您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
@Conditional注解如何在Spring中使用?相信很多沒有經驗的人對此束手無策,為此本文總結了問題出現的原因和解決方法,通過這篇文章希望你能解決這個問題。
前言:
@Conditional是Spring4新提供的注解,它的作用是按照一定的條件進行判斷,滿足條件給容器注冊bean。
@Conditional的定義:
//此注解可以標注在類和方法上
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Conditional {
Class<? extends Condition>[] value();
}從代碼中可以看到,需要傳入一個Class數組,并且需要繼承Condition接口:
public interface Condition {
boolean matches(ConditionContext var1, AnnotatedTypeMetadata var2);
}Condition是個接口,需要實現matches方法,返回true則注入bean,false則不注入。
示例:
首先,創建Person類:
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Person(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}';
}
}創建BeanConfig類,用于配置兩個Person實例并注入,一個是比爾蓋茨,一個是林納斯。
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean(name = "bill")
public Person person1(){
return new Person("Bill Gates",62);
}
@Bean("linus")
public Person person2(){
return new Person("Linus",48);
}
}接著寫一個測試類進行驗證這兩個Bean是否注入成功。
public class ConditionalTest {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanConfig.class);
@Test
public void test1(){
Map<String, Person> map = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(Person.class);
System.out.println(map);
}
}運行,輸出結果是這樣的,兩個Person實例被注入進容器。
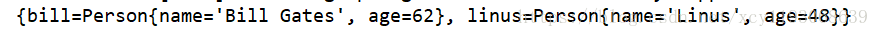
這是一個簡單的例子,現在問題來了,如果我想根據當前操作系統來注入Person實例,windows下注入bill,linux下注入linus,怎么實現呢?
這就需要我們用到@Conditional注解了,前言中提到,需要實現Condition接口,并重寫方法來自定義match規則。
首先,創建一個WindowsCondition類:
public class WindowsCondition implements Condition {
/**
* @param conditionContext:判斷條件能使用的上下文環境
* @param annotatedTypeMetadata:注解所在位置的注釋信息
* */
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext conditionContext, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) {
//獲取ioc使用的beanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = conditionContext.getBeanFactory();
//獲取類加載器
ClassLoader classLoader = conditionContext.getClassLoader();
//獲取當前環境信息
Environment environment = conditionContext.getEnvironment();
//獲取bean定義的注冊類
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = conditionContext.getRegistry();
//獲得當前系統名
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
//包含Windows則說明是windows系統,返回true
if (property.contains("Windows")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}matches方法的兩個參數的意思在注釋中講述了,值得一提的是,conditionContext提供了多種方法,方便獲取各種信息,也是SpringBoot中 @ConditonalOnXX注解多樣擴展的基礎。
接著,創建LinuxCondition類:
public class LinuxCondition implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext conditionContext, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) {
Environment environment = conditionContext.getEnvironment();
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
if (property.contains("Linux")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}接著就是使用這兩個類了,因為此注解可以標注在方法上和類上,所以分開測試:
標注在方法上:
修改BeanConfig:
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
//只有一個類時,大括號可以省略
//如果WindowsCondition的實現方法返回true,則注入這個bean
@Conditional({WindowsCondition.class})
@Bean(name = "bill")
public Person person1(){
return new Person("Bill Gates",62);
}
//如果LinuxCondition的實現方法返回true,則注入這個bean
@Conditional({LinuxCondition.class})
@Bean("linus")
public Person person2(){
return new Person("Linus",48);
}
}修改測試方法,使其可以打印當前系統名:
@Test
public void test1(){
String osName = applicationContext.getEnvironment().getProperty("os.name");
System.out.println("當前系統為:" + osName);
Map<String, Person> map = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(Person.class);
System.out.println(map);
}運行結果如下:
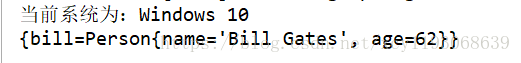
我是運行在windows上的所以只注入了bill,嗯,沒毛病。
接著實驗linux下的情況,不能運行在linux下,但可以修改運行時參數:

修改后啟動測試方法:
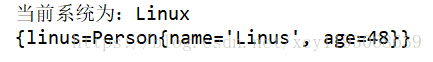
一個方法只能注入一個bean實例,所以@Conditional標注在方法上只能控制一個bean實例是否注入。
標注在類上:
一個類中可以注入很多實例,@Conditional標注在類上就決定了一批bean是否注入。
我們試一下,將BeanConfig改寫,這時,如果WindowsCondition返回true,則兩個Person實例將被注入(注意:上一個測試將os.name改為linux,這是我將把這個參數去掉):
@Conditional({WindowsCondition.class})
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean(name = "bill")
public Person person1(){
return new Person("Bill Gates",62);
}
@Bean("linus")
public Person person2(){
return new Person("Linus",48);
}
}結果兩個實例都被注入:

如果將類上的WindowsCondition.class改為LinuxCondition.class,結果應該可以猜到:

結果就是空的,類中所有bean都沒有注入。
多個條件類:
前言中說,@Conditional注解傳入的是一個Class數組,存在多種條件類的情況。
這種情況貌似判斷難度加深了,測試一波,新增新的條件類,實現的matches返回false(這種寫死返回false的方法純屬測試用,沒有實際意義O(∩_∩)O)
public class ObstinateCondition implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext conditionContext, AnnotatedTypeMetadata annotatedTypeMetadata) {
return false;
}
}BeanConfig修改一下:
@Conditional({WindowsCondition.class,ObstinateCondition.class})
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean(name = "bill")
public Person person1(){
return new Person("Bill Gates",62);
}
@Bean("linus")
public Person person2(){
return new Person("Linus",48);
}
}結果:

現在如果將ObstinateCondition的matches方法返回值改成true,兩個bean就被注入進容器:
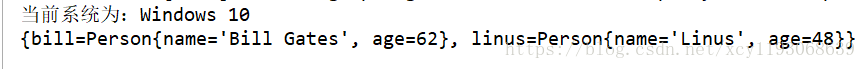
結論得:
第一個條件類實現的方法返回true,第二個返回false,則結果false,不注入進容器。
第一個條件類實現的方法返回true,第二個返回true,則結果true,注入進容器中。
看完上述內容,你們掌握@Conditional注解如何在Spring中使用的方法了嗎?如果還想學到更多技能或想了解更多相關內容,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝各位的閱讀!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。