您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
一,準備工作
1.下載node.js 和 npm
2.將鏡像源替換為淘寶鏡像
二,創建項目
1.vue環境搭建
創建目錄resume
1)npm init -y
2)npm install vue-cli -g (安裝vue-cli )
3)vue init webpack --dirname(為空時默認當前目錄)
輸入命令后,會詢問我們幾個簡單的選項,我們根據自己的需要進行填寫就可以了。
等待安裝完畢后,文件目錄結構如下
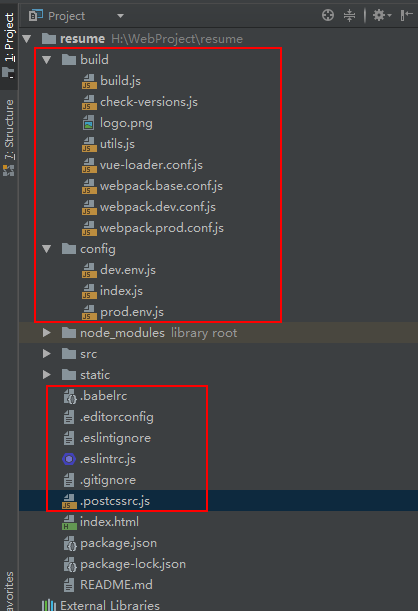
此時已經搭建好了vue的開發環境。
打開package.json我們可以看到官方腳手架提供的4個腳本
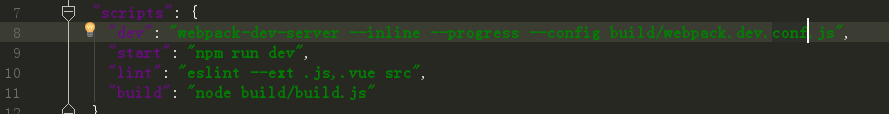
我們直接在命令行輸入npm run star,即可看到vue提供的demo。
三,腳手架解析
當我們鍵入npm run start時,其實執行的是build目錄下的webpack.dev.conf.js。
webpack.dev.conf.js
'use strict'
/*工具類 主要提供以下幾個方法
* assetsPath 獲取靜態資源路徑
* exports.cssLoaders 返回針對各類型的樣式文件的處理方式
* exports.styleLoaders 返回webpack需要的css相關的loader的配置,它也使用了cssLoaders()
* exports.createNotifierCallback node-notifier'是一個跨平臺系統通知的頁面。
* 當遇到錯誤時,它能用系統原生的推送方式給你推送信息這個方法用于推送錯誤信息
* 跳轉至utils
*/
const utils = require('./utils')
//引入webpack模塊
const webpack = require('webpack')
/*引入配置文件 他下面有3個文件
* dev.env.js 導出開發環境的名稱
* prod.env.js 到處生產環境的名稱
* index.js 到處不同環境需要的具體配置
* 跳轉至config
*/
const config = require('../config')
//webpack-merge這個包,這個包的作用是來合并兩個配置文件對象并生成一個新的配置文件,有點兒類似于es6的Object.assign()方法。合并沖突時,第二個參數的屬性值會覆蓋第一個參數的屬性值。
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
//處理文件路徑的模塊
const path = require('path')
/* 配置webpack編譯入口
* 配置webpack輸出路徑和命名規則
* 配置模塊resolve規則
* 配置不同類型模塊的處理規則
* 跳轉至webpack.base.conf
*/
const baseWebpackConfig = require('./webpack.base.conf')
//一個負責拷貝資源的插件
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin')
// 一個用于生成HTML文件并自動注入依賴文件(link/script)的webpack插件
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
//一個更友好的展示webpack錯誤提示的插件
const FriendlyErrorsPlugin = require('friendly-errors-webpack-plugin')
//一個自動檢索端口的包
const portfinder = require('portfinder')
//當前環境HOST
const HOST = process.env.HOST
//當前環境端口
const PORT = process.env.PORT && Number(process.env.PORT)
//baseWebpackConfig請跳到./webpack.base.conf小節
const devWebpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, {
module: {
//此處的配置會覆蓋掉baseWebpackConfig的 sourceMap是否開啟,是否使用postcss
//postcssloader 為CSS3自動加上瀏覽器前綴
rules: utils.styleLoaders({ sourceMap: config.dev.cssSourceMap, usePostCSS: true })
},
// cheap-module-eval-source-map在開發環境中最快
devtool: config.dev.devtool,
// devServer的配置大家看文檔就好了 配置太大不一一贅述了
devServer: {
clientLogLevel: 'warning',
historyApiFallback: {
rewrites: [
{ from: /.*/, to: path.posix.join(config.dev.assetsPublicPath, 'index.html') },
],
},
hot: true,
contentBase: false, // since we use CopyWebpackPlugin.
