您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹了Redis偶發連接失敗怎么辦,具有一定借鑒價值,感興趣的朋友可以參考下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章之后大有收獲,下面讓小編帶著大家一起了解一下。
前言
本文主要給大家介紹了關于Redis偶發連接失敗的相關內容,分享出來供大家參考學習,下面話不多說了,來一起看看詳細的介紹吧
【作者】
張延俊:攜程技術保障中心資深DBA,對數據庫架構和疑難問題分析排查有濃厚的興趣。
壽向晨:攜程技術保障中心高級DBA,主要負責攜程Redis及DB的運維工作,在自動化運維,流程化及監控排障等方面有較多的實踐經驗,喜歡深入分析問題,提高團隊運維效率。
【問題描述】
?生產環境有一個Redis會偶爾發生連接失敗的報錯,報錯的時間點、客戶端IP并沒有特別明顯的規律,過一會兒,報錯會自動恢復。
?以下是客戶端報錯信息:
CRedis.Client.RExceptions.ExcuteCommandException: Unable to Connect redis server: ---> CRedis.Third.Redis.RedisException: Unable to Connect redis server: 在 CRedis.Third.Redis.RedisNativeClient.CreateConnectionError() 在 CRedis.Third.Redis.RedisNativeClient.SendExpectData(Byte[][] cmdWithBinaryArgs) 在 CRedis.Client.Entities.RedisServer.<>c__DisplayClassd`1.
?從報錯的信息來看,應該是連接不上Redis所致。Redis的版本是2.8.19。雖然版本有點老,但基本運行穩定。
?線上環境只有這個集群有偶爾報錯。這個集群的一個比較明顯的特征是客戶端服務器比較多,有上百臺。
【問題分析】
?從報錯的信息來看,客戶端連接不到服務端。常見的原因有以下幾點:
一個常見的原因是由于端口耗盡,對網絡連接進行排查,在出問題的點上,TCP連接數遠沒有達到端口耗盡的場景,因此這個不是Redis連接不上的根本原因。
另外一種常見的場景是在服務端有慢查詢,導致Redis服務阻塞。我們在Redis服務端,把運行超過10毫秒的語句進行抓取,也沒有抓到運行慢的語句。
?從服務端的部署的監控來看,出問題的點上,連接數有一個突然飆升,從3500個連接突然飆升至4100個連接。如下圖顯示:
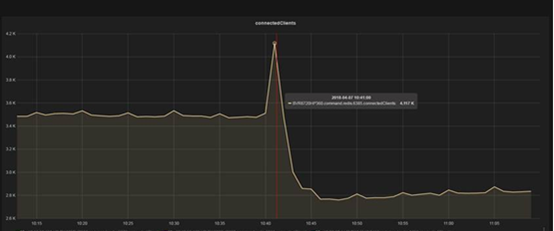
同時間,服務器端顯示Redis服務端有丟包現象:345539 – 344683 = 856個包。
Sat Apr 7 10:41:40 CST 2018 1699 outgoing packets dropped 92 dropped because of missing route 344683 SYNs to LISTEN sockets dropped 344683 times the listen queue of a socket overflowed
Sat Apr 7 10:41:41 CST 2018 1699 outgoing packets dropped 92 dropped because of missing route 345539 SYNs to LISTEN sockets dropped 345539 times the listen queue of a socket overflowed
?客戶端報錯的原因基本確定,是因為建連速度太快,導致服務端backlog隊列溢出,連接被server端reset。
【關于backlog overflow】
?在高并發的短連接服務中,這是一種很常見的tcp報錯類型。一個正常的tcp建連過程如下:
?1.client發送一個(SYN)給server
?2.server返回一個(SYN,ACK)給client
?3.client返回一個(ACK)
?三次握手結束,對client來說建連成功,client可以繼續發送數據包給server,但是這個時候server端未必ready,如下圖所示 :

在BSD版本內核實現的tcp協議中,server端建連過程需要兩個隊列,一個是SYN queue,一個是accept queue。前者叫半開連接(或者半連接)隊列,在接收到client發送的SYN時加入隊列。(一種常見的網絡攻擊方式就是不斷發送SYN但是不發送ACK從而導致server端的半開隊列撐爆,server端拒絕服務。)后者叫全連接隊列,server返回(SYN,ACK),在接收到client發送ACK后(此時client會認為建連已經完成,會開始發送PSH包),如果accept queue沒有滿,那么server從SYN queue把連接信息移到accept queue;如果此時accept queue溢出的話,server的行為要看配置。如果tcp_abort_on_overflow為0(默認),那么直接drop掉client發送的PSH包,此時client會進入重發過程,一段時間后server端重新發送SYN,ACK,重新從建連的第二步開始;如果tcp_abort_on_overflow為1,那么server端發現accept queue滿之后直接發送reset。
通過wireshark搜索發現在一秒內有超過2000次對Redis Server端發起建連請求。我們嘗試修改tcp backlog大小,從511調整到2048, 問題并沒有得到解決。所以此類微調,并不能徹底的解決問題。
【網絡包分析】
我們用wireshark來識別網絡擁塞的準確時間點和原因。我們已經有了準確的報錯時間點,先用editcap把超大的tcp包裁剪一下,裁成30秒間隔,并通過wireshark I/O 100ms間隔分析網絡阻塞的準確時間點:

