您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
1、正則表達式:用一串字符驗證是否符合一種規范,這個規范就是正則表達式。
2、正則表達式中常用的元字符:
. 匹配除換行符以外的任意字符
\w 匹配字母或數字或下劃線或漢字
\s 匹配空白符
\d 匹配數字
\b 匹配單詞的開始或結束
^ 匹配字符串的開始
$ 匹配字符串的結束
例: string regstr = @"^\d\d\d$";
Regex reg = new Regex(regstr);
string intputstr = "163";
if (reg.IsMatch(intputstr))
{
Console.WriteLine("正確");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("錯誤");
}
注意:添加命名空間
3、正則表達式中的轉義字符:
一般字符 除.$^{}[(|)*+?\外,其他字符與自身匹配
\a 與響鈴匹配
\b 轉義字符\b是一個特例。在正則表達式中,\b表示單詞邊界(在\w和\W之間),不過,在[]字符類中,\b表示退格符。在替換模式中,\b始終表示退格符。
\t 與Tab符匹配
\r 與回車符匹配
\v 與垂直符匹配
\f 與換頁符匹配
\n 與換行符匹配
\e 與Esc符匹配
\ 在后面帶有不識別為轉義字符時,與該字符匹配
例:string regstr = @"^0\d{2}-\d{8}$";
Regex reg = new Regex(regstr);
string intputstr = "010-99999999";
if (reg.IsMatch(intputstr))
{
Console.WriteLine("正確");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("錯誤");
}
4、正則表達式中的重復:
* 重復零次或更多次
+ 重復一次或更多次
? 重復一次或零次
{n} 重復n次
{n,}重復n次或更多次
{n,m}重復n到m次,m不能小于n
5、字符類:
[abcde]匹配a,b,c,d,e中的任一個字符
[0-9]含義與\d相同,匹配任意數字
[a-z0-9A-Z]含義與\w相同,匹配數字,字母,下劃線
例:電話號碼的驗證
string regstr = @"^\(?0\d{2}[) -]?\d{8}$";
Regex reg = new Regex(regstr);
string intputstr = "010-22222222";
if (reg.IsMatch(intputstr))
{
Console.WriteLine("正確");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("錯誤");
}
說明:^開始標記
\(?表示(可出現0次和一次
0表示本身
\d{2}表示數字出現兩次
[) -]?表示在),空格,-中的一個字符出現0次或一次
\d{8}8個數字
$結束標記
6、分支條件:指有幾種規則,如果滿足其中任意一種規則都應該當成匹配,具體方法是用|把不同的規則分隔開。
例:電話號碼驗證
string regstr = @"^\(0\d{2}\)[- ]?\d{8}$|^0\d{2}[- ]?\d{8}$";
Regex reg = new Regex(regstr);
string intputstr = "(010)-22222222";
if (reg.IsMatch(intputstr))
{
Console.WriteLine("正確");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("錯誤");
}
說明:條件的匹配是從左到右的,第一個匹配成功,就不再匹配第二個條件。
^\(0\d{2}\)[- ]?\d{8}$|^匹配(010)-22222222或(010) 22222222
^0\d{2}[- ]?\d{8}$匹配010-22222222或010 22222222
7、分組表達式:單個字符的重復可以用限定符來實現,比如\d?是一個整數出現一次或不出現
string regstr = @"^(([01]?\d\d?|2[0-4]\d|25[0-5])\.){3}([01]?\d\d?|2[0-4]\d|25[0-5])$";
Regex reg = new Regex(regstr);
string intputstr = "001.020.030.040";
if (reg.IsMatch(intputstr))
{
Console.WriteLine("正確");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("錯誤");
}
說明:IP地址是0到255每個段,前三節數字后都有一個“.”所以可以分組。這個三個數字中,百位只能是0,1,2,當是0或1時,十位,個位什么數字都可以,當百位為2時,十位不能超過5,當十為5時,個位不能超過5,所以可以這樣分組,當百位為0和1時分一組,當百位為2時,十位為5時分一組,當百位為2,十位為0到4時,個位什么都可以分一組,共三組。
8、反義:
\W 匹配任意不是字母,數字下劃線,漢字的字符
\S 匹配任意不是空白符的字符
\D 匹配任意非數字的字符
\B 匹配不是單詞開頭或結束的位置
[^x] 匹配除了x以外的任意字符
