而言,若未指定字體大小則繼承自上級元素,以此類推,直至 body,若 body 未指定則為瀏覽器默認大小。
<body>
<div class="element"></div>
</body>
<style>
body {
font-size: 14px;
}
.element {
font-size: 16px;
width: 2em;
/* 2em === 32px */
}
</style>rem Root element meter 根據根文檔( body/html )字體計算尺寸
相對于根文檔對象( body/html )內文本的字體尺寸而言,若未指定字體大小則繼承為瀏覽器默認字體大小。
<body>
<div class="element"></div>
</body>
<style>
body {
font-size: 14px;
}
.element {
font-size: 16px;
width: 2rem;
/* 2rem === 28px */
}
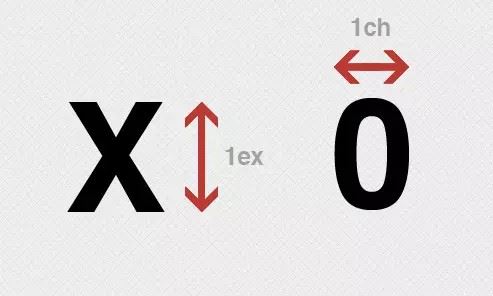
</style>ex 文檔字符“x”的高度
相對于字符“x”的高度,通常為字體高度的一半,若未指定字體尺寸,則相對于瀏覽器的默認字體尺寸。
至于為啥是x,我TM也不知道。
<body>
<div class="x"></div>
</body>
<style>
.x {
height: 1ex;
overflow: hidden;
background: #aaa;
}
</style>ch 文檔數字“0”的的寬度
同上,相對于數字“0”的寬度。
<body>
<h2>定義一個寬度正好能裝下10個0的容器:</h2>
<div class="0">0000000000</div>
</body>
<style>
.0 {
width: 10ch;
overflow: hidden;
background: #ccc;
}
</style>一張圖解釋:
vh View height / vw View Width - 可視范圍
相對于可視范圍的高度和寬度,可視范圍被均分為 100 單位的 vh/vw;可視范圍是指屏幕可見范圍,不是父元素的,百分比是相對于包含它的最近的父元素的高度和寬度。
假設設備可視范圍為高度 900px,寬度 750px,則,1 vh = 900px/100 = 9px,1vw = 750px/100 = 7.5px。
<body>
<h2>article title</h2>
<div class="element"></div>
<div class="full-height"></div>
</body>
<style>
.element {
width: 50vw;
height: 80vh;
/* 如果屏幕高度為1000px,則該元素高度為800px,vw 同理 */
}
.full-height {
height: 100vh;
/* 輕易實現了與屏幕同等高度的元素 */
}
h2 {
width: 100vw;
/* 設置一個和屏幕同寬的標題,標題的字體大小就會自動根據瀏覽器的寬度進行縮放,以達到字體和viewport大小同步的效果。 */
}
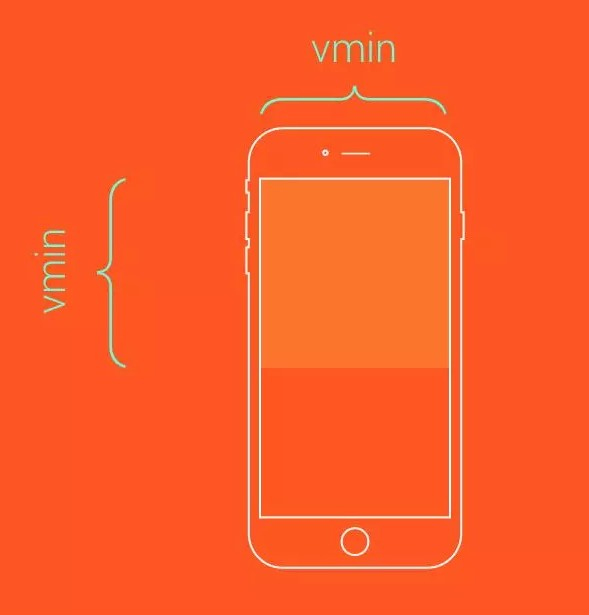
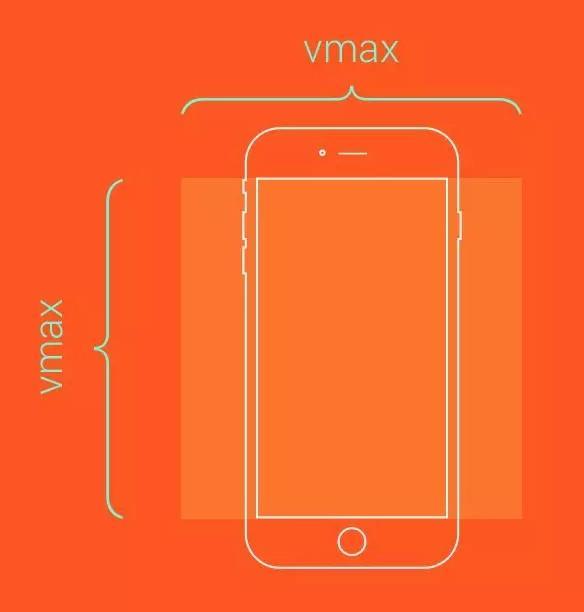
</style>vmin / vmax 可視范圍的寬度或高度中較小/較大的那個尺寸
假設瀏覽器的寬度設置為 1200px,高度設置為 800px, 則1vmax = 1200/100px = 12px, 1vmin = 800/100px = 8px。
如果寬度設置為 600px,高度設置為 1080px, 則1vmin = 6px, 1vmax = 10.8px。
假設需要讓一個元素始終在屏幕上可見:
.box {
height: 100vmin;
width: 100vmin;
}
假設需要讓這個元素始終鋪滿整個視口的可見區域:
.box {
height: 100vmax;
width: 100vmax;
}
上述內容就是CSS中有哪些尺寸單位,你們學到知識或技能了嗎?如果還想學到更多技能或者豐富自己的知識儲備,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。