您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
就像 android 有 handle 一樣,消息隊列這東西好像還真是系統必備,Flutter 也有自己的消息隊列,只不過隊列直接封裝在了 Dart 的線程類型 Isolate 里面了,不過 Flutter 還是提供了 Futrue 這個 API 來專門來操作各種消息,以及實現基于消息隊列的假異步
Flutter 的“異步”機制
這里的異步是加了引號的,可見此異步非真異步,而是假異步。Flutter 的 異步 不是開新線程,而是往所屬線程的 消息隊列 中添加任務,當然大家也可以按上文那樣自己展開真異步操作
Flutter 對代碼分2類: 同步代碼和異步代碼
為啥,很明顯啊,異步代碼是往消息隊列里添加任務,那肯定得等現在的代碼運行完了,線程有空閑了才能開始執行消息隊列里的任務呀~
舉個例子:
void test() {
print("AA");
Future(() => print("Futrue"));
print("BB");
}
~~~~~~~~~~~log~~~~~~~~~~~~~
I/flutter (10064): AA
I/flutter (10064): BB
I/flutter (10064): Futrue
print("Futrue")) 任務等到最后才執行的...
Flutter 提供了往 消息隊列 添加數據的 API: Future
往 MicroTask 隊列添加任務
scheduleMicrotask((){
// ...code goes here...
});
new Future.microtask((){
// ...code goes here...
});
往 Event 隊列添加任務
new Future(() {
// ...code goes here...
});
Future 的基本使用
Future 對象是 Flutter 專門提供的,基于消息隊列實現異步的類,Future 對象會把自身當做一個任務添加到消息隊列中去排隊執行
Future 對象接受的是一個函數,就是要執行的任務,用 () => ... 簡寫也是可以的
void task() {
print("AA");
}
var futrue = Future(task);
創建 Future 任務方式:
我們來看幾個代表性的:
Future.sync() - 阻塞任務,會阻塞當前代碼,sync 的任務執行完了,代碼才能走到下一行
void test() {
print("AA");
Future.sync(() => print("Futrue"));
print("BB");
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~log~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
I/flutter (10573): AA
I/flutter (10573): Futrue
I/flutter (10573): BB
Future.delayed() - 延遲任務,指定xx時間后把任務添加到消息隊列,要是消息隊列前面有人執行的時間太長了,那么執行時間點就不能把握了,這點大家要知道
void test() {
print("AA");
Future.delayed(Duration(milliseconds: 500),() => print("Futrue"));
print("BB");
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~log~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
I/flutter (10573): AA
I/flutter (10573): BB
I/flutter (10573): Futrue
Future 的鏈式調用
Future 也支持鏈式調用的,在 API 使用上也是很靈活的,提供了下面的選擇給大家
.then - 在 Future 執行完后執行,相當于一個 callback,而不是重新創建了一個 Future
Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 1),(){
print(("AAA"));
return "AA";
}).then((value){
print(value);
});
.catchError - future 不管在任何位置發生了錯誤,都會立即執行 catchError
Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 1),(){
throw Exception("AAA");
}).then((value){
print(value);
}).catchError((error){
print(error);
});
.whenComplete - 不管是否發生異常,在執行完成后,都會執行該方法
Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 1), () {
throw Exception("AAA");
}).then((value) {
print(value);
}).catchError((error) {
print(error);
}).whenComplete(() {
print("complete...");
});
.wait - 可以等待所有的 future 都執行完畢再走 then 的方法
Future.wait([
// 2秒后返回結果
Future.delayed(new Duration(seconds: 2), () {
return "hello";
}),
// 4秒后返回結果
Future.delayed(new Duration(seconds: 4), () {
return " world";
})
]).then((results) {
print(results[0] + results[1]);
}).catchError((e) {
print(e);
});
大家想想啊
Futrue() .then() .then() ...
