您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
tree-sharking 簡介
tree-sharking 是 Webpack 2 后續版本的優化功能,顧名思義,就是將多余的代碼給 “搖晃” 掉,在開發中我們經常使用一些第三方庫,而這些第三方庫只使用了這個庫的一部門功能或代碼,未使用的代碼也要被打包進來,這樣出口文件會非常大,tree-sharking 幫我們解決了這個問題,它可以將各個模塊中沒有使用的方法過濾掉,只對有效代碼進行打包。
AST 語法樹分析
假設我們現在使用了 ElementUI 庫的兩個組件,通常會使用解構賦值來引入。
優化前
import { Button, Alert } from "element-ui";
這樣引用資源, Webpack 在打包的時候會找到 element-ui 并把里面所有的代碼全部打包到出口文件,我們只使用了兩個組件,全部打包不是我們所希望的,tree-sharking 是通過在 Webpack 中配置 babel-plugin-import 插件來實現的,它可以將解構的代碼轉換成下面的形式。
優化后
import Button from "element-ui/lib/button"; import Alert from "element-ui/lib/Alert";
轉化后會去 node_modules 中的 element-ui 模塊找到 Button 和 Alert 兩個組件對應的文件,并打包到出口文件中。
通過上面的轉換可以看出,其實 tree-sharking 的實現原理是通過改變 AST 語法樹的結構來實現的,我們可以通過在線轉換網站 http://esprima.org/demo/parse.html 將 JS 代碼裝換成 AST 語法樹。
優化前的 AST 語法樹
{
"type": "Program",
"body": [
{
"type": "ImportDeclaration",
"specifiers": [
{
"type": "ImportSpecifier",
"local": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "Button"
},
"imported": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "Button"
}
},
{
"type": "ImportSpecifier",
"local": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "Alert"
},
"imported": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "Alert"
}
}
],
"source": {
"type": "Literal",
"value": "element-ui",
"raw": "\"element-ui\""
}
}
],
"sourceType": "module"
}
優化后的 AST 語法樹
{
"type": "Program",
"body": [
{
"type": "ImportDeclaration",
"specifiers": [
{
"type": "ImportDefaultSpecifier",
"local": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "Button"
}
}
],
"source": {
"type": "Literal",
"value": "element-ui/lib/button",
"raw": "\"element-ui/lib/button\""
}
},
{
"type": "ImportDeclaration",
"specifiers": [
{
"type": "ImportDefaultSpecifier",
"local": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "Alert"
}
}
],
"source": {
"type": "Literal",
"value": "element-ui/lib/Alert",
"raw": "\"element-ui/lib/Alert\""
}
}
],
"sourceType": "module"
}
從上面的語法樹對比,可以看出在優化前 body 里面只有一個對象,使用的組件信息存在 specifiers 里,source 指向了 element-ui,而在優化后,將兩個組件分別拆成了兩個對象存在 body 中,每個對象的的 specifiers 只存儲一個組件,并在 source 里面指向了當前組件對應的路徑。
模擬 tree-starking
既然我們已經清楚要修改語法樹的位置,下面就使用 AST 來模擬 tree-sharking 功能,對語法樹的操作是依賴于 babel-core 和 babel-types 兩個核心模塊的,下面先安裝依賴。
npm install babel-core babel-types
文件:babel-plugin-my-import.js
const babel = require("babel-core");
const types = require("babel-types");
let code = `import { Button, Alert } from "element-ui"`;
let importPlugin = {
visitor: {
ImportDeclaration(path) {
let node = path.node;
let source = node.source.value;
let specifiers = node.specifiers;
// 判斷是否是默認導出,其中一個不是默認導出,則都不是默認導出
if (!types.isImportDefaultSpecifier(specifiers[0])) {
// 如果不是默認導出,則需要轉換
specifiers = specifiers.map(specifier => {
// 數組內容:當前默認導出的標識、從哪里導入
return types.importDeclaration(
[types.importDefaultSpecifier(specifier.local)],
types.stringLiteral(`${source}/lib/${specifier.local.name.toLowerCase()}`)
);
});
// 替換樹結構
path.replaceWithMultiple(specifiers);
}
}
}
};
let result = babel.transform(code, {
plugins: [importPlugin]
});
