您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
軟件工程由于需要不斷迭代開發,因此要對源代碼進行版本管理。Android源代碼工程(AOSP)也不例外,它采用Git來進行版本管理。AOSP作為一個大型開放源代碼工程,由許許多多子項目組成,因此不能簡單地用Git進行管理,它在Git的基礎上建立了一套自己的代碼倉庫,并且使用工具Repo進行管理。工欲善其事,必先利其器。本文就對AOSP代碼倉庫及其管理工具repo進行分析,以便提高我們日常開發效率。
《Android系統源代碼情景分析》——點擊下載
現代的代碼版本管理工具,SVN和Git是最流行的。SVN是一種集中式的代碼管理工具,需要有一個中心服務器,而Git是一種分布式的代碼管理工具。不需要一個中心服務器。不需要中心服務器意味著在沒有網絡的情況下,Git也能進行版本管理。因此,單從這一點出發,Git就比SVN要方便很多。當然,Git和SVN相比,還有許多不同的理念設計,但是總的來說,Git越來越受到大家的青睞,尤其是在開源社區。君不見,Linux是采用Git進行版本管理,而越來越火的GitHub,提供也是Git代碼管理服務。本文不打算分析Git與SVN的區別,以及Git的使用方法,不過強烈建議大家先去了解Git,然后再看下面的內容。這里推薦一本Git書籍《Pro Git》,它是GitHub的員工Scott Chacon撰寫的,對Git的使用及其原理都介紹得非常詳細和清晰。
前面提到,AOSP是由許許多項目組成的,例如,在Android 4.2中,就包含了329個項目,每一個項目都是一個獨立的Git倉庫。這意味著,如果我們要創建一個AOSP分支來做feature開發,那么就需要到每一個子項目去創建對應的分支。這顯然不能手動地到每一個子項目里面去創建分支,必須要采用一種自動化的方式來處理。這些自動化處理工作就是由Repo工具來完成的。當然,Repo工具所負責的自動化工作不只是創建分支那么簡單,查看分支狀態、提交代碼、更新代碼等基礎Git操作它都可以完成。
Repo工具實際上是由一系列的Python腳本組成的,這些Python腳本通過調用Git命令來完成自己的功能。比較有意思的是,組成Repo工具的那些Python腳本本身也是一個Git倉庫。這個Git倉庫在AOSP里面就稱為Repo倉庫。我們每次執行Repo命令的時候,Repo倉庫都會對自己進行一次更新。
上面我們討論的是Repo倉庫,但是實際上我們執行Repo命令想操作的是AOSP。這就要求Repo命令要知道AOSP都包含有哪些子項目,并且要知道這些子項目的名稱、倉庫地址是什么。換句話說,就是Repo命令要知道AOSP所有子項目的Git倉庫元信息。我們知道,AOSP也是不斷地迭代法變化的,例如,它的每一個版本所包含的子項目可能都是不一樣的。這意味著需要通過另外一個Git倉庫來管理AOSP所有的子項目的Git倉庫元信息。這個Git倉庫在AOSP里面就稱為Manifest倉庫。
到目前為止,我們提到了三種類型的Git倉庫,分別是Repo倉庫、Manifest倉庫和AOSP子項目倉庫。Repo倉庫通過Manifest倉庫可以獲得所有AOSP子項目倉庫的元信息。有了這些元信息之后,我們就可以通過Repo倉庫里面的Python腳本來操作AOSP的子項目。那么,Repo倉庫和Manifest倉庫又是怎么來的呢?答案是通過一個獨立的Repo腳本來獲取,這個Repo腳本位于AOSP的一個官方網站上,我們可以通過HTTP協議來下載。
現在,我們就通過一個圖來來勾勒一下整個AOSP的Picture,它由Repo腳本、Repo倉庫、Manifest倉庫和AOSP子項目倉庫組成,如圖1所示:
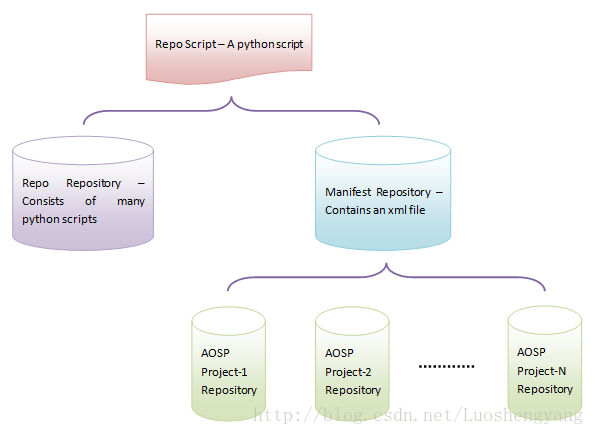
圖1 Repo腳本、Repo倉庫、Manifest倉庫和AOSP子項目倉庫
接下來我們就看看上述腳本和倉庫是怎么來的。
1. Repo腳本
從官方網站可以知道,Repo腳本可以通過以下命令來獲取:
$ curl http://commondatastorage.googleapis.com/git-repo-downloads/repo > ~/bin/repo $ chmod a+x ~/bin/repo
也就是可以通過curl工具從http://commondatastorage.googleapis.com/git-repo-downloads/repo獲得,并且保存在文件~/bin/repo中。由于~/bin/repo是一個python腳本,我們通過chmod命令賦予它可執行的權限,以便接下來我們可以通過repo命令來運行它。
2. Repo倉庫
我們下載好Repo腳本之后,要選通過以下命令來安裝一個Repo倉庫:
$ repo init -u https://android.googlesource.com/platform/manifest
這個命令實際上是包含了兩個操作:安裝Repo倉庫和Manifest倉庫。其中,Manifest倉庫的地址由-u后來帶的參數給出。這一小節我們先分析Repo倉庫的安裝過程,在接下來的第3小節中,再分析Manifest倉庫的安裝過程。
我們看看Repo腳本是如何執行repo init命令的:
def main(orig_args):
repo_main, rel_repo_dir = _FindRepo()
cmd, opt, args = _ParseArguments(orig_args)
wrapper_path = os.path.abspath(__file__)
my_main, my_git = _RunSelf(wrapper_path)
if not repo_main:
if opt.help:
_Usage()
if cmd == 'help':
_Help(args)
if not cmd:
_NotInstalled()
if cmd == 'init':
if my_git:
_SetDefaultsTo(my_git)
try:
_Init(args)
except CloneFailure:
......
sys.exit(1)
repo_main, rel_repo_dir = _FindRepo()
else:
_NoCommands(cmd)
if my_main:
repo_main = my_main
ver_str = '.'.join(map(str, VERSION))
me = [repo_main,
'--repo-dir=%s' % rel_repo_dir,
'--wrapper-version=%s' % ver_str,
'--wrapper-path=%s' % wrapper_path,
'--']
me.extend(orig_args)
me.extend(extra_args)
try:
os.execv(repo_main, me)
except OSError as e:
......
