您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天就跟大家聊聊有關在Android中跨進程時拋出異常如何解決,可能很多人都不太了解,為了讓大家更加了解,小編給大家總結了以下內容,希望大家根據這篇文章可以有所收獲。
怎樣將異常從服務端拋到客戶端
也就是說在Service端拋出的異常需要可以在Client端接收。印象中binder是可以傳異常的,所以aidl直接走起:
// aidl文件
interface ITestExceptionAidl {
boolean testThrowException();
}
// service端實現
public class AidlService extends Service {
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new ITestExceptionAidl.Stub() {
@Override
public boolean testThrowException() throws RemoteException {
if (true) {
throw new RuntimeException("TestException");
}
return true;
}
};
}
}
// client端實現
bindService(intent, new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
ITestExceptionAidl aidl = ITestExceptionAidl.Stub.asInterface(service);
try {
aidl.testThrowException();
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e("testtest", "Exception", e);
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
}, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);但是這個程序實際上運行起來是這樣的:
01-01 05:31:55.475 4868 4880 E JavaBinder: *** Uncaught remote exception! (Exceptions are not yet supported across processes.)
01-01 05:31:55.475 4868 4880 E JavaBinder: java.lang.RuntimeException: TestException
01-01 05:31:55.475 4868 4880 E JavaBinder: at me.linjw.demo.ipcdemo.AidlService$1.testThrowException(AidlService.java:22)
01-01 05:31:55.475 4868 4880 E JavaBinder: at me.linjw.demo.ipcdemo.ITestExceptionAidl$Stub.onTransact(ITestExceptionAidl.java:48)
01-01 05:31:55.475 4868 4880 E JavaBinder: at android.os.Binder.execTransact(Binder.java:565)
看日志里面的ITestExceptionAidl$Stub.onTransact,也就是說在service端就已經被異常打斷了,并沒有傳給client端,而且第一個大大的”Exceptions are not yet supported across processes.”是說異常不允許跨進程嗎?但是我明明記得AIDL生成的代碼里面就有向Parcel寫入異常啊:
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION: {
reply.writeString(DESCRIPTOR);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_testThrowException: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
boolean _result = this.testThrowException();
reply.writeNoException(); // 這里寫入的是沒有拋出異常
reply.writeInt(((_result) ? (1) : (0)));
return true;
}
}
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}查找Parcel的源碼,其實是有writeException方法的:
public final void writeException(Exception e) {
int code = 0;
if (e instanceof Parcelable
&& (e.getClass().getClassLoader() == Parcelable.class.getClassLoader())) {
// We only send Parcelable exceptions that are in the
// BootClassLoader to ensure that the receiver can unpack them
code = EX_PARCELABLE;
} else if (e instanceof SecurityException) {
code = EX_SECURITY;
} else if (e instanceof BadParcelableException) {
code = EX_BAD_PARCELABLE;
} else if (e instanceof IllegalArgumentException) {
code = EX_ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT;
} else if (e instanceof NullPointerException) {
code = EX_NULL_POINTER;
} else if (e instanceof IllegalStateException) {
code = EX_ILLEGAL_STATE;
} else if (e instanceof NetworkOnMainThreadException) {
code = EX_NETWORK_MAIN_THREAD;
} else if (e instanceof UnsupportedOperationException) {
code = EX_UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION;
} else if (e instanceof ServiceSpecificException) {
code = EX_SERVICE_SPECIFIC;
}
writeInt(code);
StrictMode.clearGatheredViolations();
if (code == 0) {
if (e instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) e;
}
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
writeString(e.getMessage());
...