console.log(result.code);
// import Button from "element-ui/lib/button";
// import Alert from "element-ui/lib/alert";
通過上面的代碼可以發現我們使用 babel-core 和 babel-types 兩個模塊的核心方法對語法書進行了遍歷、修改和替換,更詳細的 API 可以查看 https://github.com/babel/babel/tree/6.x/packages/babel-types。
結合 Webpack 使用插件
前面只是驗證了 tree-sharking 中 JS 語法的轉換過程,接下來將上面的代碼轉換成插件配合 Webpack 使用,來徹底感受 tree-sharking 的工作過程。
文件:~node_modules/babel-plugin-my-import.js
const babel = require("babel-core");
const types = require("babel-types");
let importPlugin = {
visitor: {
ImportDeclaration(path) {
let node = path.node;
let source = node.source.value;
let specifiers = node.specifiers;
// 判斷是否是默認導出,其中一個不是默認導出,則都不是默認導出
if (!types.isImportDefaultSpecifier(specifiers[0])) {
// 如果不是默認導出,則需要轉換
specifiers = specifiers.map(specifier => {
// 數組內容:當前默認導出的標識、從哪里導入
return types.importDeclaration(
[types.importDefaultSpecifier(specifier.local)],
types.stringLiteral(`${source}/lib/${specifier.local.name.toLowerCase()}`)
);
});
// 替換樹解構
path.replaceWithMultiple(specifiers);
}
}
}
};
module.exports = importPlugin;
上面刪掉了多余的測試代碼,將模塊中的 importPlugin 插件導出,并把 babel-plugin-my-import.js 移入了 node_modules 當中。
接下來安裝需要的依賴:
npm install webpack webpack-cli babel-loader babel-presets-env
npm install vue element-ui --save
安裝完依賴,寫一個要編譯的文件,使用 Webpack 進行打包,查看使用插件前和使用插件后出口文件的大小。
文件:import.js
import Vue from "vue";
import { Button, Alert } from "element-ui";
下面來寫一個簡單的 Webpack 配置文件。
文件:webpcak.config.js
module.exports = {
mode: "development",
entry: "import.js",
output: {
filename: "bundle.js",
path: __dirname
},
module: {
rules: [{
test: /\.js$/,
use: {
loader: "babel-loader",
options: {
presets: [
"env",
],
plugins: [
// 插件:不使用插件打包注釋掉該行即可
["my-import", { libararyName: "element-ui" }]
]
}
},
exclude: /node_modules/
}]
}
};
為了防止 babel 相關的依賴升級 7.0 后出現一些問題導致 Webpack 無法啟動,再此貼出 package.json 文件,按照對應版本下載依賴保證上面 Webpack 配置生效。
文件:package.json
{
"name": "ast-lesson",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "tree-starking",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"babel-core": "^6.26.3",
"babel-loader": "^7.1.5",
"babel-preset-env": "^1.7.0",
"babel-types": "^6.26.0",
"escodegen": "^1.10.0",
"esprima": "^4.0.0",
"estraverse": "^4.2.0",
"webpack": "^4.16.0",
"webpack-cli": "^3.0.8"
},
"devDependencies": {
"vue": "^2.5.17",
"element-ui": "^2.4.6"
}
}
對比使用插件前后的出口文件
接下來分別在使用插件和不使用插件時執行打包命令,查看出口文件 bondle.js 的大小。
npx webpack
使用 babel-plugin-my-import 前:
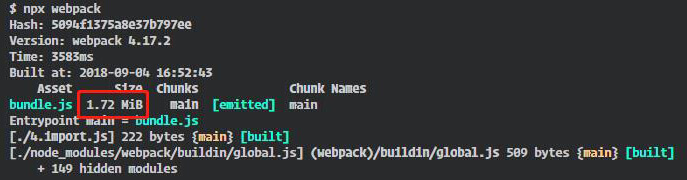
使用 babel-plugin-my-import 后:
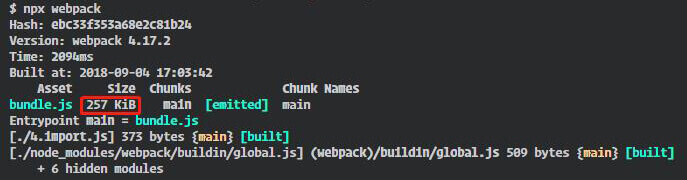
通過對比,可以看到使用 tree-sharking 即我們自己實現的 babel-plugin-my-import 插件后,打包的出口文件大大減小,其原因是將引入第三方庫沒有使用的代碼全都過濾掉了,只打包了有效代碼。
總結
上面對 Webpack 的 tree-sharking 進行了分析,并模擬 babel-plugin-import 簡易的實現了一版 tree-sharking 的優化插件,這個過程中相信大家已經了解了 tree-sharking 的原理以及實現類似插件的思路,并已經具備了開發類似插件的基本條件,最后還有一點需要補充,tree-sharking 優化的方式是根據 ES6 語法 import “靜態” 引入的特性實現的,如果要說 tree-sharking 很強大,還不如說 ES6 模塊化規范 “靜態” 引入的特性強大,正由于是基于 “靜態” 引入,所以目前 tree-sharking 只支持遍歷一層 import 關鍵字。
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持億速云。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。