sys.exit(148)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(sys.argv[1:])
_FindRepo在從當前目錄開始往上遍歷直到根據目錄。如果中間某一個目錄下面存在一個.repo/repo目錄,并且該.repo/repo存在一個main.py文件,那么就會認為當前是AOSP中執行Repo腳本,這時候它就會返回文件main.py的絕對路徑和當前查找目錄下的.repo子目錄的絕對路徑給調用者。在上述情況下,實際上是說明Repo倉庫已經安裝過了。
_FindRepo的實現如下所示:
repodir = '.repo' # name of repo's private directory S_repo = 'repo' # special repo repository REPO_MAIN = S_repo + '/main.py' # main script def _FindRepo(): """Look for a repo installation, starting at the current directory. """ curdir = os.getcwd() repo = None olddir = None while curdir != '/' \ and curdir != olddir \ and not repo: repo = os.path.join(curdir, repodir, REPO_MAIN) if not os.path.isfile(repo): repo = None olddir = curdir curdir = os.path.dirname(curdir) return (repo, os.path.join(curdir, repodir))
_ParseArguments無非是對Repo的參數進行解析,得到要執行的命令及其對應的參數。例如,當我們調用“repo init -u https://android.googlesource.com/platform/manifest”的時候,就表示要執行的命令是init,這個命令后面跟的參數是“-u https://android.googlesource.com/platform/manifest”。同時,如果我們調用“repo sync”,就表示要執行的命令是sync,這個命令沒有參數。
_RunSelf檢查Repo腳本所在目錄是否存在一個Repo倉庫,如果存在的話,就從該倉庫克隆一個新的倉庫到執行Repo腳本的目錄來。實際上就是從本地克隆一個新的Repo倉庫。如果不存在的話,那么就需要從遠程地址克隆一個Repo倉庫到本地來。這個遠程地址是Hard Code在Repo腳本里面。
_RunSelf的實現如下所示:
def _RunSelf(wrapper_path):
my_dir = os.path.dirname(wrapper_path)
my_main = os.path.join(my_dir, 'main.py')
my_git = os.path.join(my_dir, '.git')
if os.path.isfile(my_main) and os.path.isdir(my_git):
for name in ['git_config.py',
'project.py',
'subcmds']:
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(my_dir, name)):
return None, None
return my_main, my_git
return None, None
從這里我們就可以看出,如果Repo腳本所在的目錄存在一個Repo倉庫,那么要滿足以下條件:
(1). 存在一個.git目錄;
(2). 存在一個main.py文件;
(3). 存在一個git_config.py文件;
(4). 存在一個project.py文件;
(5). 存在一個subcmds目錄。
上述目錄和文件實際上都是一個標準的Repo倉庫所具有的。
我們再回到main函數中。如果調用_FindRepo得到的repo_main的值等于空,那么就說明當前目錄還沒有安裝Repo倉庫,這時候Repo后面所跟的參數只能是help或者init,否則的話,就會顯示錯誤信息。如果Repo后面跟的參數是help,就打印出Repo腳本的幫助文檔。
我們關注Repo后面跟的參數是init的情況。這時候看一下調用_RunSelf的返回值my_git是否不等于空。如果不等于空的話,那么就說明Repo腳本所在目錄存一個Repo倉庫,這時候就調用_SetDefaultsTo設置等一會要克隆的Repo倉庫源。
_SetDefaultsTo的實現如下所示:
GIT = 'git'
REPO_URL = 'https://gerrit.googlesource.com/git-repo'
REPO_REV = 'stable'
def _SetDefaultsTo(gitdir):
global REPO_URL
global REPO_REV
REPO_URL = gitdir
proc = subprocess.Popen([GIT,
'--git-dir=%s' % gitdir,
'symbolic-ref',
'HEAD'],
stdout = subprocess.PIPE,
stderr = subprocess.PIPE)
REPO_REV = proc.stdout.read().strip()
proc.stdout.close()
proc.stderr.read()
proc.stderr.close()
if proc.wait() != 0:
_print('fatal: %s has no current branch' % gitdir, file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(1)
如果Repo腳本所在目錄不存在一個Repo倉庫,那么默認就將https://gerrit.googlesource.com/git-repo設置為一會要克隆的Repo倉庫源,并且要克隆的分支是stable。否則的話,就以該Repo倉庫作為克隆源,并且以該Repo倉庫的當前分支作為要克隆的分支。
從前面的分析就可以知道,當我們執行"repo init"命令的時候:
(1). 如果我們只是從網上下載了一個Repo腳本,那么在執行Repo命令的時候,就會從遠程克隆一個Repo倉庫到當前執行Repo腳本的目錄來。
(2). 如果我們從網上下載的是一個帶有Repo倉庫的Repo腳本,那么在執行Repo命令的時候,就可以從本地克隆一個Repo倉庫到當前執行Repo腳本的目錄來。
我們再繼續看main函數的實現,它接下來調用_Init在當前執行Repo腳本的目錄下安裝一個Repo倉庫:
def _Init(args):
"""Installs repo by cloning it over the network.
"""
opt, args = init_optparse.parse_args(args)
......
url = opt.repo_url
if not url:
url = REPO_URL
extra_args.append('--repo-url=%s' % url)
branch = opt.repo_branch
if not branch:
branch = REPO_REV
extra_args.append('--repo-branch=%s' % branch)
......
if not os.path.isdir(repodir):
try:
os.mkdir(repodir)
except OSError as e:
......
sys.exit(1)
_CheckGitVersion()
try:
if NeedSetupGnuPG():
can_verify = SetupGnuPG(opt.quiet)
else:
can_verify = True
dst = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(repodir, S_repo))
_Clone(url, dst, opt.quiet)
if can_verify and not opt.no_repo_verify:
rev = _Verify(dst, branch, opt.quiet)
else:
rev = 'refs/remotes/origin/%s^0' % branch
_Checkout(dst, branch, rev, opt.quiet)
except CloneFailure:
......
如果我們在執行Repo腳本的時候,沒有通過--repo-url和--repo-branch來指定Repo倉庫的源地址和分支,那么就使用由REPO_URL和REPO_REV所指定的源地址和分支。從前面的分析可以知道,REPO_URL和REPO_REV要么指向遠程地址https://gerrit.googlesource.com/git-repo和分支stable,要么指向Repo腳本所在目錄的Repo倉庫和該倉庫的當前分支。
_Init函數繼續檢查當前執行Repo腳本的目錄是否存在一個.repo目錄。如果不存在的話,那么就新創建一個。接著是否需要驗證等一會克隆回來的Repo倉庫的GPG。如果需要驗證的話,那么就會在調用_Clone函數來克隆好Repo倉庫之后,調用_Verify函數來驗證該Repo倉庫的GPG。
最關鍵的地方就在于函數_Clone函數和_Checkout函數的調用,前者用來從url指定的地方克隆一個倉庫到dst指定的地方來,實際上就是克隆到當前目錄下的./repo/repo目錄來,后者在克隆回來的倉庫中將branch分支checkout出來。
函數_Clone的實現如下所示:
def _Clone(url, local, quiet):
"""Clones a git repository to a new subdirectory of repodir
"""
try:
os.mkdir(local)
except OSError as e:
_print('fatal: cannot make %s directory: %s' % (local, e.strerror),
file=sys.stderr)
raise CloneFailure()
cmd = [GIT, 'init', '--quiet']
try:
proc = subprocess.Popen(cmd, cwd = local)
except OSError as e:
......
......
