您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章給大家介紹怎么在VS2019與VScode中對python接口進行調用,內容非常詳細,感興趣的小伙伴們可以參考借鑒,希望對大家能有所幫助。
看到這個標題有些人說了,為什么好好的C++你非要調用python?人家明明是兩種語言呀!
但是在實際應用中,有時候會用到C/C++調用python來更簡單地去完成一些功能,不然人家python為什么有一個文件夾叫include,里邊全是.h文件呢?
首先是在VScode中為C++調用python接口配置環境,這里假設你已經配置好了c++編程環境!
用快捷鍵Ctrl+Shift+X打開Extensions 商店,輸入python,install:

用快捷鍵Ctrl+Shift+P打開命令面板,打開C/C++:編輯配置(UI):
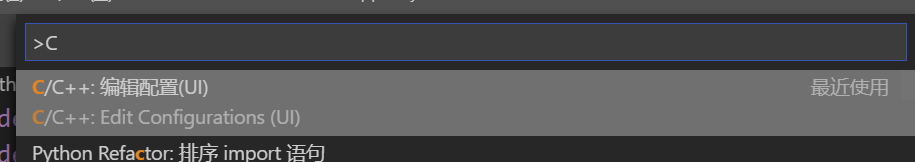
然后編輯c_cpp_properties.json文件,在文件中的includePath項添加自己的python include路徑:“D:\\Python\\Python37\\include”,注意格式。
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Win32",
"includePath": [
"${workspaceFolder}/**",
"D:\\Python\\Python37\\include"
],
"defines": [
"_DEBUG",
"UNICODE",
"_UNICODE"
],
"compilerPath": "D:\\MinGW\\bin\\gcc.exe",
"cStandard": "c11",
"cppStandard": "c++17",
"intelliSenseMode": "clang-x64"
}
],
"version": 4
}測試一下:編輯hello.py:
def printHello():
print("Hello World")c++調用python有兩種方式,我在代碼中都進行了測試,編輯main.cpp:
#include "D:\Python\Python37\include\Python.h"
//#include <Python.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void cython1()
{
Py_Initialize(); //初始化python解釋器,告訴編譯器要用的python編譯器
PyRun_SimpleString("import hello"); //調用python文件
PyRun_SimpleString("hello.printHello()"); //調用上述文件中的函數
Py_Finalize(); //結束python解釋器,釋放資源
}
void cython2()
{
Py_Initialize();
PyObject *pModule = NULL;
PyObject *pFunc = NULL;
pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("hello"); //這里是要調用的文件名
pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "printHello"); //這里是要調用的函數名
PyEval_CallObject(pFunc, NULL); //調用函數
Py_Finalize();
}
int main()
{
int select;
cin >> select;
select == 1 ? cython1():cython2();
return 0;
}1、為什么我包含了Python.h,c++代碼中調用也沒有報錯,但是運行時會出現如下錯誤?(暫未從根本上解決問題,仿照后面linux上的頭文件調用方法也是無效,稍后解決會更新)
main.cpp:2:10: fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory #include "Python.h" ^~~~~~~~~~ compilation terminated.
說明沒有include成功啊,這里我猜測是由于版本問題導致的,暫未得到解決,但是有一種方式是絕對可以使用的,并且已經在代碼中體現了,那就是…直接inlcude絕對路徑!
