您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹了Pytorch.nn.conv2d驗證方式的示例分析,具有一定借鑒價值,感興趣的朋友可以參考下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章之后大有收獲,下面讓小編帶著大家一起了解一下。
首先提出兩個問題:
1.輸入圖片是單通道情況下的filters是如何操作的? 即一通道卷積核卷積過程
2.輸入圖片是多通道情況下的filters是如何操作的? 即多通道多個卷積核卷積過程
這里首先貼出官方文檔:
classtorch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True)[source]
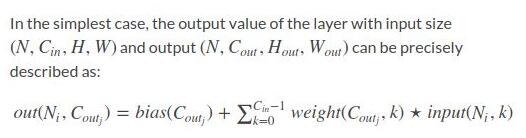
Parameters:
in_channels (int) – Number of channels in the input image
out_channels (int) – Number of channels produced by the convolution
kernel_size (intortuple) – Size of the convolving kernel
stride (intortuple,optional) – Stride of the convolution. Default: 1
padding (intortuple,optional) – Zero-padding added to both sides of the input. Default: 0
dilation (intortuple,optional) – Spacing between kernel elements. Default: 1
groups (int,optional) – Number of blocked connections from input channels to output channels. Default: 1
bias (bool,optional) – If True, adds a learnable bias to the output. Default: True
這個文檔中的公式對我來說,并不能看的清楚
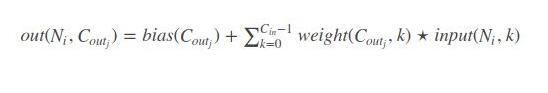
一通道卷積核卷積過程:
比如32個卷積核,可以學習32種特征。在有多個卷積核時,如下圖所示:輸出就為32個feature map
也就是, 當conv2d( in_channels = 1 , out_channels = N)
有N個filter對輸入進行濾波。同時輸出N個結果即feature map,每個filter濾波輸出一個結果.
import torch from torch.autograd import Variable ##單位矩陣來模擬輸入 input=torch.ones(1,1,5,5) input=Variable(input) x=torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1,out_channels=3,kernel_size=3,groups=1) out=x(input) print(out) print(list(x.parameters()))
輸出out的結果和conv2d 的參數如下,可以看到,conv2d是有3個filter加一個bias
# out的結果 Variable containing: (0 ,0 ,.,.) = -0.3065 -0.3065 -0.3065 -0.3065 -0.3065 -0.3065 -0.3065 -0.3065 -0.3065 (0 ,1 ,.,.) = -0.3046 -0.3046 -0.3046 -0.3046 -0.3046 -0.3046 -0.3046 -0.3046 -0.3046 (0 ,2 ,.,.) = 0.0710 0.0710 0.0710 0.0710 0.0710 0.0710 0.0710 0.0710 0.0710 [torch.FloatTensor of size 1x3x3x3] # conv2d的參數 [Parameter containing: (0 ,0 ,.,.) = -0.0789 -0.1932 -0.0990 0.1571 -0.1784 -0.2334 0.0311 -0.2595 0.2222 (1 ,0 ,.,.) = -0.0703 -0.3159 -0.3295 0.0723 0.3019 0.2649 -0.2217 0.0680 -0.0699 (2 ,0 ,.,.) = -0.0736 -0.1608 0.1905 0.2738 0.2758 -0.2776 -0.0246 -0.1781 -0.0279 [torch.FloatTensor of size 3x1x3x3] , Parameter containing: 0.3255 -0.0044 0.0733 [torch.FloatTensor of size 3] ]
驗證如下,因為是單位矩陣,所以直接對參數用sum()來模擬卷積過程:
f_p=list(x.parameters())[0]
f_p=f_p.data.numpy()
print("the result of first channel in image:", f_p[0].sum()+(0.3255))可以看到結果是和(0 ,0 ,.,.) = -0.3065 ....一樣的. 說明操作是通過卷積求和的.