?根據圖標可以明顯看到tcp的packets來往存在block。
?對該block前后的網絡包進行明細分析,網絡包來往情況如下:
| Time | Source | Dest | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ??12:01:54.6536050?? | ??Redis-Server?? | ??Clients?? | ??TCP:Flags=…AP… |
| ??12:01:54.6538580?? | ??Redis-Server?? | ??Clients?? | ??TCP:Flags=…AP… |
| ??12:01:54.6539770?? | ??Redis-Server?? | ??Clients?? | ??TCP:Flags=…AP… |
| ??12:01:54.6720580?? | ??Redis-Server?? | ??Clients?? | ??TCP:Flags=…A..S.. |
| ??12:01:54.6727200?? | ??Redis-Server?? | ??Clients?? | ??TCP:Flags=…A…… |
| ??12:01:54.6808480?? | ??Redis-Server?? | ??Clients?? | ??TCP:Flags=…AP….. |
| ??12:01:54.6910840?? | ??Redis-Server?? | ??Clients?? | ??TCP:Flags=…A…S., |
| ??12:01:54.6911950?? | ??Redis-Server?? | ??Clients?? | ??TCP:Flags=…A…… |
| ??… ?? | ??… ?? | ?? … ?? | ?? … |
| ??12:01:56.1181350?? | ??Redis-Server?? | ??Clients?? | ??TCP:Flags=…AP…. |
12:01:54.6808480, Redis Server端向客戶端發送了一個Push包,也就是對于查詢請求的一個結果返回。后面的包都是在做連接處理,包括Ack包,Ack確認包,以及重置的RST包,緊接著下面一個Push包是在12:01:56.1181350發出的。中間的間隔是1.4372870秒。也就是說,在這1.4372870秒期間,Redis的服務器端,除了做一個查詢,其他的操作都是在做建連,或拒絕連接。
客戶端報錯的前后邏輯已經清楚了,redis-server卡了1.43秒,client的connection pool被打滿,瘋狂新建連接,server的accept queue滿,直接拒絕服務,client報錯。開始懷疑client發送了特殊命令,這時需要確認一下client的最后幾個命令是什么,找到redis-server卡死前的第一個包,裝一個wireshark的redis插件,看到最后幾個命令是簡單的get,并且key-value都很小,不至于需要耗費1.43秒才能完成。服務端也沒有slow log,此時排障再次陷入僵局。
【進一步分析】
為了了解這1.43秒之內,Redis Server在做什么事情,我們用pstack來抓取信息。Pstack本質上是gdb attach. 高頻率的抓取會影響redis的吞吐。死循環0.5秒一次無腦抓,在redis-server卡死的時候抓到堆棧如下(過濾了沒用的棧信息):
Thu May 31 11:29:18 CST 2018
Thread 1 (Thread 0x7ff2db6de720 (LWP 8378)):
#0 0x000000000048cec4 in ?? ()
#1 0x00000000004914a4 in je_arena_ralloc ()
#2 0x00000000004836a1 in je_realloc ()
#3 0x0000000000422cc5 in zrealloc ()
#4 0x00000000004213d7 in sdsRemoveFreeSpace ()
#5 0x000000000041ef3c in clientsCronResizeQueryBuffer ()
#6 0x00000000004205de in clientsCron ()
#7 0x0000000000420784 in serverCron ()
#8 0x0000000000418542 in aeProcessEvents ()
#9 0x000000000041873b in aeMain ()
#10 0x0000000000420fce in main ()
Thu May 31 11:29:19 CST 2018
Thread 1 (Thread 0x7ff2db6de720 (LWP 8378)):
#0 0x0000003729ee5407 in madvise () from /lib64/libc.so.6
#1 0x0000000000493a4e in je_pages_purge ()
#2 0x000000000048cf70 in ?? ()
#3 0x00000000004914a4 in je_arena_ralloc ()
#4 0x00000000004836a1 in je_realloc ()
#5 0x0000000000422cc5 in zrealloc ()
#6 0x00000000004213d7 in sdsRemoveFreeSpace ()
#7 0x000000000041ef3c in clientsCronResizeQueryBuffer ()
#8 0x00000000004205de in clientsCron ()
#9 0x0000000000420784 in serverCron ()
#10 0x0000000000418542 in aeProcessEvents ()