這樣的鏈式寫法不就是標準的去 callback 回調地獄的方式嘛
async/await 關鍵字
async/await 這組關鍵字是系統提供的另一種實現 異步 任務的 API, async/await 底層還是用 Futrue 實現的,從使用上看是對 Futrue 的簡化,本質上還是基于 消息隊列 實現的異步,是 假異步 ,和 Isoalte 是不一樣的
async/await 的特點就是: 成對出現
比如這樣:
anysncTest() async {
print("async 休眠 start...");
sleep(Duration(seconds: 1));
print("async 休眠 end...");
}
await anysncTest();
本質上 await 調用的方法其實是把這個方法包裝到 Futrue 中去消息隊列里執行,只不過是: Future.sync() 阻塞式的 Future 任務
這 async 在布局中也是可以直接用的
class TestWidgetState extends State<TestWidget> {
int _count = 0;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Material(
FlatButton(
onPressed: () async {
_count = countEven(1000000000);
setState(() {});
},
child: Text(
_count.toString(),
)),
);
}
async/await 是阻塞式的函數
實驗1:
// 這是異步任務代碼
aaa() async{
print("main1...");
await anysncTest();
print("main2...");
print("main3...");
}
anysncTest() async {
print("async 休眠 start...");
sleep(Duration(seconds: 1));
print("async 休眠 end...");
}
// 點擊按鈕去執行
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return RaisedButton(
child: (Text("click!")),
onPressed: () async {
await aaa();
},
);
}
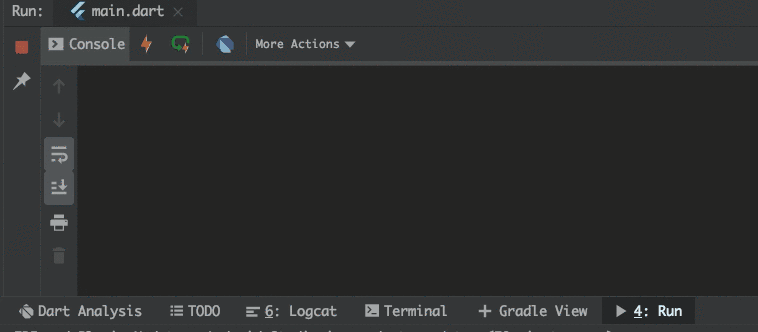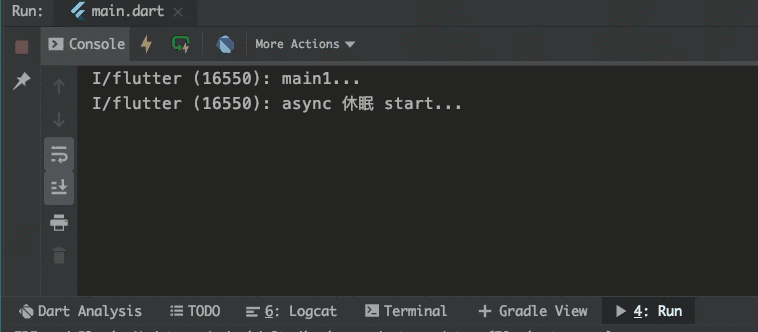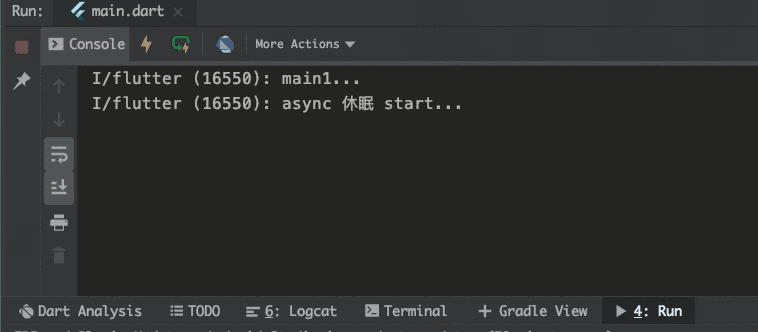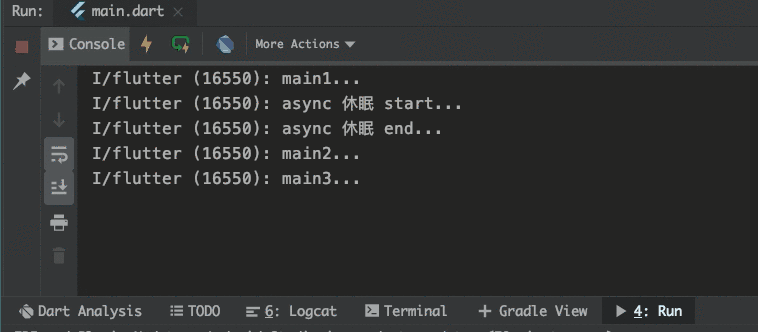
可以看到 async/await
執行的方法的確是阻塞時的,至少在這個 async 方法里絕對是阻塞式的
實驗2:
那么范圍擴展一下,在 async 外面再來看看 async/await 是不是阻塞式的? 有人說 async/await 和協程一樣 ,協程的關鍵點在于非競爭式資源,協程的概念中,當多個協程中有一個協程掛起之后,并不會阻塞 CPU,CPU 回去執行其他協程方法,直到有空閑了再來執行之前掛起后恢復的協程,雖然在協程看來我掛起了線程,但其實 CPU 不會被協程掛起阻塞,這點就是協程的核心優勢,大大提升多線程下的執行效率。
從這點出發我們就能知道 async/await 是不是又一個協程了,看看他阻塞 CPU,我們在 await 之后看看 async 后面的代碼會不會執行就 OK了
// 還是這組方法
aaa() async{
print("main1...");
await anysncTest();
print("main2...");
print("main3...");
}
anysncTest() async {
print("async 休眠 start...");
sleep(Duration(seconds: 1));
print("async 休眠 end...");
}
// 執行,注意此時按鈕的點擊方法不是 async 的
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return RaisedButton(
child: (Text("click!")),
onPressed: () {
print("click1...");
aaa();
print("click2...");
print("click3...");
},
);
}