_InitHttp()
_SetConfig(local, 'remote.origin.url', url)
_SetConfig(local, 'remote.origin.fetch',
'+refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*')
if _DownloadBundle(url, local, quiet):
_ImportBundle(local)
else:
_Fetch(url, local, 'origin', quiet)
這個函數首先是調用"git init"在當前目錄下的.repo/repo子目錄初始化一個Git倉庫,接著再調用_SetConfig函來設置該Git倉庫的url信息等。再接著調用_DownloadBundle來檢查指定的url是否存在一個clone.bundle文件。如果存在這個clone.bundle文件的話,就以它作為Repo倉庫的克隆源。
函數_DownloadBundle的實現如下所示:
def _DownloadBundle(url, local, quiet):
if not url.endswith('/'):
url += '/'
url += 'clone.bundle'
......
if not url.startswith('http:') and not url.startswith('https:'):
return False
dest = open(os.path.join(local, '.git', 'clone.bundle'), 'w+b')
try:
try:
r = urllib.request.urlopen(url)
except urllib.error.HTTPError as e:
if e.code in [403, 404]:
return False
......
raise CloneFailure()
except urllib.error.URLError as e:
......
raise CloneFailure()
try:
if not quiet:
_print('Get %s' % url, file=sys.stderr)
while True:
buf = r.read(8192)
if buf == '':
return True
dest.write(buf)
finally:
r.close()
finally:
dest.close()
Bundle文件是Git提供的一種機制,用來解決不能正常通過git、ssh和http等網絡協議從遠程地址克隆Git倉庫的問題。簡單來說,就是我們可以用“git bundle”命令來在一個Git倉庫創建一個Bundle文件,這個Bundle文件就會包含Git倉庫的提交歷史。把這個Bundle文件通過其它方式拷貝到另一臺機器上,就可以將它作為一個本地Git倉庫來使用,而不用去訪問遠程網絡。
回到函數_Clone中,如果存在對應的clone.bundle文件,并且能成功下載到該clone.bundle,接下來就調用函數_ImportBundle將它作為源倉庫克隆為新的Repo倉庫。函數_ImportBundle的實現如下所示:
def _ImportBundle(local): path = os.path.join(local, '.git', 'clone.bundle') try: _Fetch(local, local, path, True) finally: os.remove(path)
結合_Clone函數和_ImportBundle函數就可以看出,從clone.bundle文件克隆Repo倉庫和從遠程url克隆Repo倉庫都是通過函數_Fetch來實現的。區別就在于調用函數_Fetch時指定的第三個參數,前者是已經下載到本地的一個clone.bundle文件路徑,后者是origin(表示遠程倉庫名稱)。
函數_Fetch的實現如下所示:
def _Fetch(url, local, src, quiet):
if not quiet:
_print('Get %s' % url, file=sys.stderr)
cmd = [GIT, 'fetch']
if quiet:
cmd.append('--quiet')
err = subprocess.PIPE
else:
err = None
cmd.append(src)
cmd.append('+refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*')
cmd.append('refs/tags/*:refs/tags/*')
proc = subprocess.Popen(cmd, cwd = local, stderr = err)
if err:
proc.stderr.read()
proc.stderr.close()
if proc.wait() != 0:
raise CloneFailure()
函數_Fetch實際上就是通過“git fetch”從指定的倉庫源克隆一個新的Repo倉庫到當前目錄下的.repo/repo子目錄來。
注意,以上只是克隆好了一個Repo倉庫,接下來還需要從這個Repo倉庫checkout出一個分支來,才能正常工作。從Repo倉庫checkout出一個分支是通過調用函數_Checkout來實現的:
def _Checkout(cwd, branch, rev, quiet):
"""Checkout an upstream branch into the repository and track it.
"""
cmd = [GIT, 'update-ref', 'refs/heads/default', rev]
if subprocess.Popen(cmd, cwd = cwd).wait() != 0:
raise CloneFailure()
_SetConfig(cwd, 'branch.default.remote', 'origin')
_SetConfig(cwd, 'branch.default.merge', 'refs/heads/%s' % branch)
cmd = [GIT, 'symbolic-ref', 'HEAD', 'refs/heads/default']
if subprocess.Popen(cmd, cwd = cwd).wait() != 0:
raise CloneFailure()
cmd = [GIT, 'read-tree', '--reset', '-u']
if not quiet:
cmd.append('-v')
cmd.append('HEAD')
if subprocess.Popen(cmd, cwd = cwd).wait() != 0:
raise CloneFailure()
要checkout出來的分支由參數branch指定。從前面的分析可以知道,如果當前執行的Repo腳本所在目錄存在一個Repo倉庫,那么參數branch描述的就是該倉庫當前checkout出來的分支。否則的話,參數branch描述的就是從遠程倉庫克隆回來的“stable”分支。
需要注意的是,這里從倉庫checkout出分支不是使用“git checkout”命令來實現的,而是通過更底層的Git命令“git update-ref”來實現的。實際上,“git checkout”命令也是通過“git update-ref”命令來實現的,只不過它進行了更高層的封裝,更方便使用。如果我們去分析組成Repo倉庫的那些Python腳本命令,就會發現它們基本上都是通過底層的Git命令來完成Git功能的。
3. Manifest倉庫
我們接著再分析下面這個命令的執行:
repo init -u https://android.googlesource.com/platform/manifest
如前所述,這個命令安裝好Repo倉庫之后,就會調用該Repo倉庫下面的main.py腳本,對應的文件為.repo/repo/main.py,它的入口函數的實現如下所示:
def _Main(argv):
result = 0
opt = optparse.OptionParser(usage="repo wrapperinfo -- ...")
opt.add_option("--repo-dir", dest="repodir",
help="path to .repo/")
......
repo = _Repo(opt.repodir)
try:
try:
init_ssh()
init_http()
result = repo._Run(argv) or 0
finally:
close_ssh()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
......
result = 1
except ManifestParseError as mpe:
......
result = 1
except RepoChangedException as rce:
# If repo changed, re-exec ourselves.
#
argv = list(sys.argv)
argv.extend(rce.extra_args)
try:
os.execv(__file__, argv)
except OSError as e:
......
result = 128
sys.exit(result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
_Main(sys.argv[1:])
從前面的分析可以知道,通過參數--repo-dir傳進來的是AOSP根目錄下的.repo目錄,這是一個隱藏目錄,里面保存的是Repo倉庫、Manifest倉庫,以及各個AOSP子項目倉庫。函數_Main首先是調用init_ssh和init_http來初始化網絡環境,接著再調用前面創建的一個_Repo對象的成員函數_Run來解析要執行的命令,并且執行這個命令。
_Repo類的成員函數_Run的實現如下所示:
from subcmds import all_commands
class _Repo(object):
def __init__(self, repodir):
self.repodir = repodir
self.commands = all_commands
# add 'branch' as an alias for 'branches'
all_commands['branch'] = all_commands['branches']
def _Run(self, argv):
result = 0
name = None
glob = []
for i in range(len(argv)):
if not argv[i].startswith('-'):
name = argv[i]
if i > 0:
glob = argv[:i]
argv = argv[i + 1:]
break
if not name:
glob = argv
name = 'help'
argv = []
gopts, _gargs = global_options.parse_args(glob)
......
try:
cmd = self.commands[name]
except KeyError:
......
