您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這期內容當中小編將會給大家帶來有關如何在Struts1中使用ActionMapping,文章內容豐富且以專業的角度為大家分析和敘述,閱讀完這篇文章希望大家可以有所收獲。
首先斷點走出了processpath方法,
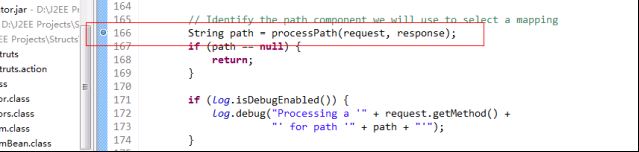
這個方法是用來截取字符串的,今天我們來看怎樣獲得ActionMapping的方法---processMapping。
在此之前簡單說一下ActionMapping,它的源代碼中可以看出,其中最重要的屬性和我們的mvc小實例中的ActionMapping類似,都是有path、type還有forwardMap,主要是對應的struts-config配置文件而來,這個就是保存這個配置文件的信息到內存中。
具體的mvc小實例的ActionMapping代碼如下:
package com.cjq.servlet;
import java.util.Map;
public class ActionMapping {
private String path;
private Object type;
private Map forwardMap;
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public Object getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(Object type) {
this.type = type;
}
public Map getForwardMap() {
return forwardMap;
}
public void setForwardMap(Map forwardMap) {
this.forwardMap = forwardMap;
}
}
而Struts中的Actionconfig(因為ActionMapping是繼承這個ActionConfig的,所以我們來看ActionConfig更加直接)的代碼如下:

從這兩部分代碼來看,更加印證了我在開篇寫的mvc小實例是一個struts框架的雛形。
講完ActionMapping的一些內容后,相信對ActionMapping有所了解,那么系統是如何生成ActionMapping和如何找到ActionMapping的呢?這就是今天要說的整體:
我們看下web.xml中有一個<load-on-startup>2</load-on-startup> 配置信息,這個信息就是說明了但服務器已啟動就動態讀取struts-config配置文件把配置文件的信息put到ActionMapping中。所以當我們運行服務器的時候,我們在內存中已經存在對應struts-config配置文件信息對應的ActionMapping。今天就是要通過processMapping讀取這個ActionMapping類。
進入斷點調試,首先在processMapping方法上設置斷點。
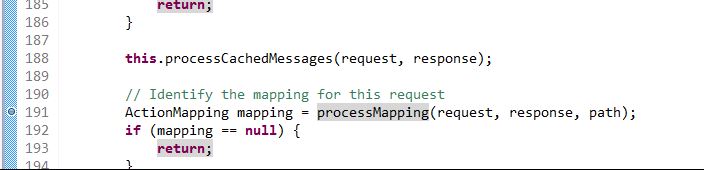
進入源代碼中:
/**
* <p>Select the mapping used to process theselection path for this request
* If no mapping can be identified, createan error response and return
* <code>null</code>.</p>
*
* @param request The servlet request weare processing
* @param response The servlet response weare creating
* @param path The portion of the requestURI for selecting a mapping
*
* @exception IOException if an input/outputerror occurs
*/
protectedActionMapping processMapping(HttpServletRequestrequest,
HttpServletResponse response,
String path)
throws IOException {
// Is there a mapping for this path?
ActionMapping mapping = (ActionMapping)
moduleConfig.findActionConfig(path);
// If a mapping is found, put it in the request and return it
if (mapping != null) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}
// Locate the mapping for unknown paths (if any)
ActionConfig configs[] = moduleConfig.findActionConfigs();
for (int i = 0; i < configs.length; i++) {
if (configs[i].getUnknown()) {
mapping = (ActionMapping)configs[i];
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}
}
// No mapping can be found to process this request
String msg = getInternal().getMessage("processInvalid");
log.error(msg + " " + path);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, msg);
return null;
}
首先我們傳入我們在上一步截取的路徑,通過moduleConfig的findAction方法來查找ActionConfig,并且返回ActionMapping。具體代碼是:
ActionMapping mapping =(ActionMapping) moduleConfig.findActionConfig(path);
如果找到,那么就講ActionMapping存放到request的context中。代碼:
if (mapping != null) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
} 如果沒有通過path找到mapping,則在Actionconfig中遍歷為未知路徑尋找mapping,如果找到則存放到request中,如果沒有找到,則返回錯誤信息,具體代碼如下:
// Locate the mapping for unknownpaths (if any)
ActionConfig configs[] = moduleConfigfindActionConfigs();
for (int i = 0; i < configslength; i++) {
if (configs[i].getUnknown()) {
mapping = (ActionMapping)configs[i];
request.setAttribute(Globals.MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
return (mapping);
}
}
// No mapping can be found to process this request
String msg = getInternal().getMessage("processInvalid");
log.error(msg + " " + path);
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, msg);
return null;
來看下ActionServlet中的一個方法processActionForm,當我們在截取字符串,再根據字符串取得ActionMapping(這是前兩篇文章中介紹的)之后,我們就要用利用ActionMapping來創建ActionForm了,并且把ActionForm放到request或session中管理。
先來看具體struts中processActionForm方法的具體實現:
/**
* <p>Retrieve and return the <code>ActionForm</code> associatedwith
* this mapping, creating and retaining oneif necessary. If there is no