the result of first channel in image: -0.306573044777
多通道卷積核卷積過程:
下圖展示了在四個通道上的卷積操作,有兩個卷積核,生成兩個通道。其中需要注意的是,四個通道上每個通道對應一個卷積核,先將w2忽略,只看w1,那么在w1的某位置(i,j)處的值,是由四個通道上(i,j)處的卷積結果相加得到的。 所以最后得到兩個feature map, 即輸出層的卷積核核個數為 feature map 的個數。
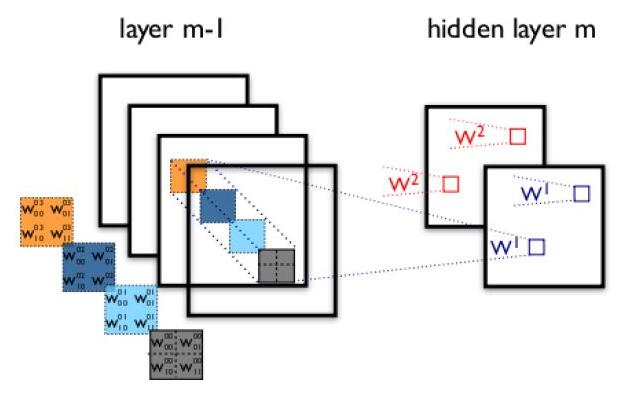
在pytorch 中的展示為
conv2d( in_channels = X(x>1) , out_channels = N)
有N乘X個filter(N組filters,每組X 個)對輸入進行濾波。即每次有一組里X個filter對原X個channels分別進行濾波最后相加輸出一個結果,最后輸出N個結果即feature map。
驗證如下:
##單位矩陣來模擬輸入 input=torch.ones(1,3,5,5) input=Variable(input) x=torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3,out_channels=4,kernel_size=3,groups=1) out=x(input) print(list(x.parameters()))
可以看到共有4*3=12個filter 和一個1×4的bias 作用在這個(3,5,5)的單位矩陣上
## out輸出的結果 Variable containing: (0 ,0 ,.,.) = -0.6390 -0.6390 -0.6390 -0.6390 -0.6390 -0.6390 -0.6390 -0.6390 -0.6390 (0 ,1 ,.,.) = -0.1467 -0.1467 -0.1467 -0.1467 -0.1467 -0.1467 -0.1467 -0.1467 -0.1467 (0 ,2 ,.,.) = 0.4138 0.4138 0.4138 0.4138 0.4138 0.4138 0.4138 0.4138 0.4138 (0 ,3 ,.,.) = -0.3981 -0.3981 -0.3981 -0.3981 -0.3981 -0.3981 -0.3981 -0.3981 -0.3981 [torch.FloatTensor of size 1x4x3x3] ## x的參數設置 [Parameter containing: (0 ,0 ,.,.) = -0.0803 0.1473 -0.0762 0.0284 -0.0050 -0.0246 0.1438 0.0955 -0.0500 (0 ,1 ,.,.) = 0.0716 0.0062 -0.1472 0.1793 0.0543 -0.1764 -0.1548 0.1379 0.1143 (0 ,2 ,.,.) = -0.1741 -0.1790 -0.0053 -0.0612 -0.1856 -0.0858 -0.0553 0.1621 -0.1822 (1 ,0 ,.,.) = -0.0773 -0.1385 0.1356 0.1794 -0.0534 -0.1110 -0.0137 -0.1744 -0.0188 (1 ,1 ,.,.) = -0.0396 0.0149 0.1537 0.0846 -0.1123 -0.0556 -0.1047 -0.1783 -0.0630 (1 ,2 ,.,.) = 0.1850 0.0325 0.0332 -0.0487 0.0018 0.1668 0.0569 0.0267 0.0124 (2 ,0 ,.,.) = 0.1880 -0.0152 -0.1088 -0.0105 0.1805 -0.0343 -0.1676 0.1249 0.1872 (2 ,1 ,.,.) = 0.0299 0.0449 0.1179 0.1280 -0.1545 0.0593 -0.1489 0.1378 -0.1495 (2 ,2 ,.,.) = -0.0922 0.1873 -0.1163 0.0970 -0.0682 -0.1110 0.0614 -0.1877 0.1918 (3 ,0 ,.,.) = -0.1257 -0.0814 -0.1923 0.0048 -0.0789 -0.0048 0.0780 -0.0290 0.1287 (3 ,1 ,.,.) = -0.0649 0.0773 -0.0584 0.0092 -0.1168 -0.0923 0.0614 0.1159 0.0134 (3 ,2 ,.,.) = 0.0426 -0.1055 0.1022 -0.0810 0.0540 -0.1011 0.0698 -0.0799 -0.0786 [torch.FloatTensor of size 4x3x3x3] , Parameter containing: -0.1367 -0.0410 0.0424 0.1353 [torch.FloatTensor of size 4] ]
因為是單位矩陣,所以直接對參數用sum()來模擬卷積過程,結果-0.639065589142 與之前的out結果的(0 ,0 ,.,.) = -0.6390 相同, 即conv2d 是通過利用4組filters,每組filter對每個通道分別卷積相加得到結果。
f_p=list(x.parameters())[0] f_p=f_p.data.numpy() print(f_p[0].sum()+(-0.1367)) -0.639065589142
再更新
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
input=torch.ones(1,1,5,5)
input=Variable(input)
x=torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1,out_channels=3,kernel_size=3,groups=1)
out=x(input)
f_p=list(x.parameters())[0]
f_p=f_p.data.numpy()
f_b=list(x.parameters())[1]
f_b=f_b.data.numpy()
print("output result is:", out[0][0])
print("the result of first channel in image:", f_p[0].sum()+f_b[0])output result is: Variable containing:
0.6577 0.6577 0.6577
0.6577 0.6577 0.6577
0.6577 0.6577 0.6577
[torch.FloatTensor of size 3x3]
the result of first channel in image: 0.657724
input=torch.ones(1,3,5,5)
input=Variable(input)
print(input.size())
x=torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3,out_channels=4,kernel_size=3,groups=1)
out=x(input)
f_p=list(x.parameters())[0]
f_b=list(x.parameters())[1]
f_p=f_p.data.numpy()
f_b=f_b.data.numpy()
# print(f_p[...,0])
# print(f_p[...,0].shape)
# print(f_p[...,0].sum()+f_b[0])
print("output result :",out[0][0])
print("simlatuate the result:", f_p[0].sum()+f_b[0])torch.Size([1, 3, 5, 5])
output result : Variable containing:
-0.2087 -0.2087 -0.2087
-0.2087 -0.2087 -0.2087
-0.2087 -0.2087 -0.2087
[torch.FloatTensor of size 3x3]
simlatuate the result: -0.208715
感謝你能夠認真閱讀完這篇文章,希望小編分享的“Pytorch.nn.conv2d驗證方式的示例分析”這篇文章對大家有幫助,同時也希望大家多多支持億速云,關注億速云行業資訊頻道,更多相關知識等著你來學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。