return 1
cmd.repodir = self.repodir
cmd.manifest = XmlManifest(cmd.repodir)
......
try:
result = cmd.Execute(copts, cargs)
except DownloadError as e:
......
result = 1
except ManifestInvalidRevisionError as e:
......
result = 1
except NoManifestException as e:
......
result = 1
except NoSuchProjectError as e:
......
result = 1
finally:
......
return result
Repo腳本能執行的命令都放在目錄.repo/repo/subcmds中,該目錄每一個python文件都對應一個Repo命令。例如,“repo init”表示要執行命令腳本是.repo/repo/subcmds/init.py。
_Repo類的成員函數_Run首先是在repo后面所帶的參數中,不是以橫線“-”開始的第一個選項,該選項就代表要執行的命令,該命令的名稱就保存在變量name中。接著根據變量name的值在_Repo類的成員變量commands中找到對應的命令模塊cmd,并且指定該命令模塊cmd的成員變量repodir和manifest的值。命令模塊cmd的成員變量repodir描述的就是AOSP的.repo目錄,成員變量manifest指向的是一個XmlManifest對象,它描述的是AOSP的Repo倉庫和Manifest倉庫。
我們看看XmlManifest類的構造函數,它定義在文件.repo/repo/xml_manifest.py文件中:
class XmlManifest(object): """manages the repo configuration file""" def __init__(self, repodir): self.repodir = os.path.abspath(repodir) self.topdir = os.path.dirname(self.repodir) self.manifestFile = os.path.join(self.repodir, MANIFEST_FILE_NAME) ...... self.repoProject = MetaProject(self, 'repo', gitdir = os.path.join(repodir, 'repo/.git'), worktree = os.path.join(repodir, 'repo')) self.manifestProject = MetaProject(self, 'manifests', gitdir = os.path.join(repodir, 'manifests.git'), worktree = os.path.join(repodir, 'manifests')) ......
XmlManifest作了描述了AOSP的Repo目錄(repodir)、AOSP 根目錄(topdir)和Manifest.xml文件(manifestFile)之外,還使用兩個MetaProject對象描述了AOSP的Repo倉庫(repoProject)和Manifest倉庫(manifestProject)。
在AOSP中,每一個子項目(或者說倉庫)都用一個Project對象來描述。Project類定義在文件.repo/repo/project.py文件中,用來封裝對各個項目的基礎Git操作,例如,對項目進行暫存、提交和更新等。它的構造函數如下所示:
class Project(object):
def __init__(self,
manifest,
name,
remote,
gitdir,
worktree,
relpath,
revisionExpr,
revisionId,
rebase = True,
groups = None,
sync_c = False,
sync_s = False,
clone_depth = None,
upstream = None,
parent = None,
is_derived = False,
dest_branch = None):
"""Init a Project object.
Args:
manifest: The XmlManifest object.
name: The `name` attribute of manifest.xml's project element.
remote: RemoteSpec object specifying its remote's properties.
gitdir: Absolute path of git directory.
worktree: Absolute path of git working tree.
relpath: Relative path of git working tree to repo's top directory.
revisionExpr: The `revision` attribute of manifest.xml's project element.
revisionId: git commit id for checking out.
rebase: The `rebase` attribute of manifest.xml's project element.
groups: The `groups` attribute of manifest.xml's project element.
sync_c: The `sync-c` attribute of manifest.xml's project element.
sync_s: The `sync-s` attribute of manifest.xml's project element.
upstream: The `upstream` attribute of manifest.xml's project element.
parent: The parent Project object.
is_derived: False if the project was explicitly defined in the manifest;
True if the project is a discovered submodule.
dest_branch: The branch to which to push changes for review by default.
"""
self.manifest = manifest
self.name = name
self.remote = remote
self.gitdir = gitdir.replace('\\', '/')
if worktree:
self.worktree = worktree.replace('\\', '/')
else:
self.worktree = None
self.relpath = relpath
self.revisionExpr = revisionExpr
if revisionId is None \
and revisionExpr \
and IsId(revisionExpr):
self.revisionId = revisionExpr
else:
self.revisionId = revisionId
self.rebase = rebase
self.groups = groups
self.sync_c = sync_c
self.sync_s = sync_s
self.clone_depth = clone_depth
self.upstream = upstream
self.parent = parent
self.is_derived = is_derived
self.subprojects = []
self.snapshots = {}
self.copyfiles = []
self.annotations = []
self.config = GitConfig.ForRepository(
gitdir = self.gitdir,
defaults = self.manifest.globalConfig)
if self.worktree:
self.work_git = self._GitGetByExec(self, bare=False)
else:
self.work_git = None
self.bare_git = self._GitGetByExec(self, bare=True)
self.bare_ref = GitRefs(gitdir)
self.dest_branch = dest_branch
# This will be filled in if a project is later identified to be the
# project containing repo hooks.
self.enabled_repo_hooks = []
Project類構造函數的各個參數的含義見注釋,這里為了方便描述,用中文描述一下:
revisionExpr、revisionId、rebase、groups、sync_c、sync_s和upstream:每一個項目在.repo/repo/manifest.xml文件中都有對應的描述,這幾個屬性的值就來自于該manifest.xml文件對自己的描述的,它們的含義可以參考.repo/repo/docs/manifest-format.txt文件
parent:父項目
is_derived:如果一個項目含有子模塊(也是一個Git倉庫),那么這些子模塊也會用一個Project對象來描述,這些Project的
is_derived屬性會設置為true
dest_branch:用來code review的分支
這里重點說一下項目的Git倉庫目錄和工作目錄的概念。一般來說,一個項目的Git倉庫目錄(默認為.git目錄)是位于工作目錄下面的,但是Git支持將一個項目的Git倉庫目錄和工作目錄分開來存放。在AOSP中,Repo倉庫的Git目錄(.git)位于工作目錄(.repo/repo)下,Manifest倉庫的Git目錄有兩份拷貝,一份(.git)位于工作目錄(.repo/manifests)下,另外一份位于.repo/manifests.git目錄,其余的AOSP子項目的工作目錄和Git目錄都是分開存放的,其中,工作目錄位于AOSP根目錄下,Git目錄位于.repo/repo/projects目錄下。
此外,每一個AOSP子項目的工作目錄也有一個.git目錄,不過這個.git目錄是一個符號鏈接,鏈接到.repo/repo/projects對應的Git目錄。這樣,我們就既可以在AOSP子項目的工作目錄下執行Git命令,也可以在其對應的Git目錄下執行Git命令。一般來說,要訪問到工作目錄的命令(例如git status)需要在工作目錄下執行,而不需要訪問工作目錄(例如git log)可以在Git目錄下執行。
Project類有兩個成員變量work_git和bare_git,它們指向的都是一個_GitGetByExec對象。用來封裝對Git命令的執行。其中,前者在執行Git命令的時候,會將當前目錄設置為項目的工作目錄,而后者在執行的時候,不會設置當前目錄,但是會將環境變量GIT_DIR的值設置為項目的Git目錄,也就是.repo/projects目錄下面的那些目錄。通過這種方式,Project類就可以根據需要來在工作目錄或者Git目錄下執行Git命令。
回到XmlManifest類的構造函數中,由于Repo和Manifest也是屬于Git倉庫,所以我們也需要創建一個Project對象來描述它們。不過,由于它們是比較特殊的Git倉庫(用來描述AOSP子項目元信息的Git倉庫),所以我們就使用另外一個類型為MetaProject的對象來描述它們。MetaProject類是從Project類繼承下來的,定義在project.py文件中,如下所示:
class MetaProject(Project):
"""A special project housed under .repo.
