您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章將為大家詳細講解有關Android 中如何實現三級NestedScroll嵌套滾動,文章內容質量較高,因此小編分享給大家做個參考,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后對相關知識有一定的了解。
嵌套滾動介紹
我們知道 NestedScrolling(Parent/Child) 這對接口是用來實現嵌套滾動的,一般實現這對接口的 Parent 和 Child 沒有直接嵌套,否則直接用 onInterceptTouchEvent() 和 onTouchEvent() 這對方法實現就可以了。能夠越級嵌套滾動正是它的厲害之處。
嵌套滾動的接口有兩對:NestedScrolling(Parent/Child) 和 NestedScrolling(Parent2/Child2) 后者相比前者對 fling 的處理更加細致。相比第一代 Child 簡單地將 fling 拋給 Parent,第二代 Child 將 fling 轉化為 scroll 后再分發給 Parent,為了和普通的 scroll 區分增加了一個參數 type, 當 type 是 ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH 時表示普通的 scroll,當是 ViewCompat.TYPE_NON_TOUCH 時表示由 fling 轉化而來的 scroll。這樣做的好處是當 Child 檢測到一個 fling 時,它可以選擇將這個 fling 引起的 scroll 一部分作用在 Parent 上一部分作用在自己身上,而不是只作用在 Parent 或者 Child 上。或許你會問 fling 為什么不能選擇 Parent 和 Child 都作用,事實上你可以,但 fling 的話 Parent 沒法告訴 Child 消費了多少,剩下多少,因為 fling 傳遞的值是速度,不像 scroll 是距離。所以通過 NestedScrolling(Parent2/Child2) 實現嵌套滾動時,當你觸發了一個 fling 時,也可以做很順滑連貫的交替滾動,而 1 就很難達到相同的效果。現在官方 View 的實現也是通過 NestedScrolling(Parent2/Child2),所以我們在實現自定義的嵌套滾動時盡量用 2。
上面簡單介紹了 NestedScrolling 2 和 1 的區別以及為什么要使用2。現在我們來看看 NestedScrolling(Parent2/Child2) 的方法,1 就不看了,和 2 差不多。
public interface NestedScrollingChild2 {
void setNestedScrollingEnabled(boolean enabled);
boolean isNestedScrollingEnabled();
boolean startNestedScroll(@ScrollAxis int axes, @NestedScrollType int type);
void stopNestedScroll(@NestedScrollType int type);
boolean hasNestedScrollingParent(@NestedScrollType int type);
boolean dispatchNestedScroll(int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed,
int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, @Nullable int[] offsetInWindow,
@NestedScrollType int type);
boolean dispatchNestedPreScroll(int dx, int dy, @Nullable int[] consumed,
@Nullable int[] offsetInWindow, @NestedScrollType int type);
}public interface NestedScrollingParent2 {
boolean onStartNestedScroll(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, @ScrollAxis int axes,
@NestedScrollType int type);
void onNestedScrollAccepted(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, @ScrollAxis int axes,
