您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
前面在一篇文章中介紹了 Spring 中的一些重要的 context。有一些在此文中提到的 context,可以參看上篇文章。
SpringBoot 項目之所以部署簡單,其很大一部分原因就是因為不用自己折騰 Tomcat 相關配置,因為其本身內置了各種 Servlet 容器。一直好奇: SpringBoot 是怎么通過簡單運行一個 main 函數,就能將容器啟動起來,并將自身部署到其上 。此文想梳理清楚這個問題。
我們從SpringBoot的啟動入口中分析:
Context 創建
// Create, load, refresh and run the ApplicationContext context = createApplicationContext();
在SpringBoot 的 run 方法中,我們發現其中很重要的一步就是上面的一行代碼。注釋也寫的很清楚:
創建、加載、刷新、運行 ApplicationContext。
繼續往里面走。
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
contextClass = Class.forName(this.webEnvironment
? DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS : DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, "
+ "please specify an ApplicationContextClass",
ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiate(contextClass);
}
邏輯很清楚:
先找到 context 類,然后利用工具方法將其實例化。
其中 第5行 有個判斷:如果是 web 環境,則加載 DEFAULT _WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS類。參看成員變量定義,其類名為:
AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext
此類的繼承結構如圖:
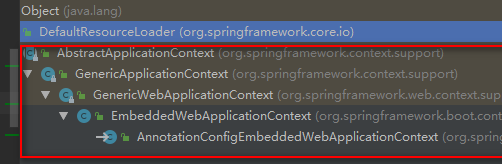
直接繼承 GenericWebApplicationContext。關于該類前文已有介紹,只要記得它是專門為 web application提供context 的就好。
refresh
在經歷過 Context 的創建以及Context的一些列初始化之后,調用 Context 的 refresh 方法,真正的好戲才開始上演。
從前面我們可以看到AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext的繼承結構,調用該類的refresh方法,最終會由其直接父類:EmbeddedWebApplicationContext 來執行。
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createEmbeddedServletContainer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start embedded container",
ex);
}
}
我們重點看第5行。
private void createEmbeddedServletContainer() {
EmbeddedServletContainer localContainer = this.embeddedServletContainer;
ServletContext localServletContext = getServletContext();
if (localContainer == null && localServletContext == null) {
EmbeddedServletContainerFactory containerFactory = getEmbeddedServletContainerFactory();
this.embeddedServletContainer = containerFactory
.getEmbeddedServletContainer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (localServletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(localServletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context",
ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
代碼第5行,獲取到了一個EmbeddedServletContainerFactory,顧名思義,其作用就是為了下一步創建一個嵌入式的 servlet 容器:EmbeddedServletContainer。
public interface EmbeddedServletContainerFactory {
/**
* 創建一個配置完全的但是目前還處于“pause”狀態的實例.
* 只有其 start 方法被調用后,Client 才能與其建立連接。
*/
EmbeddedServletContainer getEmbeddedServletContainer(
ServletContextInitializer... initializers);
}
第6、7行,在 containerFactory 獲取EmbeddedServletContainer的時候,參數為 getSelfInitializer 函數的執行結果。暫時不管其內部機制如何,只要知道它會返回一個 ServletContextInitializer 用于容器初始化的對象即可,我們繼續往下看。
由于 EmbeddedServletContainerFactory 是個抽象工廠,不同的容器有不同的實現,因為SpringBoot默認使用Tomcat,所以就以 Tomcat 的工廠實現類 TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory 進行分析:
@Override
public EmbeddedServletContainer getEmbeddedServletContainer(
ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir("tomcat"));
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
tomcat.getEngine().setBackgroundProcessorDelay(-);
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatEmbeddedServletContainer(tomcat);
}
從第8行一直到第16行完成了 tomcat 的 connector 的添加。tomcat 中的 connector 主要負責用來處理 http 請求,具體原理可以參看 Tomcat 的源碼,此處暫且不提。
第17行的 方法有點長,重點看其中的幾行:
if (isRegisterDefaultServlet()) {
addDefaultServlet(context);
}
if (isRegisterJspServlet() && ClassUtils.isPresent(getJspServletClassName(),
getClass().getClassLoader())) {
addJspServlet(context);
addJasperInitializer(context);
context.addLifecycleListener(new StoreMergedWebXmlListener());
}
ServletContextInitializer[] initializersToUse = mergeInitializers(initializers);
configureContext(context, initializersToUse);
前面兩個分支判斷添加了默認的 servlet類和與 jsp 相關的 servlet 類。
對所有的 ServletContextInitializer 進行合并后,利用合并后的初始化類對 context 進行配置。
第 18 行,順著方法一直往下走,開始正式啟動 Tomcat。
private synchronized void initialize() throws EmbeddedServletContainerException {
TomcatEmbeddedServletContainer.logger
.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false));
try {
addInstanceIdToEngineName();
// Remove service connectors to that protocol binding doesn't happen yet
removeServiceConnectors();
// Start the server to trigger initialization listeners
this.tomcat.start();
// We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread
rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
// Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a
// blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown
startDaemonAwaitThread();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new EmbeddedServletContainerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat",
ex);
}
}
第11行正式啟動 tomcat。
現在我們回過來看看之前的那個 getSelfInitializer 方法:
private ServletContextInitializer getSelfInitializer() {
return new ServletContextInitializer() {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
selfInitialize(servletContext);
}
};
}
private void selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
prepareEmbeddedWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
ExistingWebApplicationScopes existingScopes = new ExistingWebApplicationScopes(
beanFactory);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory,
getServletContext());
existingScopes.restore();
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory,
getServletContext());
for (ServletContextInitializer beans : getServletContextInitializerBeans()) {
beans.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
在第2行的prepareEmbeddedWebApplicationContext方法中主要是將 EmbeddedWebApplicationContext 設置為rootContext。
第4行允許用戶存儲自定義的 scope。
第6行主要是用來將web專用的scope注冊到BeanFactory中,比如("request", "session", "globalSession", "application")。
第9行注冊web專用的environment bean(比如 ("contextParameters", "contextAttributes"))到給定的 BeanFactory 中。
第11和12行,比較重要,主要用來配置 servlet、filters、listeners、context-param和一些初始化時的必要屬性。
以其一個實現類ServletContextInitializer試舉一例:
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
Assert.notNull(this.servlet, "Servlet must not be null");
String name = getServletName();
if (!isEnabled()) {
logger.info("Servlet " + name + " was not registered (disabled)");
return;
}
logger.info("Mapping servlet: '" + name + "' to " + this.urlMappings);
Dynamic added = servletContext.addServlet(name, this.servlet);
if (added == null) {
logger.info("Servlet " + name + " was not registered "
+ "(possibly already registered?)");
return;
}
configure(added);
}
可以看第9行的打印: 正是在這里實現了 servlet 到 URLMapping的映射。
總結
這篇文章從主干脈絡分析找到了為什么在SpringBoot中不用自己配置Tomcat,內置的容器是怎么啟動起來的,順便在分析的過程中找到了我們常用的 urlMapping 映射 Servlet 的實現。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。