您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
深入淺析SpringMVC零XML配置的實現原理?針對這個問題,這篇文章詳細介紹了相對應的分析和解答,希望可以幫助更多想解決這個問題的小伙伴找到更簡單易行的方法。
先來看一下原始的web.xml配置:
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" > <web-app> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value> <!--加載spring配置--> classpath:spring.xml </param-value> </context-param> <context-param> <param-name>webAppRootKey</param-name> <param-value>ServicePlatform.root</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> <!--<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextListener</listener-class>--> </listener> <servlet> <servlet-name>spring-dispatcher</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <!--springmvc的配置文件--> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring-dispatcher.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>0</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>spring-dispatcher</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
這里各個配置的作用簡單說下,context-param是加載我們主的sping.xml配置,比如一些bean的配置和開啟注解掃描等;listener是配置監聽器,Tomcat啟動會觸發監聽器調用;servlet則是配置我們自定義的Servlet實現,比如DispatcherServlet。還有其它很多配置就不一一說明了,在這里主要看到記住context-param和servlet配置,這是SpringIOC父子容器的體現。
在之前的I文章中講過IOC容器是以父子關系組織的,但估計大部分人都不能理解,除了看到復雜的繼承體系,并沒有看到父容器作用的體現,稍后來分析。
了解了配置,我們就需要思考如何替換掉這些繁瑣的配置。實際上Tomcat提供了一個規范,有一個ServletContainerInitializer接口:
public interface ServletContainerInitializer {
void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> var1, ServletContext var2) throws ServletException;
}Tomcat啟動時會調用該接口實現類的onStartup方法,這個方法有兩個參數,第二個不用說,主要是第一個參數什么?從哪里來?另外我們自定義的實現類又怎么讓Tomcat調用呢?
首先解答最后一個問題,這里也是利用SPI來實現的,因此我們實現了該接口后,還需要在META-INF.services下配置。其次,這里傳入的第一個參數也是我們自定義的擴展接口的實現類,我們可以通過我們自定義的接口實現很多需要在啟動時做的事,比如加載Servlet,但是Tomcat又是怎么知道我們自定義的接口是哪個呢?
這就需要用到@HandlesTypes注解,該注解就是標注在ServletContainerInitializer的實現類上,其值就是我們擴展的接口,這樣Tomcat就知道需要傳入哪個接口實現類到這個onStartup方法了。
來看一個簡單的實現:
@HandlesTypes(LoadServlet.class)
public class MyServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> set, ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
Iterator var4;
if (set != null) {
var4 = set.iterator();
while (var4.hasNext()) {
Class<?> clazz = (Class<?>) var4.next();
if (!clazz.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(clazz.getModifiers()) && LoadServlet.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
try {
((LoadServlet) clazz.newInstance()).loadOnstarp(servletContext);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
public interface LoadServlet {
void loadOnstarp(ServletContext servletContext);
}
public class LoadServletImpl implements LoadServlet {
@Override
public void loadOnstarp(ServletContext servletContext) {
ServletRegistration.Dynamic initServlet = servletContext.addServlet("initServlet", "org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet");
initServlet.setLoadOnStartup(1);
initServlet.addMapping("/init");
}
}這就是Tomcat給我們提供的規范,通過這個規范我們就能實現Spring的零xml配置啟動,直接來看Spring是如何做的。根據上面所說我們可以在spring-web工程下找到META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer配置:
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList<>();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes,
// no matter what @HandlesTypes says...
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer)
ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
return;
}
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
}核心的實現就是WebApplicationInitializer,先看看其繼承體系
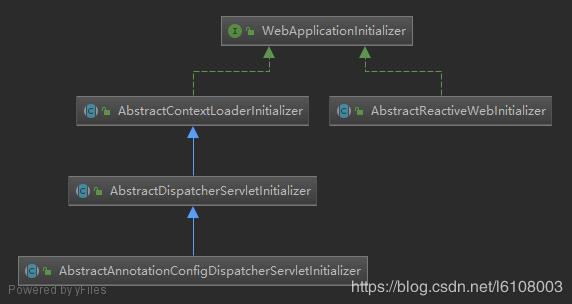
AbstractReactiveWebInitializer不用管,主要看另外一邊,但是都是抽象類,也就是說真的實例也是由我們自己實現,但需要我們實現什么呢?我們一般直接繼承AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer類,有四個抽象方法需要我們實現:
//父容器
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class<?>[]{SpringContainer.class};
}
//SpringMVC配置子容器
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class<?>[]{MvcContainer.class};
}
//獲取DispatcherServlet的映射信息
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
// filter配置
@Override
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
MyFilter myFilter = new MyFilter();
CorsFilter corsFilter = new CorsFilter();
return new Filter[]{myFilter,corsFilter};
}這里主要注意getRootConfigClasses和getServletConfigClasses方法,分別加載父、子容器:
@ComponentScan(value = "com.dark",excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
})
public class SpringContainer {
}
@ComponentScan(value = "com.dark",includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
},useDefaultFilters = false)
public class MvcContainer {
}看到這兩個類上的注解應該不陌生了吧,父容器掃描裝載了所有不帶@Controller注解的類,子容器則相反,但需要對象時首先從當前容器中找,如果沒有則從父容器中獲取,為什么要這么設計呢?