"""
def __init__(self, manifest, name, gitdir, worktree):
Project.__init__(self,
manifest = manifest,
name = name,
gitdir = gitdir,
worktree = worktree,
remote = RemoteSpec('origin'),
relpath = '.repo/%s' % name,
revisionExpr = 'refs/heads/master',
revisionId = None,
groups = None)
既然MetaProject類是從Project類繼承下來的,那么它們的Git操作幾乎都可以通過Project類來完成的。實際上,MetaProject類和Project類目前的區別不是太大,可以認為是基本相同的。使用MetaProject類來描述Repo倉庫和Manifest倉庫,主要是為了強調它們是用來描述AOSP子項目倉庫的元信息的。
回到_Repo類的成員函數_Run中,創建好用來描述Repo倉庫和Manifest倉庫的XmlManifest對象之后,就開始執行跟在repo腳本后面的不帶橫線“-”的選項所表示的命令。在我們這個場景中,這個命令就是init,它對應的Python模塊為.repo/repo/subcmds/init.py,入口函數為定義在該模塊的Init類的成員函數Execute,它的實現如下所示:
class Init(InteractiveCommand, MirrorSafeCommand): ...... def Execute(self, opt, args): ...... self._SyncManifest(opt) self._LinkManifest(opt.manifest_name) ......
Init類的成員函數Execute主要就是調用另外兩個成員函數_SyncManifest和_LinkManifest來完成克隆Manifest倉庫的工作。
Init類的成員函數_SyncManifest的實現如下所示:
class Init(InteractiveCommand, MirrorSafeCommand):
......
def _SyncManifest(self, opt):
m = self.manifest.manifestProject
is_new = not m.Exists
if is_new:
......
m._InitGitDir(mirror_git=mirrored_manifest_git)
if opt.manifest_branch:
m.revisionExpr = opt.manifest_branch
else:
m.revisionExpr = 'refs/heads/master
else:
if opt.manifest_branch:
m.revisionExpr = opt.manifest_branch
else:
m.PreSync()
......
if not m.Sync_NetworkHalf(is_new=is_new):
......
sys.exit(1)
if opt.manifest_branch:
m.MetaBranchSwitch(opt.manifest_branch)
......
m.Sync_LocalHalf(syncbuf)
......
if is_new or m.CurrentBranch is None:
if not m.StartBranch('default'):
......
sys.exit(1)
Init類的成員函數_SyncManifest執行以下操作:
(1). 檢查本地是否存在Manifest倉庫,即檢查用來描述Manifest倉庫MetaProject對象m的成員變量mExists值是否等于true。如果不等于的話,那么就說明本地還沒有安裝過Manifest倉庫。這時候就需要調用該MetaProject對象m的成員函數_InitGitDir來在.repo/manifests目錄初始化一個Git倉庫。
(2). 調用用來描述Manifest倉庫MetaProject對象m的成員函數Sync_NetworkHalf來從遠程倉庫中克隆一個新的Manifest倉庫到本地來,或者更新本地的Manifest倉庫。這個遠程倉庫的地址即為在執行"repo init"命令時,通過-u指定的url,即https://android.googlesource.com/platform/manifest。
(3). 檢查"repo init"命令后面是否通過-b指定要在Manifest倉庫中checkout出來的分支。如果有的話,那么就調用用來描述Manifest倉庫MetaProject對象m的成員函數MetaBranchSwitch做一些清理工作,以便接下來可以checkout到指定的分支。
(4). 調用用來描述Manifest倉庫MetaProject對象m的成員函數Sync_LocaHalf來執行checkout分支的操作。注意,要切換的分支在前面已經記錄在MetaProject對象m的成員變量revisionExpr中。
(5). 如果前面執行的是新安裝Manifest倉庫的操作,并且沒有通過-b選項指定要checkout的分支,那么默認就checkout出一個default分支。
接下來,我們就主要分析MetaProject類的成員函數_InitGitDir、Sync_NetworkHalf和Sync_LocaHalf的實現。這幾個函數實際上都是由MetaProject的父類Project來實現的,因此,下面我們就分析Project類的成員函數_InitGitDir、Sync_NetworkHalf和Sync_LocaHalf的實現。
Project類的成員函數_InitGitDir的成員函數的實現如下所示:
class Project(object): ...... def _InitGitDir(self, mirror_git=None): if not os.path.exists(self.gitdir): os.makedirs(self.gitdir) self.bare_git.init() ......
Project類的成員函數_InitGitDir首先是檢查項目的Git目錄是否已經存在。如果不存在,那么就會首先創建這個Git目錄,然后再調用成員變量bare_git所描述的一個_GitGetByExec對象的成員函數init來在該目錄下初始化一個Git倉庫。
_GitGetByExec類的成員函數init是通過另外一個成員函數__getattr__來實現的,如下所示:
class Project(object):
......
class _GitGetByExec(object):
......
def __getattr__(self, name):
"""Allow arbitrary git commands using pythonic syntax.
This allows you to do things like:
git_obj.rev_parse('HEAD')
Since we don't have a 'rev_parse' method defined, the __getattr__ will
run. We'll replace the '_' with a '-' and try to run a git command.
Any other positional arguments will be passed to the git command, and the
following keyword arguments are supported:
config: An optional dict of git config options to be passed with '-c'.
Args:
name: The name of the git command to call. Any '_' characters will
be replaced with '-'.
Returns:
A callable object that will try to call git with the named command.
"""
name = name.replace('_', '-')
def runner(*args, **kwargs):
cmdv = []
config = kwargs.pop('config', None)
......
if config is not None:
......
for k, v in config.items():
cmdv.append('-c')
cmdv.append('%s=%s' % (k, v))
cmdv.append(name)
cmdv.extend(args)
p = GitCommand(self._project,
cmdv,
bare = self._bare,
capture_stdout = True,
capture_stderr = True)
if p.Wait() != 0:
......
r = p.stdout
try:
r = r.decode('utf-8')
except AttributeError:
pass
if r.endswith('\n') and r.index('\n') == len(r) - 1:
return r[:-1]
return r
return runner
從注釋可以知道,_GitGetByExec類的成員函數__getattr__使用了一個trick,將_GitGetByExec類沒有實現的成員函數間接地以屬性的形式來獲得,并且將該沒有實現的成員函數的名稱作為git的一個參數來執行。也就是說,當執行_GitGetByExec.init()的時候,實際上是透過成員函數__getattr__執行了一個"git init"命令。這個命令就正好是用來初始化一個Git倉庫。
我們再來看Project類的成員函數Sync_NetworkHalf的實現:
class Project(object):
......
def Sync_NetworkHalf(self,
quiet=False,
is_new=None,
current_branch_only=False,
clone_bundle=True,
no_tags=False):
"""Perform only the network IO portion of the sync process.
Local working directory/branch state is not affected.