compress: true,
host: HOST || config.dev.host,
port: PORT || config.dev.port,
open: config.dev.autoOpenBrowser,
overlay: config.dev.errorOverlay
? { warnings: false, errors: true }
: false,
publicPath: config.dev.assetsPublicPath,
proxy: config.dev.proxyTable,
quiet: true, // necessary for FriendlyErrorsPlugin
watchOptions: {
poll: config.dev.poll,
}
},
//插件
plugins: [
//配置開發環境
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': require('../config/dev.env')
}),
//模塊熱替換的插件,修改模塊不需要刷新頁面
new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin(),
//當使用HotModuleReplacementPlugin時,這個插件會顯示模塊正確的相對路徑
new webpack.NamedModulesPlugin(),
//在編譯出錯時,使用NoEmitOnErrorsPlugin來跳過輸出階段,這樣可以確保輸出資源不會包含錯誤
new webpack.NoEmitOnErrorsPlugin(),
//這里將resume/index.html作為模版,生成一份新的index.html在build下。
// https://github.com/ampedandwired/html-webpack-plugin
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: 'index.html',
template: 'index.html',
inject: true
}),
// 復制靜態資源
new CopyWebpackPlugin([
{
from: path.resolve(__dirname, '../static'),
to: config.dev.assetsSubDirectory,
ignore: ['.*']
}
])
]
})
//這里主要是做端口的檢索以及npm run dev后對錯誤的處理
module.exports = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
portfinder.basePort = process.env.PORT || config.dev.port
portfinder.getPort((err, port) => {
if (err) {
reject(err)
} else {
// publish the new Port, necessary for e2e tests
process.env.PORT = port
// add port to devServer config
devWebpackConfig.devServer.port = port
// Add FriendlyErrorsPlugin
devWebpackConfig.plugins.push(new FriendlyErrorsPlugin({
compilationSuccessInfo: {
messages: [`Your application is running here: http://${devWebpackConfig.devServer.host}:${port}`],
},
onErrors: config.dev.notifyOnErrors
? utils.createNotifierCallback()
: undefined
}))
resolve(devWebpackConfig)
}
})
})
utils.js
'use strict'
const path = require('path')
//跳轉至config
const config = require('../config')
//這個plugin的作用是將打包后生成的css文件通過link的方式引入到html中,如果不適用這個插件css代碼會放到head標簽的style中
const ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin')
const packageConfig = require('../package.json')
//process.env.NODE_ENV是一個環境變量,它是由webpack.dev/prod.conf.js這兩個文件聲明的;
//這里的意思是判斷當前是否是開發環境,如果是就把config下index.js文件中build.assetsSubDirectory或
//dev.assetsSubDirectory的值賦給assetsSubDirectory
exports.assetsPath = function (_path) {
const assetsSubDirectory = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
? config.build.assetsSubDirectory
: config.dev.assetsSubDirectory
return path.posix.join(assetsSubDirectory, _path)
}
//cssLoaders的作用是導出一個供vue-loader的options使用的一個配置;
exports.cssLoaders = function (options) {
options = options || {}
const cssLoader = {
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
sourceMap: options.sourceMap
}
}
const postcssLoader = {
loader: 'postcss-loader',
options: {
sourceMap: options.sourceMap
}
}
// generate loader string to be used with extract text plugin
function generateLoaders (loader, loaderOptions) {
const loaders = options.usePostCSS ? [cssLoader, postcssLoader] : [cssLoader]
if (loader) {
loaders.push({
loader: loader + '-loader',
options: Object.assign({}, loaderOptions, {
sourceMap: options.sourceMap
})
})
}
// Extract CSS when that option is specified
// (which is the case during production build)
if (options.extract) {
return ExtractTextPlugin.extract({
use: loaders,
fallback: 'vue-style-loader'
})
} else {
return ['vue-style-loader'].concat(loaders)
}
}
// https://vue-loader.vuejs.org/en/configurations/extract-css.html
return {
css: generateLoaders(),
postcss: generateLoaders(),
less: generateLoaders('less'),