直接放到一個容器中不行么?先思考下, 稍后解答。回到onStartup方法中,直接回調用到AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer類:
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
super.onStartup(servletContext);
//注冊DispatcherServlet
registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext);
}先是調用父類:
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
registerContextLoaderListener(servletContext);
}
protected void registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext servletContext) {
//創建spring上下文,注冊了SpringContainer
WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = createRootApplicationContext();
if (rootAppContext != null) {
//創建監聽器
ContextLoaderListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext);
listener.setContextInitializers(getRootApplicationContextInitializers());
servletContext.addListener(listener);
}
}然后調用createRootApplicationContext創建父容器:
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
Class<?>[] configClasses = getRootConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
context.register(configClasses);
return context;
}
else {
return null;
}
}可以看到就是創建了一個AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext對象,并將我們的配置類SpringContainer注冊了進去。接著創建Tomcat啟動加載監聽器ContextLoaderListener,該監聽器有一個contextInitialized方法,會在Tomcat啟動時調用。
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
*/
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
return this.context;
}
}可以看到就是去初始化容器,這個和之前分析xml解析是一樣的,主要注意這里封裝了ServletContext對象,并將父容器設置到了該對象中。
父容器創建完成后自然就是子容器的創建,來到registerDispatcherServlet方法:
protected void registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext servletContext) {
String servletName = getServletName();
Assert.hasLength(servletName, "getServletName() must not return null or empty");
//創建springmvc的上下文,注冊了MvcContainer類
WebApplicationContext servletAppContext = createServletApplicationContext();
Assert.notNull(servletAppContext, "createServletApplicationContext() must not return null");
//創建DispatcherServlet
FrameworkServlet dispatcherServlet = createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
Assert.notNull(dispatcherServlet, "createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext) must not return null");
dispatcherServlet.setContextInitializers(getServletApplicationContextInitializers());
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet(servletName, dispatcherServlet);
if (registration == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to register servlet with name '" + servletName + "'. " +
"Check if there is another servlet registered under the same name.");
}
/*
* 如果該元素的值為負數或者沒有設置,則容器會當Servlet被請求時再加載。
如果值為正整數或者0時,表示容器在應用啟動時就加載并初始化這個servlet,
值越小,servlet的優先級越高,就越先被加載
* */
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping(getServletMappings());
registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported());
Filter[] filters = getServletFilters();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(filters)) {
for (Filter filter : filters) {
registerServletFilter(servletContext, filter);
}
}
customizeRegistration(registration);
}
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
Class<?>[] configClasses = getServletConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
context.register(configClasses);
}
return context;
}這里也是創建了一個AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext對象,不同的只是這里注冊的配置類就是我們的Servlet配置了。然后創建了DispatcherServlet對象,并將上下文對象設置了進去。
看到這你可能會疑惑,既然父子容器創建的都是相同類的對象,何來的父子容器之說?
別急,這個在初始化該上文時就明白了。但是這里的初始化入口在哪呢?沒有看到任何監聽器的創建和調用。
實際上這里的上下文對象初始化是在Servlet初始化時實現的,即init方法,直接來到HttpServletBean的init方法(分析SpringMVC源碼時講過):
public final void init() throws ServletException {
...省略
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
}
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
}
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//這里會從servletContext中獲取到父容器,就是通過監聽器加載的容器
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
//容器加載
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}關于深入淺析SpringMVC零XML配置的實現原理問題的解答就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,如果你還有很多疑惑沒有解開,可以關注億速云行業資訊頻道了解更多相關知識。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。