@NestedScrollType int type);
void onStopNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, @NestedScrollType int type);
void onNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed,
int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, @NestedScrollType int type);
void onNestedPreScroll(@NonNull View target, int dx, int dy, @NonNull int[] consumed,
@NestedScrollType int type);
}從這兩個接口的方法可以看出這些方法都是一一對應的,比如 startNestedScroll 和 onStartNestedScroll,stopNestedScroll 和 onStopNestedScroll 等。從這些方法的命名上也能看出來嵌套滾動的交互順序是 Child 主動觸發,Parent 被動接受,所以決定是否打開嵌套滾動的方法 setNestedScrollingEnabled 由 Child 實現,決定開始和結束的方法 startNestedScroll 和 stopNestedScroll 也由 Child 實現。
這里用一個圖來表示嵌套滾動流程

整個過程大概分為兩部分:綁定和滾動分發。綁定部分可以理解為 Child 向上遍歷找 NestedScrollingParent2 的過程,找到后調用它的 onStartNestedScroll 方法,如果返回 true 則說明這個 Parent 想接收 nested scroll,Child 會緊接著調 onNestedScrollAccepted 方法表示同意 Parent 處理自己分發的 nested scroll,對應上圖中的 1 2 3。滾動分發部分 Child 將自己的 scroll 分為三個階段 before scroll after,before 和 after 分發給 parent 消費,scroll 階段讓自己消費,這三個階段是按順序進行的,換句話說如果前一步消耗完了 scroll,那后面的階段就沒有 scroll 可以消費。這樣做的好處是讓 Parent 可以在自己消費之前或者之后消費 scroll,如果 Parent 想在 Child 之前消費就在 onNestedPreScroll 方法里處理,否則就在 onNestedScroll 方法里,對應上圖中的 4 5 步。上面介紹到的一些通用邏輯被封裝在 NestedScrollingChildHelper 和 NestedScrollingParentHelper 中,在 NestedScrolling(Parent2/Child2) 的方法中可以調用 Helper 類中的同名方法,比如 NestedScrollingChild2.startNestedScroll 方法中實現了向上遍歷尋找 NestedScrollingParent 的邏輯。
三級嵌套滾動
一個常見的嵌套滾動例子是 CoordinatorLayout/AppbarLayout - RecyclerView, 實現的效果是向上滑動列表時,會先將 AppbarLayout 向上滑動直到完全折疊,向下滑動至列表最頂部后會展開 AppbarLayout, 如下圖:

這里實現 NestedScrollingParent2 的是 CoordinatorLayout/AppbarLayout, 實現 NestedScrollingChild2 的是 RecyclerView。對于這種兩級嵌套滾動的需求使用 CoordinatorLayout 幾乎都能實現,如果遇到特殊的業務需求基于 CoordinatorLayout 和 RecyclerView 的實現改改也能實現。
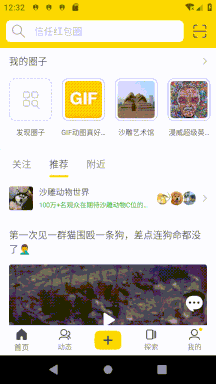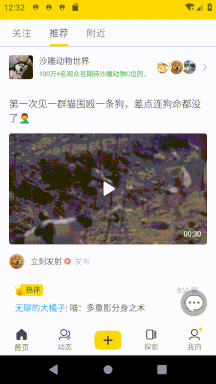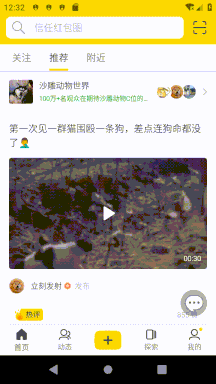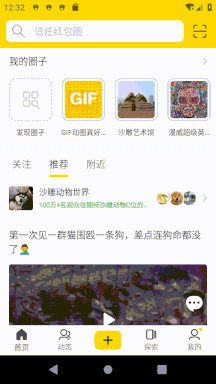
我這里遇到的需求是即刻首頁的樣式(可參考即刻5.4.2版本),除了要有 AppbarLayout 折疊效果之外還要在 AppbarLayout 頂部展示搜索框和刷新動畫。這里的滑動邏輯是:
向上滑動時,最先折疊刷新動畫,向下滑動時最后展開刷新動畫。
向上滑動列表時先折疊 AppbarLayout,AppbarLayout 完全折疊后再折疊搜索框。