"""
if is_new is None:
is_new = not self.Exists
if is_new:
self._InitGitDir()
......
if not self._RemoteFetch(initial=is_new, quiet=quiet, alt_dir=alt_dir,
current_branch_only=current_branch_only,
no_tags=no_tags):
return False
......
Project類的成員函數Sync_NetworkHalf主要執行以下的操作:
(1). 檢查本地是否已經存在對應的Git倉庫。如果不存在,那么就先調用另外一個成員函數_InitGitDir來初始化該Git倉庫。
(2). 調用另外一個成員函籹_RemoteFetch來從遠程倉庫更新本地倉庫。
Project類的成員函數_RemoteFetch的實現如下所示:
class Project(object):
......
def _RemoteFetch(self, name=None,
current_branch_only=False,
initial=False,
quiet=False,
alt_dir=None,
no_tags=False):
......
cmd = ['fetch']
......
ok = False
for _i in range(2):
ret = GitCommand(self, cmd, bare=True, ssh_proxy=ssh_proxy).Wait()
if ret == 0:
ok = True
break
elif current_branch_only and is_sha1 and ret == 128:
# Exit code 128 means "couldn't find the ref you asked for"; if we're in sha1
# mode, we just tried sync'ing from the upstream field; it doesn't exist, thus
# abort the optimization attempt and do a full sync.
break
time.sleep(random.randint(30, 45))
......
Project類的成員函數_RemoteFetch的核心操作就是調用“git fetch”命令來從遠程倉庫更新本地倉庫。
接下來我們再看MetaProject類的成員函數Sync_LocaHalf的實現:
class Project(object):
......
def Sync_LocalHalf(self, syncbuf):
"""Perform only the local IO portion of the sync process.
Network access is not required.
"""
......
revid = self.GetRevisionId(all_refs)
......
self._InitWorkTree()
head = self.work_git.GetHead()
if head.startswith(R_HEADS):
branch = head[len(R_HEADS):]
try:
head = all_refs[head]
except KeyError:
head = None
else:
branch = None
......
if head == revid:
# No changes; don't do anything further.
#
return
branch = self.GetBranch(branch)
......
if not branch.LocalMerge:
# The current branch has no tracking configuration.
# Jump off it to a detached HEAD.
#
syncbuf.info(self,
"leaving %s; does not track upstream",
branch.name)
try:
self._Checkout(revid, quiet=True)
except GitError as e:
syncbuf.fail(self, e)
return
......
return
......
這里我們只分析一種比較簡單的情況,就是當前要checkout的分支是一個干凈的分支,它沒有做過修改,也沒有設置跟蹤遠程分支。這時候Project類的成員函數_RemoteFetch的主要執行以下操作:
(1). 調用另外一個成員函數GetRevisionId獲得即將要checkout的分支,保存在變量revid中。
(2). 調用成員變量work_git所描述的一個_GitGetByExec對象的成員函數GetHead獲得項目當前checkout的分支,只存在變量head中。
(3). 如果即將要checkout的分支revid就是當前已經checkout分支,那么就什么也不用做。否則繼續往下執行。
(4). 調用另外一個成員函數GetBranch獲得用來描述當前分支的一個Branch對象。
(5). 如果上述Branch對象的屬性LocalMerge的值等于None,也就是屬于我們討論的情況,那么就調用另外一個成員函數_Checkout真正執行checkout分支revid的操作。
如果要checkout的分支revid不是一個干凈的分支,也就是它正在跳蹤遠程分支,并且在本地做過提交,這些提交又沒有上傳到遠程分支去,那么就需要執行一些merge或者rebase的操作。不過無論如何,這些操作都是通過標準的Git命令來完成的。
我們接著再看Project類的成員函數_Checkout的實現:
class Project(object):
......
def _Checkout(self, rev, quiet=False):
cmd = ['checkout']
if quiet:
cmd.append('-q')
cmd.append(rev)
cmd.append('--')
if GitCommand(self, cmd).Wait() != 0:
if self._allrefs:
raise GitError('%s checkout %s ' % (self.name, rev))
Project類的成員函數_Checkout的實現很簡單,它通過GitCommand類構造了一個“git checkout”命令,將參數rev描述的分支checkout出來。
至此,我們就將Manifest倉庫從遠程地址https://android.googlesource.com/platform/manifest克隆到本地來了,并且checkout出了指定的分支。回到Init類的成員函數Execute中,它接下來還要調用另外一個成員函數_LinkManifest來執行一個符號鏈接的操作。
Init類的成員函數_LinkManifest的實現如下所示:
class Init(InteractiveCommand, MirrorSafeCommand):
......
def _LinkManifest(self, name):
if not name:
print('fatal: manifest name (-m) is required.', file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(1)
try:
self.manifest.Link(name)
except ManifestParseError as e:
print("fatal: manifest '%s' not available" % name, file=sys.stderr)
print('fatal: %s' % str(e), file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(1)
參數name的值一般就等于“default.xml”,表示Manifest倉庫中的default.xml文件,Init類的成員函數_LinkManifest通過調用成員變量manifest所描述的一個XmlManifest對象的成員函數Link來執行符號鏈接的操作,它定義在文件.repo/repo/xml_manifest.py文件,它的實現如下所示:
class XmlManifest(object):
"""manages the repo configuration file"""
......
def Link(self, name):
"""Update the repo metadata to use a different manifest.
"""
......
try:
if os.path.lexists(self.manifestFile):
os.remove(self.manifestFile)
os.symlink('manifests/%s' % name, self.manifestFile)
except OSError as e:
raise ManifestParseError('cannot link manifest %s: %s' % (name, str(e)))
XmlManifest類的成員變量manifestFile的值等于$(AOSP)/.repo/manifest.xml,通過調用os.symlink就將它符號鏈接至$(AOSP)/.repo/manifests/<name>文件去。這樣無論Manifest倉庫中用來描述AOSP子項目的xml文件是什么名稱,都可以統一通過$(AOSP)/.repo/manifest.xml文件來訪問。
前面提到,Manifest倉庫中用來描述AOSP子項目的xml文件名稱默認就為default.xml,它的內容如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<manifest>
<remote name="aosp"
fetch=".."
review="https://android-review.googlesource.com/" />
<default revision="refs/tags/android-4.2_r1"
remote="aosp"
sync-j="4" />
<project path="build" name="platform/build" >
<copyfile src="core/root.mk" dest="Makefile" />
</project>
<project path="abi/cpp" name="platform/abi/cpp" />
<project path="bionic" name="platform/bionic" />
......