sass: generateLoaders('sass', { indentedSyntax: true }),
scss: generateLoaders('sass'),
stylus: generateLoaders('stylus'),
styl: generateLoaders('stylus')
}
}
//用來給webpack提供和css相關的loader的配置,它使用了cssLoaders方法;
exports.styleLoaders = function (options) {
const output = []
const loaders = exports.cssLoaders(options)
for (const extension in loaders) {
const loader = loaders[extension]
output.push({
test: new RegExp('\\.' + extension + '$'),
use: loader
})
}
return output
}
//當遇到錯誤時,給你推送信息
exports.createNotifierCallback = () => {
const notifier = require('node-notifier')
return (severity, errors) => {
if (severity !== 'error') return
const error = errors[0]
const filename = error.file && error.file.split('!').pop()
notifier.notify({
title: packageConfig.name,
message: severity + ': ' + error.name,
subtitle: filename || '',
icon: path.join(__dirname, 'logo.png')
})
}
}
webpack.base.conf.js
'use strict'
const path = require('path')
//跳轉至utils
const utils = require('./utils')
//跳轉至config
const config = require('../config')
//vue-load 處理.vue 結尾的文件
//跳轉至vue-loader.conf
const vueLoaderConfig = require('./vue-loader.conf')
//resolve這個函數返回的是當前目錄下"../dir"這個文件夾,__dirname指的是當前文件所在路徑
function resolve (dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, '..', dir)
}
//創建eslint規則
const createLintingRule = () => ({
test: /\.(js|vue)$/,
loader: 'eslint-loader',
enforce: 'pre',
include: [resolve('src'), resolve('test')],
options: {
formatter: require('eslint-friendly-formatter'),
emitWarning: !config.dev.showEslintErrorsInOverlay
}
})
module.exports = {
//基礎目錄,絕對路徑,用于從配置中解析入口起點(entry point)和加載器(loader)
context: path.resolve(__dirname, '../'),
//入口 webpack 應該使用哪個模塊 可以是數組
entry: {
app: './src/main.js'
},
//webpack 在哪里輸出它所創建的 bundles,以及如何命名這些文件
output: {
//導出目錄,絕對路徑
path: config.build.assetsRoot,
//輸出文件的名稱
filename: '[name].js',
//打包后瀏覽器訪問服務時的 url 路徑,可用于改資源請求路徑
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
? config.build.assetsPublicPath
: config.dev.assetsPublicPath
},
//主要設置模塊如何被解析。
resolve: {
//自動解析確定的拓展名,使導入模塊時不帶拓展名 例如映入./build/Test 不需要.js結尾
extensions: ['.js', '.vue', '.json'],
//常用模塊別名
//import vue = import resume/node_modules/vue/dist/vue.esm.js
alias: {
'vue$': 'vue/dist/vue.esm.js',
'@': resolve('src'),
}
},
//模塊
module: {
//指定模塊解析規則
rules: [
//ES6新加入和擴展運算符
...(config.dev.useEslint ? [createLintingRule()] : []),
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: 'vue-loader',
options: vueLoaderConfig
},
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel-loader',
include: [resolve('src'), resolve('test'), resolve('node_modules/webpack-dev-server/client')]
},
{
test: /\.(png|jpe?g|gif|svg)(\?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('img/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
{
test: /\.(mp4|webm|ogg|mp3|wav|flac|aac)(\?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('media/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
{
test: /\.(woff2?|eot|ttf|otf)(\?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('fonts/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
}
]
},
//以下選項是Node.js全局變量或模塊,這里主要是防止webpack注入一些Node.js的東西到vue中
node: {
setImmediate: false,
dgram: 'empty',
fs: 'empty',
net: 'empty',
tls: 'empty',
child_process: 'empty'
}
}
vue-loader.conf.js
'use strict'
//跳轉至utils
const utils = require('./utils')
//跳轉至config
const config = require('../config')
//開發環境生產環境標識
const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
//不同環境為sourceMapEnabled 賦值: 這里都為true
const sourceMapEnabled = isProduction
? config.build.productionSourceMap
: config.dev.cssSourceMap
//導出vue-loader的配置,這里我們用了utils文件中的cssLoaders();