向下滑動列表時在展開 AppbarLayout 之前先展開搜索框。
列表沒滑動到頂部時可以通過觸發一定速度的向下 fling 來展開搜索框。
可以發現這里除了 CoordinatorLayout/AppbarLayout - RecyclerView 這對嵌套滾動的 Parent 和 Child 之外還多了搜索框和刷新動畫,而這三者之間的滑動邏輯需要通過嵌套滾動實現,只是傳統的兩級嵌套滾動不能滿足,所以需要實現三級嵌套滾動。
所謂三級嵌套滾動是在兩級嵌套滾動之上再添加一個 Parent,這里為了表述方便將三級嵌套滾動的三級由上到下分別稱為 Grand Parent Child。具體是由兩對 NestedScrolling(Parent2/Child2) 接口實現,Grand 實現第一對接口的 Parent,Parent 實現第一對接口的 Child 和第二對接口的 Parent,Child 實現第二對接口的 Child。與兩級嵌套滾動相比三級嵌套的 Grand 和 Child 和兩級的 Parent 和 Child 區別不大,變化比較大的是三級的 Parent 既要實現兩級的 Parent 接口又要實現 Child 接口,示意圖如下:
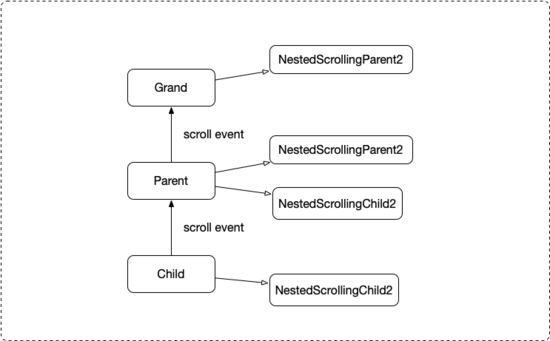
在即刻首頁這個例子里,CoordinatorLayout/AppbarLayout 屬于三級嵌套的 Parent 實現了第二對接口的 NestedScrollingParent2,RecyclerView 屬于 Child 實現了第二對接口的 NestedScrollingChild2。這里我們需要做的是實現第一對嵌套接口,新建一個自定義 Layout 實現 NestedScrollingParent2 接口作為三級嵌套的 Grand,負責搜索框和刷新動畫的折疊和展開。再新建一個自定義 Layout 繼承 CoordinatorLayout 實現 NestedScrollingChild2 接口,負責攔截列表分發上來的滾動事件或者處理 AppbarLayout 消費后剩下的滾動事件。
二級嵌套滾動可以理解為給 Parent 提供了攔截 Child 滾動事件和處理 Child 剩余滾動事件的能力,具體邏輯可參考本文最開始介紹嵌套滾動的部分。相應的三級嵌套滾動給 Grand 提供了攔截 Parent 和處理剩余滾動事件的能力,只是攔截和處理的時機多了一些,如下圖:
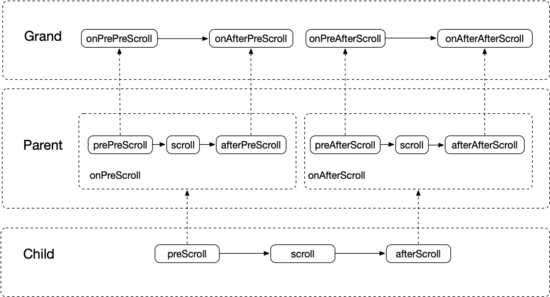
二級嵌套滾動對滾動處理時機只有三個階段:preScroll、scroll 和 afterScroll。而三級嵌套滾動的處理時機就多一些,有七個階段:prePreScroll、preScroll、afterPreScroll、scroll、preAfterScroll、afterScroll 和 afterAfterScroll,可以看出相比二級嵌套多了 prePreScroll、afterPreScroll、preAfterScroll 和 afterAfterScroll 這四個階段,多出的這幾個階段都是給 Grand 用的。到這里可以發現 NestedScrollingParent2 其實不能完全描述 Grand 的能力,確實最理想的方案應該是新建一對接口 NestedScrollingGrand2 和 NestedScrollingGrandChild2 來描述新增的四個對滾動事件的處理階段,但考慮到我這里的例子 Grand 對 Parent 的處理沒有那么精細化,所以還是通過復用 NestedScrolling(Parent2/Child2) 和一些附加方法來實現。以后如果實現了 NestedScrolling(Grand2/GrandChild2) 接口,也會及時更新。根據上圖即刻首頁滑動的實現思路就很簡單了:
onPrePreScroll 中執行折疊刷新動畫的邏輯,onAfterAfterScroll 中執行展開刷新動畫的邏輯。
onPreScroll 中執行折疊 AppbarLayout 的邏輯,onAfterPreScroll 中執行搜索框折疊的邏輯。
onAfterScroll 中執行展開 AppbarLayout 的邏輯,onPreAfterScroll 中執行搜索框展開的邏輯。
列表沒滑到頂部根據 fling 展開搜索框的邏輯單獨在 Parent 的 onNestedPreFling 里做,這條算是一個特殊處理。
關于Android 中如何實現三級NestedScroll嵌套滾動就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,可以學到更多知識。如果覺得文章不錯,可以把它分享出去讓更多的人看到。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。