#11 0x000000000041873b in aeMain ()
#12 0x0000000000420fce in main ()
Thu May 31 11:29:19 CST 2018
Thread 1 (Thread 0x7ff2db6de720 (LWP 8378)):
#0 0x000000000048108c in je_malloc_usable_size ()
#1 0x0000000000422be6 in zmalloc ()
#2 0x00000000004220bc in sdsnewlen ()
#3 0x000000000042c409 in createStringObject ()
#4 0x000000000042918e in processMultibulkBuffer ()
#5 0x0000000000429662 in processInputBuffer ()
#6 0x0000000000429762 in readQueryFromClient ()
#7 0x000000000041847c in aeProcessEvents ()
#8 0x000000000041873b in aeMain ()
#9 0x0000000000420fce in main ()
Thu May 31 11:29:20 CST 2018
Thread 1 (Thread 0x7ff2db6de720 (LWP 8378)):
#0 0x000000372a60e7cd in write () from /lib64/libpthread.so.0
#1 0x0000000000428833 in sendReplyToClient ()
#2 0x0000000000418435 in aeProcessEvents ()
#3 0x000000000041873b in aeMain ()
#4 0x0000000000420fce in main ()
重復多次抓取后,從堆棧中發現可疑堆棧clientsCronResizeQueryBuffer位置,屬于serverCron()函數下,這個redis-server內部的定時調度,并不在用戶線程下,這個解釋了為什么卡死的時候沒有出現慢查詢。
查看redis源碼,確認到底redis-server在做什么:
clientsCron(server.h):
#define CLIENTS_CRON_MIN_ITERATIONS 5
void clientsCron(void) {
/* Make sure to process at least numclients/server.hz of clients
* per call. Since this function is called server.hz times per second
* we are sure that in the worst case we process all the clients in 1
* second. */
int numclients = listLength(server.clients);
int iterations = numclients/server.hz;
mstime_t now = mstime();
/* Process at least a few clients while we are at it, even if we need
* to process less than CLIENTS_CRON_MIN_ITERATIONS to meet our contract
* of processing each client once per second. */
if (iterations < CLIENTS_CRON_MIN_ITERATIONS)
iterations = (numclients < CLIENTS_CRON_MIN_ITERATIONS) ?
numclients : CLIENTS_CRON_MIN_ITERATIONS;
while(listLength(server.clients) && iterations--) {
client *c;
listNode *head;
/* Rotate the list, take the current head, process.
* This way if the client must be removed from the list it's the
* first element and we don't incur into O(N) computation. */
listRotate(server.clients);
head = listFirst(server.clients);
c = listNodeValue(head);
/* The following functions do different service checks on the client.
* The protocol is that they return non-zero if the client was
* terminated. */
if (clientsCronHandleTimeout(c,now)) continue;
if (clientsCronResizeQueryBuffer(c)) continue;
}
}clientsCron首先判斷當前client的數量,用于控制一次清理連接的數量,生產服務器單實例的連接數量在5000不到,也就是一次清理的連接數是50個。
clientsCronResizeQueryBuffer(server.h):
/* The client query buffer is an sds.c string that can end with a lot of
* free space not used, this function reclaims space if needed.