module.exports = {
//vue-loader 處理.vue文件 將vue文件轉換為JS模塊 其中定義了其他loader,對< style >< template >中的靜態資源當做模塊來對待,并且使用webpack loaders進行處理
loaders: utils.cssLoaders({
sourceMap: sourceMapEnabled,
extract: isProduction
}),
//是否開啟cssSourceMap,Source map就是一個信息文件,主要用于開發環境的調試,里面儲存著位置信息。也就是說,轉換后的代碼的每一個位置,所對應的轉換前的位置。
cssSourceMap: sourceMapEnabled,
//一個配合devtool的配置,當給文件名插入新的hash導致清楚緩存時是否生成souce maps,默認在開發環境下為true
cacheBusting: config.dev.cacheBusting,
//transformToRequire的作用是在模板編譯的過程中,編譯器可以將某些屬性,如src轉換為require調用;
//配置這個之后就不需要在使用src時使用require
transformToRequire: {
video: ['src', 'poster'],
source: 'src',
img: 'src',
image: 'xlink:href'
}
}
config/index.js 這里的英文解釋比較全,直接粘貼了官方提供的
'use strict'
// Template version: 1.3.1
// see http://vuejs-templates.github.io/webpack for documentation.
const path = require('path')
module.exports = {
dev: {
// Paths
assetsSubDirectory: 'static',
assetsPublicPath: '/',
proxyTable: {},
// Various Dev Server settings
host: 'localhost', // can be overwritten by process.env.HOST
port: 8080, // can be overwritten by process.env.PORT, if port is in use, a free one will be determined
autoOpenBrowser: false,
errorOverlay: true,
notifyOnErrors: true,
poll: false, // https://webpack.js.org/configuration/dev-server/#devserver-watchoptions-
// Use Eslint Loader?
// If true, your code will be linted during bundling and
// linting errors and warnings will be shown in the console.
useEslint: true,
// If true, eslint errors and warnings will also be shown in the error overlay
// in the browser.
showEslintErrorsInOverlay: false,
/**
* Source Maps
*/
// https://webpack.js.org/configuration/devtool/#development
devtool: 'cheap-module-eval-source-map',
// If you have problems debugging vue-files in devtools,
// set this to false - it *may* help
// https://vue-loader.vuejs.org/en/options.html#cachebusting
cacheBusting: true,
cssSourceMap: true
},
build: {
// Template for index.html
index: path.resolve(__dirname, '../dist/index.html'),
// Paths
assetsRoot: path.resolve(__dirname, '../dist'),
assetsSubDirectory: 'static',
assetsPublicPath: '/',
/**
* Source Maps
*/
productionSourceMap: true,
// https://webpack.js.org/configuration/devtool/#production
devtool: '#source-map',
// Gzip off by default as many popular static hosts such as
// Surge or Netlify already gzip all static assets for you.
// Before setting to `true`, make sure to:
// npm install --save-dev compression-webpack-plugin
productionGzip: false,
productionGzipExtensions: ['js', 'css'],
// Run the build command with an extra argument to
// View the bundle analyzer report after build finishes:
// `npm run build --report`
// Set to `true` or `false` to always turn it on or off
bundleAnalyzerReport: process.env.npm_config_report
}
}
config/prod.env.js
'use strict'
module.exports = {
NODE_ENV: '"production"'
}
config/dev.env.js
'use strict'
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
const prodEnv = require('./prod.env')
//使用webpack-merge來進行合并,減少重復代碼。
module.exports = merge(prodEnv, {
NODE_ENV: '"development"'
})
當我們鍵入npm run build時,其實執行的是build目錄下的build.js。
build.js
'use strict'
//跳轉至check-versions
require('./check-versions')()
//指定為生成環境
process.env.NODE_ENV = 'production'
// node 終端的 loading 圖
const ora = require('ora')
// 用于深度刪除模塊
const rm = require('rimraf')
const path = require('path')
// 命令行彩色輸出
const chalk = require('chalk')
const webpack = require('webpack')
//跳轉至config
const config = require('../config')
//跳轉至webpack.prod.conf
const webpackConfig = require('./webpack.prod.conf')
const spinner = ora('building for production...')