* <code>ActionForm</code> associated with this mapping,return
* <code>null</code>.</p>
*
* @param request The servlet request weare processing
* @param response The servlet response weare creating
* @param mapping The mapping we are using
*/
protectedActionForm processActionForm(HttpServletRequestrequest,
HttpServletResponse response,
ActionMapping mapping) {
// Create (if necessary) a form bean to use
ActionForm instance = RequestUtilscreateActionForm
(request, mapping, moduleConfig, servlet);
if (instance == null) {
return (null);
}
// Store the new instance in the appropriate scope
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(" Storing ActionForm bean instance in scope '" +
mapping.getScope() + "' under attribute key '" +
mapping.getAttribute() + "'");
}
if ("request".equals(mapping.getScope())) {
request.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
} else {
HttpSession session =requestgetSession();
session.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
}
return (instance);
}
這個方法的大體流程是:根據ActionMapping中的name名稱查找ActionForm,如果配置了ActionForm,那么就到request或session中查找,如果在request或session中存在已經創建的ActionForm,那么將返回。如果不存在那么會根據ActionForm的完成路徑采用反射進行創建,再將創建好的ActionForm放到request或session中,之后返回ActionForm。
具體我們可以跟隨斷點調試來看看這個方法是如何運行的。
先設置斷點,之后進入processActionForm方法。
第一個步驟就是創建ActionForm:
// Create (if necessary) a formbean to use
ActionForm instance = RequestUtils.createActionForm
(request, mapping, moduleConfig, servlet);
if (instance == null) {
return (null);
} 通過調用RequestUtils.createActionForm的方法把ActionMapping中的ActionForm字符串生成對象,并且返回。進入這段代碼中:
publicstaticActionForm createActionForm(
HttpServletRequest request,
ActionMapping mapping,
ModuleConfig moduleConfig,
ActionServlet servlet) {
// Is there a form bean associated with this mapping?
String attribute = mappinggetAttribute();
if (attribute == null) {
return (null);
}
// Look up the form bean configuration information to use
String name = mapping.getName();
FormBeanConfig config =moduleConfigfindFormBeanConfig(name);
if (config == null) {
log.warn("No FormBeanConfig found under '"+ name + "'");
return (null);
}
ActionForm instance = lookupActionForm(request,attribute, mappinggetScope());
// Can we recycle the existing form bean instance (if there is one)?
try {
if (instance != null && canReuseActionForm(instance,config)) {
return (instance);
}
} catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
log.error(servlet.getInternal().getMessage("formBean",config.getType()), e);
return (null);
}
return createActionForm(config,servlet);
}
方法首先定義變量name,并且從mapping中獲取值,String name = mapping.getName();也就是我們實例中的LoginForm字符串。之后通過調用FormBeanConfig config =moduleConfig.findFormBeanConfig(name);這句話把相應的LoginForm字符串生成相應的對象。
這里要說明的是我們在struts-config配置文件中,配置過這樣一個標簽信息:
<form-beans>
<form-bean name="loginForm" type=".struts.LoginActionForm"/>
</form-beans> 這個標簽在服務器一啟動的時候就會利用digester讀取這里的配置信息,并且放在FormBeanConfig類中,這樣我們可以通過上面那一句話就可以把LoginForm字符串生成相應的對象。
之后調用了ActionForm instance = lookupActionForm(request,attribute, mapping.getScope());這個方法,這個方法主要是查找scope屬性中有沒有存在ActionForm。具體實現:
if ("request".equals(scope)){
instance = (ActionForm)request.getAttribute(attribute);
} else {
session = request.getSession();
instance = (ActionForm)session.getAttribute(attribute);
}
這里判斷scope屬性值是否為request,如果是則從request中讀出ActionForm,如果不是則從session中讀出。程序如果是第一次執行,那么ActionForm會是為空的。因為這里的ActionForm為空,所以就進入了if判斷語句中,最后通過調用return createActionForm(config, servlet);創建ActionForm并且返回。
之后processActionForm就會把返回來的ActionForm放入request或者session中。具體實現就是:
if ("request".equals(mapping.getScope())){
request.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
} else {
HttpSession session =request.getSession();
session.setAttribute(mapping.getAttribute(), instance);
}
到此為止,ActionForm就創建完成,當ActionForm創建完成之后,就要用其他的方法來往ActionForm中賦值了
上述就是小編為大家分享的如何在Struts1中使用ActionMapping了,如果剛好有類似的疑惑,不妨參照上述分析進行理解。如果想知道更多相關知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。