</manifest>
關于該xml文件的詳細描述可以參考.repo/repo/docs/manifest-format.txt文件。一般來說,該xml包含有四種類型的標簽:
remote:用來指定遠程倉庫信息。屬性name描述的是一個遠程倉庫的名稱,屬性fetch用作項目名稱的前緣,在構造項目倉庫遠程地址時使用到,屬性review描述的是用作code review的server地址。
default:當project標簽沒有指定default標簽的屬性時,默認就使用在default標簽列出的屬性。屬性revision描述的是項目默認檢出的分支,屬性remote描述的是默認使用的遠程倉庫名稱,必須要對應的remote標簽的name屬性值,屬性sync-j描述的是從遠程倉庫更新項目時使用的并行任務數。
project:每一個AOSP子項目在這里都對應有一個projec標簽,用來描述項目的元信息。屬性path描述的是項目相對于遠程倉庫URL的路徑,屬性name描述的是項目的名稱,也是相對于 AOSP根目錄的目錄名稱。例如,如果遠程倉庫URL為https://android.googlesource.com/platform,那么AOSP子項目bionic對應的遠程倉庫URL就為https://android.googlesource.com/platform/bionic,并且它的工作目錄位于$(AOSP)/bionic。
copyfile:作為project的子標簽,表示要將從遠程倉庫更新回來的文件拷貝到指定的另外一個文件去。
至些,我們就分析完成Manifest倉庫的克隆過程了。在此基礎上,我們再分析AOSP子項目倉庫的克隆過程或者針對AOSP子項目的各種Repo命令就容易多了。
4. AOSP子項目倉庫
執行完成repo init命令之后,我們就可以繼續執行repo sync命令來克隆或者同步AOSP子項目了:
$ repo sync
與repo init命令類似,repo sync命令的執行過程如下所示:
1. Repo腳本找到Repo倉庫里面的main.py文件,并且執行它的入口函數_Main;
2. Repo倉庫里面的main.py文件的入口函數_Main調用_Repo類的成員函數_Run對Repo腳本傳遞進來的參數進行解析;
3. _Repo類的成員函數_Run解析參數發現要執行的命令是sync,于是就在subcmds目錄中找到一個名稱為sync.py的文件,并且調用定義在它里面的一個名稱為Sync的類的成員函數Execute;
4. Sync類的成員函數Execute解析Manifest倉庫的default.xml文件,并且克隆或者同步出在default.xml文件里面列出的每一個AOSP子項目。
在第3步中,Repo倉庫的每一個Python文件是如何與一個Repo命令關聯起來的呢?原來在Repo倉庫的subcmds目錄中,有一個__init__.py文件,每當subcmds被import時,定義在它里面的命令就會被執行,如下所示:
all_commands = {}
my_dir = os.path.dirname(__file__)
for py in os.listdir(my_dir):
if py == '__init__.py':
continue
if py.endswith('.py'):
name = py[:-3]
clsn = name.capitalize()
while clsn.find('_') > 0:
h = clsn.index('_')
clsn = clsn[0:h] + clsn[h + 1:].capitalize()
mod = __import__(__name__,
globals(),
locals(),
['%s' % name])
mod = getattr(mod, name)
try:
cmd = getattr(mod, clsn)()
except AttributeError:
raise SyntaxError('%s/%s does not define class %s' % (
__name__, py, clsn))
name = name.replace('_', '-')
cmd.NAME = name
all_commands[name] = cmd
__init__.py會列出subcmds目錄中的所有Python文件(除了__init__.py),并且里面找到對應的類,然后再創建這個類的一個對象,并且以文件名為關鍵字將該對象保存在全局變量all_commands中。例如,對于sync.py文件,它的文件名稱去掉后綴名后為sync,再將sync的首字母大寫,得到Sync。也就是說,sync.py需要定義一個Sync類,并且這個類需要直接或者間接地從Command類繼承下來。Command類有一個成員函數Execute,它的各個子類需要對它進行重寫,以實現各自的功能。
_Repo類的成員函數_Run就是通過subcmds模塊里面的全局變量all_commands,并且根據Repo腳本傳進行來的第一個不帶橫線“-”的參數來找到對應的Command對象,然后調用它的成員函數Execute的。
Sync類的成員函數Execute的實現如下所示:
class Sync(Command, MirrorSafeCommand):
......
def Execute(self, opt, args):
......
mp = self.manifest.manifestProject
......
if not opt.local_only:
mp.Sync_NetworkHalf(quiet=opt.quiet,
current_branch_only=opt.current_branch_only,
no_tags=opt.no_tags)
......
if mp.HasChanges:
......
mp.Sync_LocalHalf(syncbuf)
......
all_projects = self.GetProjects(args,
missing_ok=True,
submodules_ok=opt.fetch_submodules)
......
if not opt.local_only:
to_fetch = []
......
to_fetch.extend(all_projects)
to_fetch.sort(key=self._fetch_times.Get, reverse=True)
fetched = self._Fetch(to_fetch, opt)
......
if opt.network_only:
# bail out now; the rest touches the working tree
return
# Iteratively fetch missing and/or nested unregistered submodules
while True:
......
all_projects = self.GetProjects(args,
missing_ok=True,
submodules_ok=opt.fetch_submodules)
missing = []
for project in all_projects:
if project.gitdir not in fetched:
missing.append(project)
if not missing:
break
......
fetched.update(self._Fetch(missing, opt))
if self.UpdateProjectList():
sys.exit(1)
......
for project in all_projects:
......
if project.worktree:
project.Sync_LocalHalf(syncbuf)
......
Sync類的成員函數Execute的核以執行流程如下所示:
(1). 獲得用來描述Manifest倉庫的MetaProject對象mp。
(2). 如果在執行repo sync命令時,沒有指定--local-only選項,那么就調用MetaProject對象mp的成員函數Sync_NetworkHalf從遠程倉庫下載更新本地Manifest倉庫。
(3). 如果Mainifest倉庫發生過更新,那么就調用MetaProject對象mp的成員函數Sync_LocalHalf來合并這些更新到本地的當前分支來。
(4). 調用Sync的父類Command的成員函數GetProjects獲得由Manifest倉庫的default.xml文件定義的所有AOSP子項目信息,或者由參數args所指定的AOSP子項目的信息。這些AOSP子項目信息都是通過Project對象來描述,并且保存在變量all_projects中。
(5). 如果在執行repo sync命令時,沒有指定--local-only選項,那么就對保存在變量all_projects中的AOSP子項目進行網絡更新,也就是從遠程倉庫中下載更新到本地倉庫來,這是通過調用Sync類的成員函數_Fetch來完成的。Sync類的成員函數_Fetch實際上又是通過調用Project類的成員函數Sync_NetworkHalf來將遠程倉庫的更新下載到本地倉庫來的。
(6). 由于AOSP子項目可能會包含有子模塊,因此當對它們進行了遠程更新之后,需要檢查它們是否包含有子模塊。如果包含有子模塊,并且執行repo sync腳本時指定有--fetch-submodules選項,那么就需要對AOSP子項目的子模塊進行遠程更新。調用Sync的父類Command的成員函數GetProjects的時候,如果將參數submodules_ok的值設置為true,那么得到的AOSP子項目列表就包含有子模塊。將這個AOSP子項目列表與之前獲得的AOSP子項目列表fetched進行一個比較,就可以知道有哪些子模塊是需要更新的。需要更新的子模塊都保存在變量missing中。由于子模塊也是用Project類來描述的,因此,我們可以像遠程更新AOSP子項目一樣,調用Sync類的成員函數_Fetch來更新它們的子模塊。
(7). 調用Sync類的成員函數UpdateProjectList更新$(AOSP)/.repo目錄下的project.list文件。$(AOSP)/.repo/project.list記錄的是上一次遠程同步后所有的AOSP子項目名稱。以后每一次遠程同步之后,Sync類的成員函數UpdateProjectList就會通過該文件來檢查是否存在某些AOSP子項目被刪掉了。如果存在這樣的AOSP子項目,并且這些AOSP子項目沒有發生修改,那么就會將它們的工作目錄刪掉。
(8). 到目前為止,Sync類的成員函數對AOSP子項目所做的操作僅僅是下載遠程倉庫的更新到本地來,但是還沒有將這些更新合并到本地的當前分支來,因此,這時候就需要調用Project類的成員函數Sync_LocalHalf來執行合并更新的操作。
從上面的步驟可以看出,init sync命令的核心操作就是收集每一個需要同步的AOSP子項目所對應的Project對象,然后再調用這些Project對象的成員函數Sync_NetwokHalft和Sync_LocalHalf進行同步。關于Project類的成員函數Sync_NetwokHalft和Sync_LocalHalf,我們在前面分析Manifest倉庫的克隆過程時,已經分析過了,它們無非就是通過git fetch、git rebase或者git merge等基本Git命令來完成自己的功能。
以上我們分析的就是AOSP子項目倉庫的克隆或者同步過程,為了更進一步加深對Repo倉庫的理解,接下來我們再分析另外一個用來在AOSP上創建Topic的命令repo start。
5. 在AOSP上創建Topic
在Git的世界里,分支(branch)是一個很核心的概念。Git鼓勵你在修復Bug或者開發新的Feature時,都創建一個新的分支。創建Git分支的代價是很小的,而且速度很快,因此,不用擔心創建Git分支是一件不討好的事情,而應該盡可能多地使用分支。
同樣的,我們下載好AOSP代碼之后,如果需要在上面進行修改,或者增加新的功能,那么就要在新的分支上面進行。Repo倉庫提供了一個repo start命令,用來在AOSP上創建分支,也稱為Topic。這個命令的用法如下所示:
$ repo start BRANCH_NAME [PROJECT_LIST]
參數BRANCH_NAME指定新的分支名稱,后面的PROJECT_LIST是可選的。如果指定了PROJECT_LIST,就表示只對特定的AOSP子項目創建分支,否則的話,就對所有的AOSP子項目創建分支。
根據前面我們對repo sync命令的分析可以知道,當我們執行repo start命令的時候,最終定義在Repo倉庫的subcmds/start.py文件里面的Start類的成員函數Execute會被調用,它的實現如下所示:
class Start(Command):
......