//loading圖顯示
spinner.start()
/*
*使用 rimraf 將舊的編譯輸出的文件夾刪除,然后重新編譯生成
*rimraf(f: 路徑, [opts], callback: 回調)
*/
rm(path.join(config.build.assetsRoot, config.build.assetsSubDirectory), err => {
if (err) throw err
webpack(webpackConfig, (err, stats) => {
spinner.stop()
if (err) throw err
process.stdout.write(stats.toString({
colors: true,
modules: false,
children: false, // If you are using ts-loader, setting this to true will make TypeScript errors show up during build.
chunks: false,
chunkModules: false
}) + '\n\n')
if (stats.hasErrors()) {
console.log(chalk.red(' Build failed with errors.\n'))
process.exit(1)
}
console.log(chalk.cyan(' Build complete.\n'))
console.log(chalk.yellow(
' Tip: built files are meant to be served over an HTTP server.\n' +
' Opening index.html over file:// won\'t work.\n'
))
})
})
check-versions.js
'use strict'
//用來在命令行輸出不同顏色文字的包,可以使用chalk.yellow("想添加顏色的文字....")
const chalk = require('chalk')
//版本解析插件
const semver = require('semver')
const packageConfig = require('../package.json')
//一個用來執行unix命令的包
const shell = require('shelljs')
// child_process 開啟子進程,并執行 cmd 命令 然后返回結果
function exec (cmd) {
return require('child_process').execSync(cmd).toString().trim()
}
const versionRequirements = [
{
name: 'node',
//格式化版本號
currentVersion: semver.clean(process.version),
versionRequirement: packageConfig.engines.node
}
]
// shell.which('命令')在系統環境變量搜索命令, 如果用的是 npm 就檢查 npm 版本
if (shell.which('npm')) {
versionRequirements.push({
name: 'npm',
//執行"npm --version"命令
currentVersion: exec('npm --version'),
versionRequirement: packageConfig.engines.npm
})
}
module.exports = function () {
const warnings = []
for (let i = 0; i < versionRequirements.length; i++) {
const mod = versionRequirements[i]
//如果版本不符合package.json文件中指定的版本號,返回false,進入if
if (!semver.satisfies(mod.currentVersion, mod.versionRequirement)) {
warnings.push(mod.name + ': ' +
chalk.red(mod.currentVersion) + ' should be ' +
chalk.green(mod.versionRequirement)
//把當前版本號用紅色字體 符合要求的版本號用綠色字體 給用戶提示具體合適的版本
)
}
}
if (warnings.length) {
console.log('')
console.log(chalk.yellow('To use this template, you must update following to modules:'))
console.log()
for (let i = 0; i < warnings.length; i++) {
const warning = warnings[i]
console.log(' ' + warning)
}
console.log()
process.exit(1)
//提示用戶更新版本
}
}
webpack.prod.conf.js
'use strict'
const path = require('path')
//跳轉至utils
const utils = require('./utils')
const webpack = require('webpack')
//跳轉至config
const config = require('../config')
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
//跳轉至webpack.base.conf
const baseWebpackConfig = require('./webpack.base.conf')
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
const ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin')
//是用來壓縮css代碼
const OptimizeCSSPlugin = require('optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin')
//用來壓縮JS代碼
const UglifyJsPlugin = require('uglifyjs-webpack-plugin')
//跳轉至prod.env
const env = require('../config/prod.env')
//以下同webpack.dev.conf
//跳轉至webpack.dev.conf
const webpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, {
module: {
rules: utils.styleLoaders({
sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap,
extract: true,
usePostCSS: true
})
},
devtool: config.build.productionSourceMap ? config.build.devtool : false,
output: {
path: config.build.assetsRoot,
filename: utils.assetsPath('js/[name].[chunkhash].js'),
chunkFilename: utils.assetsPath('js/[id].[chunkhash].js')
},
plugins: [
// http://vuejs.github.io/vue-loader/en/workflow/production.html
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': env
}),
new UglifyJsPlugin({
uglifyOptions: {
compress: {
warnings: false
}
},
sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap,
parallel: true
}),
// extract css into its own file
new ExtractTextPlugin({
filename: utils.assetsPath('css/[name].[contenthash].css'),
// Setting the following option to `false` will not extract CSS from codesplit chunks.