#include "D:\Python\Python37\include\Python.h"
可能心細的朋友已經發現了,你只是包含了頭文件,鏈接庫還沒有鏈接啊!但是我當時的心情不允許我這么細心啊,咳咳
這里打個廣告!強烈建議各位C/C++ develpoers,去仔細讀一下程序員的自我修養這本書,真的受益匪淺。
2、由于沒有鏈接靜態庫而報錯(同上,暫時只有傻瓜式解決辦法,使用makefile解決此問題請看我之后的博客:在makefile中鏈接靜態庫)
C:\Users\11955\AppData\Local\Temp\ccLmGIL8.o:main.cpp:(.text+0xb): undefined reference to `__imp_Py_Initialize'
C:\Users\11955\AppData\Local\Temp\ccLmGIL8.o:main.cpp:(.text+0x20): undefined reference to `__imp_PyRun_SimpleStringFlags'
C:\Users\11955\AppData\Local\Temp\ccLmGIL8.o:main.cpp:(.text+0x35): undefined reference to `__imp_PyRun_SimpleStringFlags'
C:\Users\11955\AppData\Local\Temp\ccLmGIL8.o:main.cpp:(.text+0x3e): undefined reference to `__imp_Py_Finalize'
C:\Users\11955\AppData\Local\Temp\ccLmGIL8.o:main.cpp:(.text+0x56): undefined reference to `__imp_Py_Initialize'
C:\Users\11955\AppData\Local\Temp\ccLmGIL8.o:main.cpp:(.text+0x76): undefined reference to `__imp_PyImport_ImportModule'
C:\Users\11955\AppData\Local\Temp\ccLmGIL8.o:main.cpp:(.text+0x91): undefined reference to `__imp_PyObject_GetAttrString'
C:\Users\11955\AppData\Local\Temp\ccLmGIL8.o:main.cpp:(.text+0xb0): undefined reference to `__imp_PyEval_CallObjectWithKeywords'
C:\Users\11955\AppData\Local\Temp\ccLmGIL8.o:main.cpp:(.text+0xb9): undefined reference to `__imp_Py_Finalize'
解決辦法:鏈接靜態庫,我把D:\Python\Python37\libs這個文件夾復制到了工作空間的文件夾下,為了方便鏈接直鏈接該文件夾下所有文件。
g++ -o main .\main.cpp -L .\libs\* .\main.exe
首先明確,如果你安裝的python是64位的,建議把VS 該項目下的解決方案平臺改為x64,并且環境是在特定的解決方案配置下(Debug/Release)進行的,所以不要配置在Debug,卻在Release調用Python.h,這樣肯定會報錯:無法打開Python.h。
右鍵project打開屬性,在配置屬性 - C/C++ - 常規 - 附加包含目錄下添加:
D:\Python\Python37\include
在配置屬性 - VC++目錄 - 庫目錄下添加:
D:\Python\Python37\libs
C++代碼和python代碼同上,到此我們還沒有在VS項目中添加python代碼,只需要將hello.py復制到main.cpp所在目錄即可。
1、如果遇到Link110:無法打開python36_d.lib(或者python**_d.lib),在你的python/libs目錄下會發現沒有這個靜態庫文件,這時候最簡單的做法就是拷貝復制一份python36.lib,并重命名為python36_d.lib。
2、如果出現的錯誤:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
NameError: name 'hello' is not defined
這是由于沒有找到hello.py文件,解決方案:在初始化python解釋器以后添加以下兩行代碼,用于指定模塊的路徑:
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('./')");3、如果還有錯誤,請參考C++調用python。
//#include "D:\Python\Python37\include\Python.h"
//當然,絕對路徑永遠不會失效!^o^
#include <Python.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void cython1()
{
Py_Initialize(); //初始化python解釋器,告訴編譯器要用的python編譯器
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('./')");
PyRun_SimpleString("import hello"); //調用python文件
PyRun_SimpleString("hello.printHello()"); //調用上述文件中的函數
Py_Finalize(); //結束python解釋器,釋放資源
}
void cython2()
{
Py_Initialize();
PyObject* pModule = NULL;
PyObject* pFunc = NULL;
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('./')");
pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("hello"); //這里是要調用的文件名
pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "printHello"); //這里是要調用的函數名
PyEval_CallObject(pFunc, NULL); //調用函數
Py_Finalize();
}
int main()
{
int select;
cin >> select;
select == 1 ? cython1() : cython2();
return 0;
}其實這一部分有點多余,因為我在VScode下編程也采用gcc/g++編譯器,linux與之相同,所以遇到的問題也是一致的,都是沒有辦法直接#include<Python.h>。以Ubuntu 18.04.4 LTS為例:
前提是你已經安裝了g++,如果使用g++ -v查看版本無果,采用以下命令安裝套件:
sudo apt-get install build-essential
首先查看自己的python版本以及位置,位置用于代碼編寫調用頭文件,版本用于編譯g++命令的指示鏈接庫。由于ubuntu18.04自帶python3,所以命令中都采用了python3而不是python:
python3 -V >Python 3.6.9 which python3 >/usr/bin/python3
找到版本以及位置,在C++代碼中采用絕對路徑的方法調用Python.h:
#include "/usr/include/python3.6/Python.h" //或者 #include <python3.6/Python.h>
同時也要在初始化python解釋器以后添加以下兩行代碼,用于指定模塊的路徑:
Py_Initialize();
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys"); // add 1
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('./')"); //add 2同樣在編譯時需要指定靜態鏈接庫,不然的話就用makefile吧~
注意python的版本:
g++ -o main main.cpp -lpython3.6m ./main
注意,也可以采用編譯時包含頭文件的方式,這樣就不用在代碼中調用頭文件了,不推薦(這樣的命令我要它有何用):
g++ -o main main.cpp -lpython3.6m -I /usr/include/python3.6 ./main
關于怎么在VS2019與VScode中對python接口進行調用就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,可以學到更多知識。如果覺得文章不錯,可以把它分享出去讓更多的人看到。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。