您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章將為大家詳細講解有關numpy.meshgrid()函數的作用是什么,文章內容質量較高,因此小編分享給大家做個參考,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后對相關知識有一定的了解。
示例1,創建一個2行3列的網格點矩陣。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
X = np.array([[0, 0.5, 1],[0, 0.5, 1]])
print("X的維度:{},shape:{}".format(X.ndim, X.shape))
Y = np.array([[0, 0, 0],[1, 1, 1]])
print("Y的維度:{},shape:{}".format(Y.ndim, Y.shape))
plt.plot(X, Y, 'o--')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()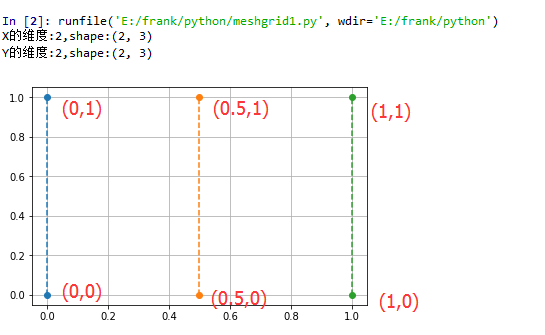
X矩陣是:[[0. 0.5 1. ],[0. 0.5 1. ]]
Y矩陣是:[[0 0 0],[1 1 1]]
step2. meshgrid()的作用;
當要描繪的 矩陣網格點的數據量小的時候,可以用上述方法構造網格點坐標數據;
但是如果是一個(256, 100)的整數矩陣網格,要怎樣構造數據呢?
方法1:將x軸上的100個整數點組成的行向量,重復256次,構成shape(256,100)的X矩陣;將y軸上的256個整數點組成列向量,重復100次構成shape(256,100)的Y矩陣
顯然方法1的數據構造過程很繁瑣,也不方便調用,那么有沒有更好的辦法呢?of course!!!
那么meshgrid()就顯示出它的作用了
使用meshgrid方法,你只需要構造一個表示x軸上的坐標的向量和一個表示y軸上的坐標的向量;然后作為參數給到meshgrid(),該函數就會返回相應維度的兩個矩陣;
例如,你想構造一個2行3列的矩陣網格點,那么x生成一個shape(3,)的向量,y生成一個shape(2,)的向量,將x,y傳入meshgrid(),最后返回的X,Y矩陣的shape(2,3)
示例2,使用meshgrid()生成step1中的網格點矩陣
x = np.array([0, 0.5, 1])
y = np.array([0,1])
xv,yv = np.meshgrid(x, y)
print("xv的維度:{},shape:{}".format(xv.ndim, xv.shape))
print("yv的維度:{},shape:{}".format(yv.ndim, yv.shape))
plt.plot(xv, yv, 'o--')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()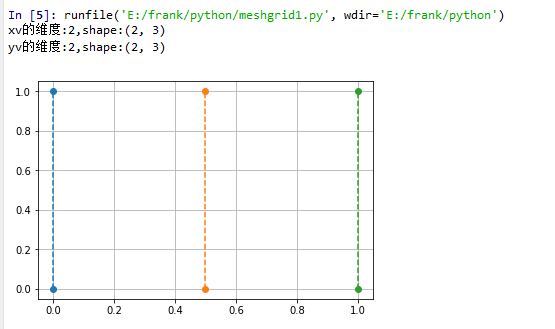
示例3,生成一個20行30列的網格點矩陣
x = np.linspace(0,500,30)
print("x的維度:{},shape:{}".format(x.ndim, x.shape))
print(x)
y = np.linspace(0,500,20)
print("y的維度:{},shape:{}".format(y.ndim, y.shape))
print(y)
xv,yv = np.meshgrid(x, y)
print("xv的維度:{},shape:{}".format(xv.ndim, xv.shape))
print("yv的維度:{},shape:{}".format(yv.ndim, yv.shape))
plt.plot(xv, yv, '.')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
step3. 詳細解讀meshgrid()的官網定義;
numpy.meshgrid(*xi, **kwargs)
Return coordinate matrices from coordinate vectors.
根據輸入的坐標向量生成對應的坐標矩陣
Parameters:
x1, x2,…, xn : array_like
1-D arrays representing the coordinates of a grid.
indexing : {‘xy', ‘ij'}, optional
Cartesian (‘xy', default) or matrix (‘ij') indexing of output. See Notes for more details.
sparse : bool, optional
If True a sparse grid is returned in order to conserve memory. Default is False.
copy : bool, optional
If False, a view into the original arrays are returned in order to conserve memory.
Default is True. Please note that sparse=False, copy=False will likely return non-contiguous arrays.
Furthermore, more than one element of a broadcast array may refer to a single memory location.
If you need to write to the arrays, make copies first.
Returns:
X1, X2,…, XN : ndarray
For vectors x1, x2,…, ‘xn' with lengths Ni=len(xi) ,
return (N1, N2, N3,...Nn) shaped arrays if indexing='ij'
or (N2, N1, N3,...Nn) shaped arrays if indexing='xy'
with the elements of xi repeated to fill the matrix along the first dimension for x1, the second for x2 and so on.
針對indexing參數的說明:
indexing只是影響meshgrid()函數返回的矩陣的表示形式,但并不影響坐標點
x = np.array([0, 0.5, 1])
y = np.array([0,1])
xv,yv = np.meshgrid(x, y)
print("xv的維度:{},shape:{}".format(xv.ndim, xv.shape))
print("yv的維度:{},shape:{}".format(yv.ndim, yv.shape))
print(xv)
print(yv)
plt.plot(xv, yv, 'o--')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()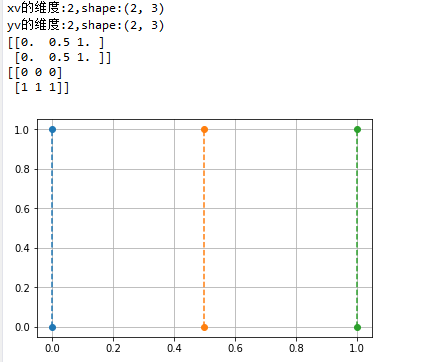
x = np.array([0, 0.5, 1])
y = np.array([0,1])
xv,yv = np.meshgrid(x, y,indexing='ij')
print("xv的維度:{},shape:{}".format(xv.ndim, xv.shape))
print("yv的維度:{},shape:{}".format(yv.ndim, yv.shape))
print(xv)
print(yv)
plt.plot(xv, yv, 'o--')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()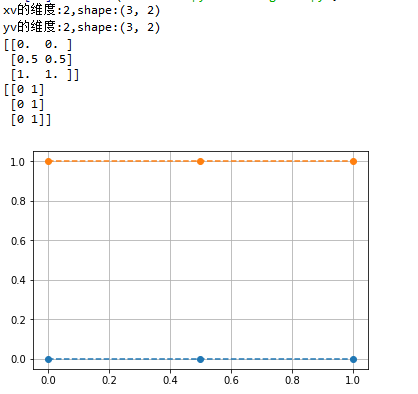
關于numpy.meshgrid()函數的作用是什么就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,可以學到更多知識。如果覺得文章不錯,可以把它分享出去讓更多的人看到。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。