您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹Java8中parallelStream并發安全的示例分析,文中介紹的非常詳細,具有一定的參考價值,感興趣的小伙伴們一定要看完!
背景
Java8的stream接口極大地減少了for循環寫法的復雜性,stream提供了map/reduce/collect等一系列聚合接口,還支持并發操作:parallelStream。
在爬蟲開發過程中,經常會遇到遍歷一個很大的集合做重復的操作,這時候如果使用串行執行會相當耗時,因此一般會采用多線程來提速。Java8的paralleStream用fork/join框架提供了并發執行能力。但是如果使用不當,很容易陷入誤區。
Java8的paralleStream是線程安全的嗎
一個簡單的例子,在下面的代碼中采用stream的forEach接口對1-10000進行遍歷,分別插入到3個ArrayList中。其中對第一個list的插入采用串行遍歷,第二個使用paralleStream,第三個使用paralleStream的同時用ReentryLock對插入列表操作進行同步:
private static List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
private static List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
private static List<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>();
private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntStream.range(0, 10000).forEach(list1::add);
IntStream.range(0, 10000).parallel().forEach(list2::add);
IntStream.range(0, 10000).forEach(i -> {
lock.lock();
try {
list3.add(i);
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
});
System.out.println("串行執行的大小:" + list1.size());
System.out.println("并行執行的大小:" + list2.size());
System.out.println("加鎖并行執行的大小:" + list3.size());
}執行結果:
串行執行的大小:10000
并行執行的大小:9595
加鎖并行執行的大小:10000
并且每次的結果中并行執行的大小不一致,而串行和加鎖后的結果一直都是正確結果。顯而易見,stream.parallel.forEach()中執行的操作并非線程安全。
那么既然paralleStream不是線程安全的,是不是在其中的進行的非原子操作都要加鎖呢?我在stackOverflow上找到了答案:
https://codereview.stackexchange.com/questions/60401/using-java-8-parallel-streams
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/22350288/parallel-streams-collectors-and-thread-safety
在上面兩個問題的解答中,證實paralleStream的forEach接口確實不能保證同步,同時也提出了解決方案:使用collect和reduce接口。
http://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/collections/streams/parallelism.html
在Javadoc中也對stream的并發操作進行了相關介紹:
The Collections Framework provides synchronization wrappers, which add automatic synchronization to an arbitrary collection, making it thread-safe.
Collections框架提供了同步的包裝,使得其中的操作線程安全。
所以下一步,來看看collect接口如何使用。
stream的collect接口
閑話不多說直接上源碼吧,Stream.java中的collect方法句柄:
<R, A> R collect(Collector<? super T, A, R> collector);
在該實現方法中,參數是一個Collector對象,可以使用Collectors類的靜態方法構造Collector對象,比如Collectors.toList(),toSet(),toMap(),etc,這塊很容易查到API故不細說了。
除此之外,我們如果要在collect接口中做更多的事,就需要自定義實現Collector接口,需要實現以下方法:
Supplier<A> supplier(); BiConsumer<A, T> accumulator(); BinaryOperator<A> combiner(); Function<A, R> finisher(); Set<Characteristics> characteristics();
要輕松理解這三個參數,要先知道fork/join是怎么運轉的,一圖以蔽之:
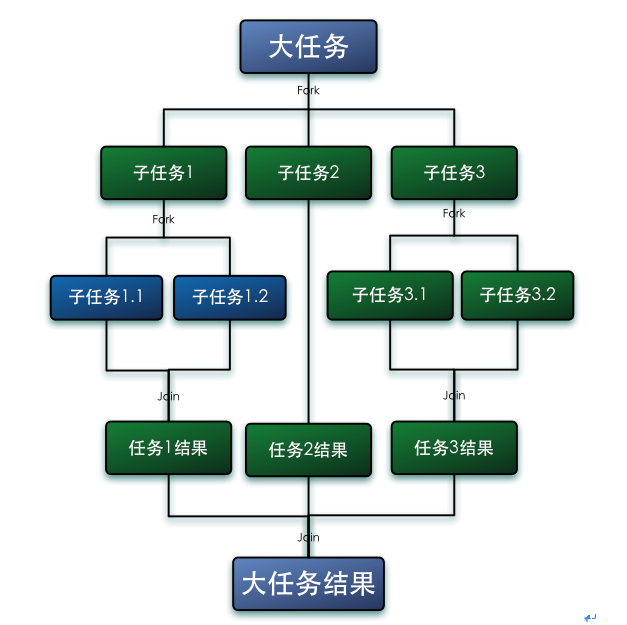
上圖來自:http://www.infoq.com/cn/articles/fork-join-introduction
簡單地說就是大任務拆分成小任務,分別用不同線程去完成,然后把結果合并后返回。所以第一步是拆分,第二步是分開運算,第三步是合并。這三個步驟分別對應的就是Collector的supplier,accumulator和combiner。talk is cheap show me the code,下面用一個例子來說明:
輸入是一個10個整型數字的ArrayList,通過計算轉換成double類型的Set,首先定義一個計算組件:
Compute.java:
public class Compute {
public Double compute(int num) {
return (double) (2 * num);
}
}接下來在Main.java中定義輸入的類型為ArrayList的nums和類型為Set的輸出結果result:
private List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>(); private Set<Double> result = new HashSet<>();
定義轉換list的run方法,實現Collector接口,調用內部類Container中的方法,其中characteristics()方法返回空set即可:
public void run() {
// 填充原始數據,nums中填充0-9 10個數
IntStream.range(0, 10).forEach(nums::add);
//實現Collector接口
result = nums.stream().parallel().collect(new Collector<Integer, Container, Set<Double>>() {
@Override
public Supplier<Container> supplier() {
return Container::new;
}
@Override
public BiConsumer<Container, Integer> accumulator() {
return Container::accumulate;
}
@Override
public BinaryOperator<Container> combiner() {
return Container::combine;
}
@Override
public Function<Container, Set<Double>> finisher() {
return Container::getResult;
}
@Override
public Set<Characteristics> characteristics() {
// 固定寫法
return Collections.emptySet();
}
});
}構造內部類Container,該類的作用是一個存放輸入的容器,定義了三個方法:
accumulate方法對輸入數據進行處理并存入本地的結果
combine方法將其他容器的結果合并到本地的結果中
getResult方法返回本地的結果
Container.java:
class Container {
// 定義本地的result
public Set<Double> set;
public Container() {
this.set = new HashSet<>();
}
public Container accumulate(int num) {
this.set.add(compute.compute(num));
return this;
}
public Container combine(Container container) {
this.set.addAll(container.set);
return this;
}
public Set<Double> getResult() {
return this.set;
}
}在Main.java中編寫測試方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main main = new Main();
main.run();
System.out.println("原始數據:");
main.nums.forEach(i -> System.out.print(i + " "));
System.out.println("\n\ncollect方法加工后的數據:");
main.result.forEach(i -> System.out.print(i + " "));
}輸出:
原始數據:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9collect方法加工后的數據:
0.0 2.0 4.0 8.0 16.0 18.0 10.0 6.0 12.0 14.0
我們將10個整型數值的list轉成了10個double類型的set,至此驗證成功~
以上是“Java8中parallelStream并發安全的示例分析”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!希望分享的內容對大家有幫助,更多相關知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。