def Execute(self, opt, args):
......
nb = args[0]
if not git.check_ref_format('heads/%s' % nb):
print("error: '%s' is not a valid name" % nb, file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(1)
err = []
projects = []
if not opt.all:
projects = args[1:]
if len(projects) < 1:
print("error: at least one project must be specified", file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(1)
all_projects = self.GetProjects(projects)
pm = Progress('Starting %s' % nb, len(all_projects))
for project in all_projects:
pm.update()
......
if not project.StartBranch(nb):
err.append(project)
pm.end()
......
參數args[0]保存的是要創建的分支的名稱,參數args[1:]保存的是要創建分支的AOSP子項目名稱列表,Start類的成員函數Execute分別將它們保存變量nb和projects中。
Start類的成員函數Execute接下來調用父類Command的成員函數GetProjects,并且以變量projects為參數,就可以獲得所有需要創建新分支nb的AOSP子項目列表all_projects。在all_projects中,每一個AOSP子項目都用一個Project對象來描述。
最后,Start類的成員函數Execute就遍歷all_projects里面的每一個Project對象,并且調用它們的成員函數StartBranch來執行創建新分支的操作。
Project類的成員函數StartBranch的實現如下所示:
class Project(object):
......
def StartBranch(self, name):
"""Create a new branch off the manifest's revision.
"""
head = self.work_git.GetHead()
if head == (R_HEADS + name):
return True
all_refs = self.bare_ref.all
if (R_HEADS + name) in all_refs:
return GitCommand(self,
['checkout', name, '--'],
capture_stdout = True,
capture_stderr = True).Wait() == 0
branch = self.GetBranch(name)
branch.remote = self.GetRemote(self.remote.name)
branch.merge = self.revisionExpr
revid = self.GetRevisionId(all_refs)
if head.startswith(R_HEADS):
try:
head = all_refs[head]
except KeyError:
head = None
if revid and head and revid == head:
ref = os.path.join(self.gitdir, R_HEADS + name)
try:
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(ref))
except OSError:
pass
_lwrite(ref, '%s\n' % revid)
_lwrite(os.path.join(self.worktree, '.git', HEAD),
'ref: %s%s\n' % (R_HEADS, name))
branch.Save()
return True
if GitCommand(self,
['checkout', '-b', branch.name, revid],
capture_stdout = True,
capture_stderr = True).Wait() == 0:
branch.Save()
return True
return False
Project類的成員函數StartBranch的執行過程如下所示:
(1). 獲得項目的當前分支head,這是通過調用Project類的成員函數GetHead來實現的。
(2). 項目當前的所有分支保存在Project類的成員變量bare_ref所描述的一個GitRefs對象的成員變量all中。如果要創建的分支name已經項目的一個分支,那么就直接通過GitCommand類調用git checkout命令來將該分支檢出即可,而不用創建新的分支。否則繼續往下執行。
(3). 創建一個Branch對象來描述即將要創建的分支。Branch類的成員變量remote描述的分支所要追蹤的遠程倉庫,另外一個成員變量merge描述的是分支要追蹤的遠程倉庫的分支。這個要追蹤的遠程倉庫分支由Manifest倉庫的default.xml文件描述,并且保存在Project類的成員變量revisionExpr中。
(4). 調用Project類的成員函數GetRevisionId獲得項目要追蹤的遠程倉庫分支的sha1值,并且保存在變量revid中。
(5). 由于新創建的分支name需要追蹤的遠程倉庫分支為revid,因此如果項目的當前分支head剛好就是項目要追蹤的遠程倉庫分支revid,那么創建新分支name就變得很簡單,只要在項目的Git目錄(位于.repo/projects目錄下)下的refs/heads子目錄以name名稱創建一個文件,并且往這個文件寫入寫入revid的值,以表明新分支name是在要追蹤的遠程分支revid的基礎上創建的。這樣的一個簡單的Git分支就創建完成了。不過我們還要修改項目工作目錄下的.git/HEAD文件,將它的內容寫為剛才創建的文件的路徑名稱,這樣才能將項目的當前分支切換為剛才新創建的分支。從這個過程就可以看出,創建的一個Git分支,不過就是創建一個包含一個sha1值的文件,因此代價是非常小的。如果項目的當前分支head剛好不是項目要追蹤的遠程倉庫分支revid,那么就繼續往下執行。
(6). 執行到這里的時候,就表明我們要創建的分支不存在,并且我們需要在一個不是當前分支的分支的基礎上創建該新分支,這時候就需要通過調用帶-b選項的git checkout命令來完成創建新分支的操作了。選項-b后面的參數就表明要在哪一個分支的基礎上創建分支。新的分支創建出來之后,還需要將它的文件拷貝到項目的工作目錄去。
至此,我們就分析完成在AOSP上創建新分支的過程了,也就是repo start命令的執行過程。更多的repo命令,例如repo uplad、repo diff和repo status等,可以以參考官方文檔http://source.android.com/source/using-repo.html,它們的執行過程和我們前面分析repo sync、repo start都是類似,不同的是它們執行其它的Git命令。有興趣的小伙伴自己嘗試自己去分析一下
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持億速云。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。