溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹了opencv3/C++如何實現光流點追蹤,具有一定借鑒價值,感興趣的朋友可以參考下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章之后大有收獲,下面讓小編帶著大家一起了解一下。
光流金字塔
calcOpticalFlowPyrLK()函數參數說明:
void calcOpticalFlowPyrLK( InputArray prevImg, //第一個8位輸入圖像或者通過 buildOpticalFlowPyramid()建立的金字塔 InputArray nextImg,//第二個輸入圖像或者和prevImg相同尺寸和類型的金字塔 InputArray prevPts, //二維點向量存儲找到的光流;點坐標必須是單精度浮點數 InputOutputArray nextPts,//輸出二維點向量(用單精度浮點坐標)包括第二幅圖像中計算的輸入特征的新點位置;當OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW 標志通過,向量必須有和輸入一樣的尺寸。 OutputArray status, //輸出狀態向量(無符號char);如果相應的流特征被發現,向量的每個元素被設置為1,否則,被置為0. OutputArray err,//輸出錯誤向量;向量的每個元素被設為相應特征的一個錯誤,誤差測量的類型可以在flags參數中設置;如果流不被發現然后錯誤未被定義(使用status(狀態)參數找到此情形)。 Size winSize = Size(21,21), //在每個金字塔水平搜尋窗口的尺寸。 int maxLevel = 3,//最大金字塔層數; 如果設置為0,則不使用金字塔(單層),如果設置為1,則使用兩個層次,依此類推; 如果將金字塔傳遞給輸入,則算法將使用與金字塔一樣多的級別,但不超過maxLevel。 TermCriteria criteria = TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS, 30, 0.01),//指定迭代搜索算法的終止標準(指定的最大迭代次數criteria.maxCount或搜索窗口移動小于criteria.epsilon) int flags = 0, //操作標志 double minEigThreshold = 1e-4 //計算光流方程的2×2標準矩陣的最小特征值除以窗口中的像素數量;如果這個值小于minEigThreshold,那么一個相應的特征被過濾出來,且它的光流不被處理,所以它允許去除壞點提升性能。 );
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
//光流跟蹤
Mat frame, gray, pr_frame, pr_gray;
std::vector<Point2f> inPoints;
std::vector<Point2f> fpts[2];
void trackFeature();
int main()
{
VideoCapture capture;
capture.open(0);
if(!capture.isOpened())
{
printf("can not open the camear......\n");
return -1;
}
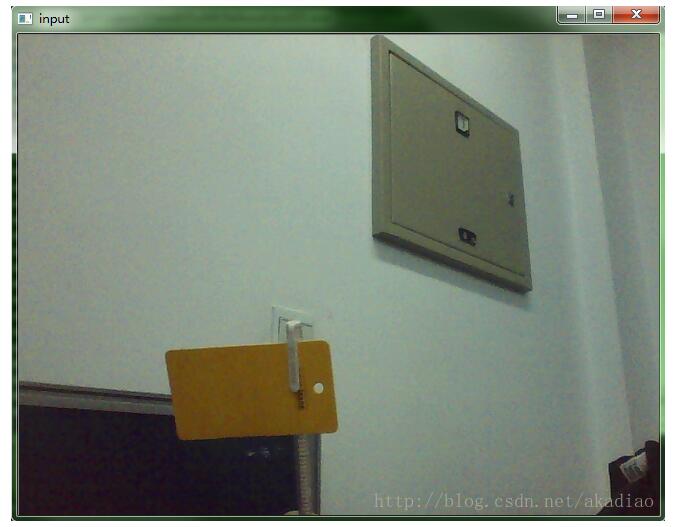
namedWindow("input", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
namedWindow("output", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
while (capture.read(frame))
{
cvtColor(frame, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
if (fpts[0].size() < 40)
{
imshow("input", frame);
std::vector<Point2f> features;
//角點檢測
goodFeaturesToTrack(gray, features, 300, 0.01, 10);
fpts[0].insert(fpts[0].end(), features.begin(), features.end());
inPoints.insert(inPoints.end(), features.begin(), features.end());
}
else
printf("object tracking......\n");
if (pr_gray.empty())
gray.copyTo(pr_gray);
trackFeature();
for (int i = 0; i < fpts[0].size(); i++)
circle(frame, fpts[0][i], 2, Scalar(0,255,0),2,8,0);
gray.copyTo(pr_gray);
frame.copyTo(pr_frame);
imshow("output", frame);
waitKey(1);
}
waitKey(0);
capture.release();
return 0;
}
void trackFeature()
{
std::vector<uchar> status;
std::vector<float> errors;
//計算稀疏特征集的光流
calcOpticalFlowPyrLK(pr_gray, gray, fpts[0], fpts[1], status, errors);
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < fpts[1].size(); i++)
{
double dist = abs(fpts[0][i].x-fpts[1][i].x) + abs(fpts[0][i].y-fpts[1][i].y);
if (dist > 2 && status[i])
{
inPoints[k] = inPoints[i];
fpts[1][k++] = fpts[1][i];
}
}
inPoints.resize(k);
fpts[1].resize(k);
//繪制光流軌跡
RNG rng(0);
for (int i = 0; i < fpts[0].size(); i++)
{
Scalar color = Scalar(rng.uniform(0,255),rng.uniform(0,255),rng.uniform(0,255));
line(frame, inPoints[i], fpts[1][i], color,2);
circle(frame, fpts[1][i], 2, Scalar(0,255,255),2);
}
std::swap(fpts[1], fpts[0]);
}
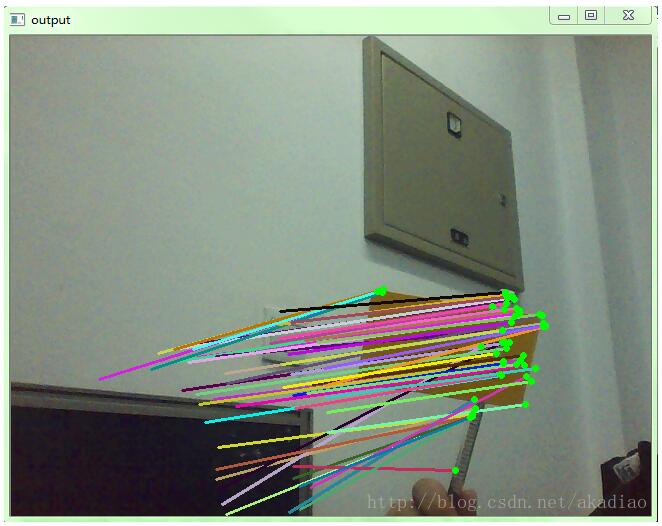
感謝你能夠認真閱讀完這篇文章,希望小編分享的“opencv3/C++如何實現光流點追蹤”這篇文章對大家有幫助,同時也希望大家多多支持億速云,關注億速云行業資訊頻道,更多相關知識等著你來學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。