}可以看到其實Parcel是支持寫入異常的,但是只支持Parcelable的異常或者下面這幾種異常:
SecurityException
BadParcelableException
IllegalArgumentException
NullPointerException
IllegalStateException
NetworkOnMainThreadException
UnsupportedOperationException
ServiceSpecificException
如果是普通的RuntimeException,這打斷寫入,繼續拋出。
于是我們將RuntimeException改成它支持的UnsupportedOperationException試試:
// service端改成拋出UnsupportedOperationException
ppublic class AidlService extends Service {
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new ITestExceptionAidl.Stub() {
@Override
public boolean testThrowException() throws RemoteException {
if (true) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("TestException");
}
return true;
}
};
}
}
// client端實現還是一樣,不變
bindService(intent, new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
ITestExceptionAidl aidl = ITestExceptionAidl.Stub.asInterface(service);
try {
aidl.testThrowException();
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e("testtest", "Exception", e);
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
}, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);這樣運行的話客戶端就能捕獲到異常:
01-01 05:49:46.770 19937 19937 E testtest: RemoteException
01-01 05:49:46.770 19937 19937 E testtest: java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException: TestException
01-01 05:49:46.770 19937 19937 E testtest: at android.os.Parcel.readException(Parcel.java:1728)
01-01 05:49:46.770 19937 19937 E testtest: at android.os.Parcel.readException(Parcel.java:1669)
01-01 05:49:46.770 19937 19937 E testtest: at me.linjw.demo.ipcdemo.ITestExceptionAidl$Stub$Proxy.testThrowException(ITestExceptionAidl.java:77)
01-01 05:49:46.770 19937 19937 E testtest: at me.linjw.demo.ipcdemo.MainActivity$3.onServiceConnected(MainActivity.java:132)
01-01 05:49:46.770 19937 19937 E testtest: at android.app.LoadedApk$ServiceDispatcher.doConnected(LoadedApk.java:1465)
01-01 05:49:46.770 19937 19937 E testtest: at android.app.LoadedApk$ServiceDispatcher$RunConnection.run(LoadedApk.java:1482)
01-01 05:49:46.770 19937 19937 E testtest: at android.os.Handler.handleCallback(Handler.java:751)
01-01 05:49:46.770 19937 19937 E testtest: at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:95)
01-01 05:49:46.770 19937 19937 E testtest: at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:154)
01-01 05:49:46.770 19937 19937 E testtest: at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:6097)
01-01 05:49:46.770 19937 19937 E testtest: at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
01-01 05:49:46.770 19937 19937 E testtest: at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(ZygoteInit.java:1052)
01-01 05:49:46.770 19937 19937 E testtest: at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:942)
跨進程傳遞異常的原理
好,知道了如何去跨進程傳遞異常之后,然后我們來看看異常到底是如何傳遞過去的。
讓我們再來看看異常寫入的代碼:
// 有異常的情況
public final void writeException(Exception e) {
int code = 0;
if (e instanceof Parcelable
&& (e.getClass().getClassLoader() == Parcelable.class.getClassLoader())) {
// We only send Parcelable exceptions that are in the
// BootClassLoader to ensure that the receiver can unpack them
code = EX_PARCELABLE;
} else if (e instanceof SecurityException) {
code = EX_SECURITY;
} else if (e instanceof BadParcelableException) {
code = EX_BAD_PARCELABLE;
} else if (e instanceof IllegalArgumentException) {
code = EX_ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT;
} else if (e instanceof NullPointerException) {
code = EX_NULL_POINTER;
} else if (e instanceof IllegalStateException) {
code = EX_ILLEGAL_STATE;
} else if (e instanceof NetworkOnMainThreadException) {
code = EX_NETWORK_MAIN_THREAD;
} else if (e instanceof UnsupportedOperationException) {
code = EX_UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION;
} else if (e instanceof ServiceSpecificException) {
code = EX_SERVICE_SPECIFIC;
}
writeInt(code);
StrictMode.clearGatheredViolations();
if (code == 0) {
if (e instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) e;
}
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
writeString(e.getMessage());
// 之后還有一些寫入堆棧的操作,比較多,這里可以不看
}
public final void writeNoException() {
if (StrictMode.hasGatheredViolations()) {
// 如果StrictMode收集到了寫違規行為會走這里,我們可以不關注它
writeInt(EX_HAS_REPLY_HEADER);
...
} else {
// 一般情況下會走這里
writeInt(0);
}
}這里給每種支持的異常都編了個號碼,它會往Parcel寫入。而0代表的是沒有發生異常。然后再看看讀取異常的代碼:
public boolean testThrowException() throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
boolean _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_testThrowException, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = (0 != _reply.readInt());
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
// android.os.Parcel.readException
public final void readException() {
int code = readExceptionCode();
if (code != 0) {
String msg = readString();
//在這個方法里面創建異常并且拋出
readException(code, msg);
}
}然后這里有個需要注意的點就是異常必須是寫在Parcel的頭部的,也就是說如果沒有異常,我們先要將0寫到頭部,然后再將返回值繼續往后面寫入。如果有異常,我們要先將異常編碼寫入頭部,然后就不需要再寫入返回值了。
這樣,在客戶端讀取的時候讀取的頭部就能知道到底有沒有異常,沒有異常就繼續讀取返回值,有異常就將異常讀取出來并且拋出。
// service端代碼 boolean _result = this.testThrowException(); reply.writeNoException(); // 先寫入異常 reply.writeInt(((_result) ? (1) : (0))); // 再寫入返回值 // client端代碼 mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_testThrowException, _data, _reply, 0); _reply.readException(); // 先讀取異常,有異常的話readException方法里面會直接拋出 _result = (0 != _reply.readInt()); // 再讀取返回值
也就是Parcel的頭部是一個標志位,標志了有異常或者無異常:
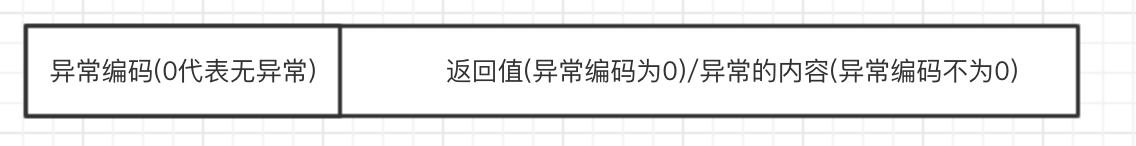
但是我們看到AIDL生成的代碼都是寫入的無異常,那我們拋出的異常是怎么傳過去的呢?還記得這個打印嗎?