*
* The function always returns 0 as it never terminates the client. */
int clientsCronResizeQueryBuffer(client *c) {
size_t querybuf_size = sdsAllocSize(c->querybuf);
time_t idletime = server.unixtime - c->lastinteraction;
/* 只在以下兩種情況下會Resize query buffer:
* 1) Query buffer > BIG_ARG(在server.h 中定義#define PROTO_MBULK_BIG_ARG (1024*32))
且這個Buffer的小于一段時間的客戶端使用的峰值.
* 2) 客戶端空閑超過2s且Buffer size大于1k. */
if (((querybuf_size > PROTO_MBULK_BIG_ARG) &&
(querybuf_size/(c->querybuf_peak+1)) > 2) ||
(querybuf_size > 1024 && idletime > 2))
{
/* Only resize the query buffer if it is actually wasting space. */
if (sdsavail(c->querybuf) > 1024) {
c->querybuf = sdsRemoveFreeSpace(c->querybuf);
}
}
/* Reset the peak again to capture the peak memory usage in the next
* cycle. */
c->querybuf_peak = 0;
return 0;
}如果redisClient對象的query buffer滿足條件,那么就直接resize掉。滿足條件的連接分成兩種,一種是真的很大的,比該客戶端一段時間內使用的峰值還大;還有一種是很閑(idle>2)的,這兩種都要滿足一個條件,就是buffer free的部分超過1k。那么redis-server卡住的原因就是正好有那么50個很大的或者空閑的并且free size超過了1k大小連接的同時循環做了resize,由于redis都屬于單線程工作的程序,所以block了client。那么解決這個問題辦法就很明朗了,讓resize 的頻率變低或者resize的執行速度變快。
既然問題出在query buffer上,我們先看一下這個東西被修改的位置:
readQueryFromClient(networking.c):
redisClient *createClient(int fd) {
redisClient *c = zmalloc(sizeof(redisClient));
/* passing -1 as fd it is possible to create a non connected client.
* This is useful since all the Redis commands needs to be executed
* in the context of a client. When commands are executed in other
* contexts (for instance a Lua script) we need a non connected client. */
if (fd != -1) {
anetNonBlock(NULL,fd);
anetEnableTcpNoDelay(NULL,fd);
if (server.tcpkeepalive)
anetKeepAlive(NULL,fd,server.tcpkeepalive);
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,fd,AE_READABLE,
readQueryFromClient, c) == AE_ERR)
{
close(fd);
zfree(c);
return NULL;
}
}
selectDb(c,0);
c->id = server.next_client_id++;
c->fd = fd;
c->name = NULL;
c->bufpos = 0;
c->querybuf = sdsempty(); 初始化是0
readQueryFromClient(networking.c):
void readQueryFromClient(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
redisClient *c = (redisClient*) privdata;
int nread, readlen;
size_t qblen;
REDIS_NOTUSED(el);
REDIS_NOTUSED(mask);
server.current_client = c;
readlen = REDIS_IOBUF_LEN;
/* If this is a multi bulk request, and we are processing a bulk reply
* that is large enough, try to maximize the probability that the query
* buffer contains exactly the SDS string representing the object, even
* at the risk of requiring more read(2) calls. This way the function
* processMultiBulkBuffer() can avoid copying buffers to create the
* Redis Object representing the argument. */
if (c->reqtype == REDIS_REQ_MULTIBULK && c->multibulklen && c->bulklen != -1
&& c->bulklen >= REDIS_MBULK_BIG_ARG)
{
int remaining = (unsigned)(c->bulklen+2)-sdslen(c->querybuf);