// Their CSS will instead be inserted dynamically with style-loader when the codesplit chunk has been loaded by webpack.
// It's currently set to `true` because we are seeing that sourcemaps are included in the codesplit bundle as well when it's `false`,
// increasing file size: https://github.com/vuejs-templates/webpack/issues/1110
allChunks: true,
}),
// Compress extracted CSS. We are using this plugin so that possible
// duplicated CSS from different components can be deduped.
new OptimizeCSSPlugin({
cssProcessorOptions: config.build.productionSourceMap
? { safe: true, map: { inline: false } }
: { safe: true }
}),
// generate dist index.html with correct asset hash for caching.
// you can customize output by editing /index.html
// see https://github.com/ampedandwired/html-webpack-plugin
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: config.build.index,
template: 'index.html',
inject: true,
minify: {
removeComments: true,
collapseWhitespace: true,
removeAttributeQuotes: true
// more options:
// https://github.com/kangax/html-minifier#options-quick-reference
},
// necessary to consistently work with multiple chunks via CommonsChunkPlugin
chunksSortMode: 'dependency'
}),
// keep module.id stable when vendor modules does not change
new webpack.HashedModuleIdsPlugin(),
// enable scope hoisting
new webpack.optimize.ModuleConcatenationPlugin(),
// split vendor js into its own file
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'vendor',
minChunks (module) {
// any required modules inside node_modules are extracted to vendor
return (
module.resource &&
/\.js$/.test(module.resource) &&
module.resource.indexOf(
path.join(__dirname, '../node_modules')
) === 0
)
}
}),
// extract webpack runtime and module manifest to its own file in order to
// prevent vendor hash from being updated whenever app bundle is updated
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'manifest',
minChunks: Infinity
}),
// This instance extracts shared chunks from code splitted chunks and bundles them
// in a separate chunk, similar to the vendor chunk
// see: https://webpack.js.org/plugins/commons-chunk-plugin/#extra-async-commons-chunk
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'app',
async: 'vendor-async',
children: true,
minChunks: 3
}),
// copy custom static assets
new CopyWebpackPlugin([
{
from: path.resolve(__dirname, '../static'),
to: config.build.assetsSubDirectory,
ignore: ['.*']
}
])
]
})
// 開啟 gzip 的配置
if (config.build.productionGzip) {
const CompressionWebpackPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin')
/*
壓縮
更多配置:https://github.com/webpack-contrib/compression-webpack-plugin
*/
webpackConfig.plugins.push(
new CompressionWebpackPlugin({
asset: '[path].gz[query]',
algorithm: 'gzip',
test: new RegExp(
'\\.(' +
config.build.productionGzipExtensions.join('|') +
')$'
),
threshold: 10240,
minRatio: 0.8
})
)
}
/*
webpack-bundle-analyzer 插件
解析出模塊構成、以及各自的大小體積,最后顯示為一個頁面
地址: https://www.npmjs.com/package/webpack-bundle-analyzer
*/
if (config.build.bundleAnalyzerReport) {
const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin
webpackConfig.plugins.push(new BundleAnalyzerPlugin())
}
module.exports = webpackConfig
三,其他配置
.babelrc
https://www.babeljs.cn/docs/usage/babelrc/
.editorconfig
https://editorconfig.org/
.eslintrc
http://eslint.cn/docs/user-guide/configuring
.gitignore
https://git-scm.com/docs/gitignore
.postcssrc.js
https://www.npmjs.com/package/postcss
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持億速云。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。