I/flutter ( 5733): click1... I/flutter ( 5733): main1... I/flutter ( 5733): async 休眠 start... I/flutter ( 5733): async 休眠 end... I/flutter ( 5733): click2... I/flutter ( 5733): click3... I/flutter ( 5733): main2... I/flutter ( 5733): main3...
await 阻塞是真的阻塞 CPU 了,所以 async/await 不是協程,但是大家注意啊,在 await 結速阻塞之后執行的是 click2 也就是 async 外部的方法,說明 await 標記的方法返回的都是 Futrue 對象的說法是正確的,隊列只有在線程空閑時才會執行,顯然此時線程不是空閑的,點擊方法還沒執行完呢
實驗3:
這次做對比實驗,把點擊事件也變成 async 的看看執行順序
// 還是這組方法
aaa() async{
print("main1...");
await anysncTest();
print("main2...");
print("main3...");
}
anysncTest() async {
print("async 休眠 start...");
sleep(Duration(seconds: 1));
print("async 休眠 end...");
}
// 執行
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return RaisedButton(
child: (Text("click!")),
onPressed: () async {
print("click1...");
await aaa();
print("click2...");
print("click3...");
},
);
}
I/flutter ( 5733): click1... I/flutter ( 5733): main1... I/flutter ( 5733): async 休眠 start... I/flutter ( 5733): async 休眠 end... I/flutter ( 5733): main2... I/flutter ( 5733): main3... I/flutter ( 5733): click2... I/flutter ( 5733): click3...
這樣看的話在 async 方法內部,是嚴格按照順序執行的
async 方法的格式
1. async 標記的方法返回值都是 Futrue 類型的
上文書哦說 await 調用的方法返回的都是 Futrue 對象,那么就是說在聲明 async 函數時,返回值都是 Futrue 類型的,Futrue 內部包裹實際的返回值類型
Futrue<String> getData() async {
data = await http.get(Uri.encodeFull(url), headers: {"Accept": "application/json"});
}
Futrue<String> 我們可以不寫,dart 也會自動推斷出來,但是我們一定要知道是 Futrue 類型的,要不有時會報類型錯誤
我們在用的時候都是配合 await 使用的,這時候可以直接用具體類型值接返回值了
String data = await getData();
記住:
Future就是event,很多Flutter內置的組件比如前幾篇用到的Http(http請求控件)的get函數、RefreshIndicator(下拉手勢刷新控件)的onRefresh函數都是event。每一個被await標記的句柄也是一個event,每創建一個Future就會把這個Future扔進event queue中排隊等候安檢~
Stream
Stream 和 Future 一樣都是假異步操作,區別是 Stream 可以接受多次數據,我不詳細展開了,有待以后詳細研究
Stream.fromFutures([
// 1秒后返回結果
Future.delayed(new Duration(seconds: 1), () {
return "hello 1";
}),
// 拋出一個異常
Future.delayed(new Duration(seconds: 2),(){
throw AssertionError("Error");
}),
// 3秒后返回結果
Future.delayed(new Duration(seconds: 3), () {
return "hello 3";
})
]).listen((data){
print(data);
}, onError: (e){
print(e.message);
},onDone: (){
});
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持億速云。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。