if (remaining < readlen) readlen = remaining;
}
qblen = sdslen(c->querybuf);
if (c->querybuf_peak < qblen) c->querybuf_peak = qblen;
c->querybuf = sdsMakeRoomFor(c->querybuf, readlen); 在這里會被擴大由此可見c->querybuf在連接第一次讀取命令后的大小就會被分配至少1024*32,所以回過頭再去看resize的清理邏輯就明顯存在問題,每個被使用到的query buffer的大小至少就是1024*32,但是清理的時候判斷條件是>1024,也就是說,所有的idle>2的被使用過的連接都會被resize掉,下次接收到請求的時候再重新分配到1024*32,這個其實是沒有必要的,在訪問比較頻繁的群集,內存會被頻繁得回收重分配,所以我們嘗試將清理的判斷條件改造為如下,就可以避免大部分沒有必要的resize操作:
if (((querybuf_size > REDIS_MBULK_BIG_ARG) &&
(querybuf_size/(c->querybuf_peak+1)) > 2) ||
(querybuf_size > 1024*32 && idletime > 2))
{
/* Only resize the query buffer if it is actually wasting space. */
if (sdsavail(c->querybuf) > 1024*32) {
c->querybuf = sdsRemoveFreeSpace(c->querybuf);
}
}這個改造的副作用是內存的開銷,按照一個實例5k連接計算,5000*1024*32=160M,這點內存消耗對于上百G內存的服務器完全可以接受。
【問題重現】
在使用修改過源碼的Redis server后,問題仍然重現了,客戶端還是會報同類型的錯誤,且報錯的時候,服務器內存依然會出現抖動。抓取內存堆棧信息如下:
Thu Jun 14 21:56:54 CST 2018
#3 0x0000003729ee893d in clone () from /lib64/libc.so.6
Thread 1 (Thread 0x7f2dc108d720 (LWP 27851)):
#0 0x0000003729ee5400 in madvise () from /lib64/libc.so.6
#1 0x0000000000493a1e in je_pages_purge ()
#2 0x000000000048cf40 in arena_purge ()
#3 0x00000000004a7dad in je_tcache_bin_flush_large ()
#4 0x00000000004a85e9 in je_tcache_event_hard ()
#5 0x000000000042c0b5 in decrRefCount ()
#6 0x000000000042744d in resetClient ()
#7 0x000000000042963b in processInputBuffer ()
#8 0x0000000000429762 in readQueryFromClient ()
#9 0x000000000041847c in aeProcessEvents ()
#10 0x000000000041873b in aeMain ()
#11 0x0000000000420fce in main ()
Thu Jun 14 21:56:54 CST 2018
Thread 1 (Thread 0x7f2dc108d720 (LWP 27851)):
#0 0x0000003729ee5400 in madvise () from /lib64/libc.so.6
#1 0x0000000000493a1e in je_pages_purge ()
#2 0x000000000048cf40 in arena_purge ()
#3 0x00000000004a7dad in je_tcache_bin_flush_large ()
#4 0x00000000004a85e9 in je_tcache_event_hard ()
#5 0x000000000042c0b5 in decrRefCount ()
#6 0x000000000042744d in resetClient ()
#7 0x000000000042963b in processInputBuffer ()
#8 0x0000000000429762 in readQueryFromClient ()
#9 0x000000000041847c in aeProcessEvents ()
#10 0x000000000041873b in aeMain ()
#11 0x0000000000420fce in main ()
顯然,Querybuffer被頻繁resize的問題已經得到了優化,但是還是會出現客戶端報錯。這就又陷入了僵局。難道還有其他因素導致query buffer resize變慢?我們再次抓取pstack。但這時,jemalloc引起了我們的注意。此時回想Redis的內存分配機制,Redis為避免libc內存不被釋放導致大量內存碎片的問題,默認使用的是jemalloc用作內存分配管理,這次報錯的堆棧信息中都是je_pages_purge () redis在調用jemalloc回收臟頁。我們看下jemalloc做了些什么:
arena_purge(arena.c)
static void
arena_purge(arena_t *arena, bool all)
{
arena_chunk_t *chunk;
size_t npurgatory;
if (config_debug) {
size_t ndirty = 0;
arena_chunk_dirty_iter(&arena->chunks_dirty, NULL,
chunks_dirty_iter_cb, (void *)&ndirty);
assert(ndirty == arena->ndirty);
}
assert(arena->ndirty > arena->npurgatory || all);
assert((arena->nactive >> opt_lg_dirty_mult) < (arena->ndirty -