01-01 05:31:55.475 4868 4880 E JavaBinder: *** Uncaught remote exception! (Exceptions are not yet supported across processes.)
01-01 05:31:55.475 4868 4880 E JavaBinder: java.lang.RuntimeException: TestException
01-01 05:31:55.475 4868 4880 E JavaBinder: at me.linjw.demo.ipcdemo.AidlService$1.testThrowException(AidlService.java:22)
01-01 05:31:55.475 4868 4880 E JavaBinder: at me.linjw.demo.ipcdemo.ITestExceptionAidl$Stub.onTransact(ITestExceptionAidl.java:48)
01-01 05:31:55.475 4868 4880 E JavaBinder: at android.os.Binder.execTransact(Binder.java:565)
我們去android.os.Binder.execTransact這里找找看, onTransact方法實際就是在這里被調用的
private boolean execTransact(int code, long dataObj, long replyObj, int flags) {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain(dataObj);
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain(replyObj);
boolean res;
try {
res = onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
} catch (RemoteException|RuntimeException e) {
...
reply.setDataPosition(0);
reply.writeException(e);
res = true;
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
RuntimeException re = new RuntimeException("Out of memory", e);
reply.setDataPosition(0);
reply.writeException(re);
res = true;
}
checkParcel(this, code, reply, "Unreasonably large binder reply buffer");
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
return res;
}看,這里如果catch到了方法,也就是說我們服務端有拋出異常,就會在catch代碼塊里面先就Parcel的游標重置回0,然后往Parcel頭部寫入異常。
好,到了這里其實整個流程就差不多了,但是我發現我沒有看到那個”Exceptions are not yet supported across processes.”字符串,這個不支持的提示又是哪里來的呢?
讓我們再回憶下代碼,在遇到不支持的異常類型的時候, writeException也會拋出異常:
public final void writeException(Exception e) {
int code = 0;
if (e instanceof Parcelable
&& (e.getClass().getClassLoader() == Parcelable.class.getClassLoader())) {
// We only send Parcelable exceptions that are in the
// BootClassLoader to ensure that the receiver can unpack them
code = EX_PARCELABLE;
} else if (e instanceof SecurityException) {
code = EX_SECURITY;
} else if (e instanceof BadParcelableException) {
code = EX_BAD_PARCELABLE;
} else if (e instanceof IllegalArgumentException) {
code = EX_ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT;
} else if (e instanceof NullPointerException) {
code = EX_NULL_POINTER;
} else if (e instanceof IllegalStateException) {
code = EX_ILLEGAL_STATE;
} else if (e instanceof NetworkOnMainThreadException) {
code = EX_NETWORK_MAIN_THREAD;
} else if (e instanceof UnsupportedOperationException) {
code = EX_UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION;
} else if (e instanceof ServiceSpecificException) {
code = EX_SERVICE_SPECIFIC;
}
writeInt(code);
StrictMode.clearGatheredViolations();
// code為0,代表不支持這種異常,繼續把異常拋出或者創建RuntimeException拋出
if (code == 0) {
if (e instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) e;
}
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
...
}由于這個writeException,已經是在catch代碼塊里面運行的了,沒有人再去catch它,于是就會打斷這個流程,直接跳出。形成了一個Uncaught remote exception。
最后我們找到/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_util_Binder.cpp的onTransact方法,這里通過jni調到Java的execTransact方法,調用完之后進行ExceptionCheck,如果發現有異常的話就report_exception:
virtual status_t onTransact(uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags = 0) {
JNIEnv* env = javavm_to_jnienv(mVM);
IPCThreadState* thread_state = IPCThreadState::self();
const int32_t strict_policy_before = thread_state->getStrictModePolicy();
jboolean res = env->CallBooleanMethod(mObject, gBinderOffsets.mExecTransact,
code, reinterpret_cast<jlong>(&data), reinterpret_cast<jlong>(reply), flags);
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
jthrowable excep = env->ExceptionOccurred();
// 就是這里啦
report_exception(env, excep,
"*** Uncaught remote exception! "
"(Exceptions are not yet supported across processes.)");
res = JNI_FALSE;
env->DeleteLocalRef(excep);
}
...
}看完上述內容,你們對在Android中跨進程時拋出異常如何解決有進一步的了解嗎?如果還想了解更多知識或者相關內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝大家的支持。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。