arena->npurgatory) || all);
if (config_stats)
arena->stats.npurge++;
npurgatory = arena_compute_npurgatory(arena, all);
arena->npurgatory += npurgatory;
while (npurgatory > 0) {
size_t npurgeable, npurged, nunpurged;
/* Get next chunk with dirty pages. */
chunk = arena_chunk_dirty_first(&arena->chunks_dirty);
if (chunk == NULL) {
arena->npurgatory -= npurgatory;
return;
}
npurgeable = chunk->ndirty;
assert(npurgeable != 0);
if (npurgeable > npurgatory && chunk->nruns_adjac == 0) {
arena->npurgatory += npurgeable - npurgatory;
npurgatory = npurgeable;
}
arena->npurgatory -= npurgeable;
npurgatory -= npurgeable;
npurged = arena_chunk_purge(arena, chunk, all);
nunpurged = npurgeable - npurged;
arena->npurgatory += nunpurged;
npurgatory += nunpurged;
}
}Jemalloc每次回收都會判斷所有實際應該清理的chunck并對清理做count,這個操作對于高響應要求的系統是很奢侈的,所以我們考慮通過升級jemalloc的版本來優化purge的性能。Redis 4.0版本發布后,性能有很大的改進,并可以通過命令回收內存,我們線上也正準備進行升級,跟隨4.0發布的jemalloc版本為4.1,jemalloc的版本使用的在jemalloc的4.0之后版本的arena_purge()做了很多優化,去掉了計數器的調用,簡化了很多判斷邏輯,增加了arena_stash_dirty()方法合并了之前的計算和判斷邏輯,增加了purge_runs_sentinel,用保持臟塊在每個arena LRU中的方式替代之前的保持臟塊在arena樹的dirty-run-containing chunck中的方式,大幅度減少了臟塊purge的體積,并且在內存回收過程中不再移動內存塊。代碼如下:
arena_purge(arena.c)
static void
arena_purge(arena_t *arena, bool all)
{
chunk_hooks_t chunk_hooks = chunk_hooks_get(arena);
size_t npurge, npurgeable, npurged;
arena_runs_dirty_link_t purge_runs_sentinel;
extent_node_t purge_chunks_sentinel;
arena->purging = true;
/*
* Calls to arena_dirty_count() are disabled even for debug builds
* because overhead grows nonlinearly as memory usage increases.
*/
if (false && config_debug) {
size_t ndirty = arena_dirty_count(arena);
assert(ndirty == arena->ndirty);
}
assert((arena->nactive >> arena->lg_dirty_mult) < arena->ndirty || all);
if (config_stats)
arena->stats.npurge++;
npurge = arena_compute_npurge(arena, all);
qr_new(&purge_runs_sentinel, rd_link);
extent_node_dirty_linkage_init(&purge_chunks_sentinel);
npurgeable = arena_stash_dirty(arena, &chunk_hooks, all, npurge,
&purge_runs_sentinel, &purge_chunks_sentinel);
assert(npurgeable >= npurge);
npurged = arena_purge_stashed(arena, &chunk_hooks, &purge_runs_sentinel,
&purge_chunks_sentinel);
assert(npurged == npurgeable);
arena_unstash_purged(arena, &chunk_hooks, &purge_runs_sentinel,
&purge_chunks_sentinel);
arena->purging = false;
}【解決問題】
實際上我們有多個選項。可以使用Google的tcmalloc來代替jemalloc,可以升級jemalloc的版本等等。我們根據上面的分析,嘗試通過升級jemalloc版本,實際操作為升級Redis版本來解決。我們將Redis的版本升級到4.0.9之后觀察,線上客戶端連接超時這個棘手的問題得到了解決。
【問題總結】
Redis在生產環境中因其支持高并發,響應快,易操作被廣泛使用,對于運維人員而言,其響應時間的要求帶來了各種各樣的問題,Redis的連接超時問題是其中比較典型的一種,從發現問題,客戶端連接超時,到通過抓取客戶端與服務端的網絡包,內存堆棧定位問題,也被其中一些假象所迷惑,最終通過升級jemalloc(Redis)的版本解決問題,這次最值得總結和借鑒的是整個分析的思路。
感謝你能夠認真閱讀完這篇文章,希望小編分享的“Redis偶發連接失敗怎么辦”這篇文章對大家有幫助,同時也希望大家多多支持億速云,關注億速云行業資訊頻道,更多相關知識等著你來學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。