[^aeiou]匹配除了aeiou這幾個字母以外的任意字符
9、后向引用:如果有分組的話,每個分組會自動有一個組號,從|開始連續排下來,也可以給組來命名代替組號。
例:string regstr = @”^(\d)(-)\1\2$”; //可以用命名來代替string regstr = @“^(?<gsw>\d)(-)\k<gsw>\1$”;如果第一個組用命名,第二個的組號從1開始。也可以把<>換成’
Regex reg = new Regex(regstr);
string intputstr = "1-1-";
if (reg.IsMatch(intputstr))
{
Console.WriteLine("正確");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("錯誤");
}
說明:給組命名格式為:(?<組名>或(?’組名’
后向引有時用\k<組名>或 \k’組名’
10、零寬斷言:在某個位職,判斷是否滿足一定條件
(1)零寬度正預測先行斷言:斷言自身出現的位置的后面能匹配表達式
例:static void Main(string[] args)
{
string regstr = @"\b\w+(?=ing\b)";
Regex reg = new Regex(regstr);
string intputstr = "this eating jumping";
Match mat = reg.Match(intputstr);
Print(mat);
}
static void Print(Match match)
{
if (match.Value != "")
{
Console.WriteLine("匹配值:{0},匹配位置:{1}", match.Value, match.Index);
Print(match .NextMatch());
}
}
說明:?=匹配以ing結尾的單詞
(2)零寬度正回顧后發斷言:斷言自身出現的位置的前面能匹配表達式
例:static void Main(string[] args)
{
string regstr = @"(?<=<(a)\s.*>).*(?=<\/\1>)";
Regex reg = new Regex(regstr);
string intputstr = "<a >必應</a>";
Match mat = reg.Match(intputstr);
Print(mat);
}
static void Print(Match match)
{
if (match.Value != "")
{
Console.WriteLine("匹配值:{0},匹配位置:{1}", match.Value, match.Index);
Print(match .NextMatch());
}
}}
說明:?<=匹配以<a >開頭以</a>結尾的標簽
(3)零寬度負預測先行斷言:斷言此位置的后面不能匹配表達式
例: static void Main(string[] args)
{
string regstr = @"\b\w*th(?!a)\w*\b";
Regex reg = new Regex(regstr);
string intputstr = "this toothache tooth";
Match mat = reg.Match(intputstr);
Print(mat);
}
static void Print(Match match)
{
if (match.Value != "")
{
Console.WriteLine("匹配值:{0},匹配位置:{1}", match.Value, match.Index);
Print(match .NextMatch());
}
}
說明:?!匹配以非表達式的單詞
(4)零寬度負回顧后發斷言:斷言此位置前面不能匹配表達式
例:static void Main(string[] args)
{
string regstr = @"\b\w*(?<!a)th\w*\b";
Regex reg = new Regex(regstr);
string intputstr = "this toothache tooth";
Match mat = reg.Match(intputstr);
Print(mat);
}
static void Print(Match match)
{
if (match.Value != "")
{
Console.WriteLine("匹配值:{0},匹配位置:{1}", match.Value, match.Index);
Print(match .NextMatch());
}
}
說明:?<!匹配以非表達式的單詞
11、注釋:?#注釋內容
注意:注釋不能加到一個表達式之間
12、后向引用的分類如圖:
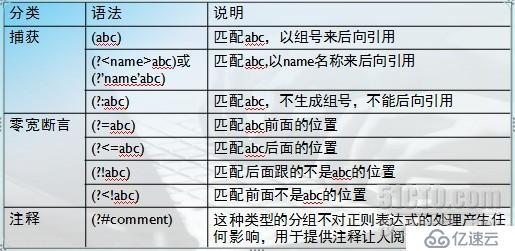
13、精確匹配與模糊匹配:模糊匹配是以從開頭到結尾,精確匹配是一個離開始最近的結尾字符匹配
*? 重復任意次,但盡可能少重復
+? 重復一次或更多次,但盡可能少重復
?? 重復0次或一次,但盡量少重復
{n,m} 重復n到m次,但盡量少重復
{n,} 重復n次以上,但盡量少重復
例:static void Main(string[] args)
{
string regstr = @”\bt.*s\b”;//模糊匹配,@“\bt.*?s\b”;精確匹配
Regex reg = new Regex(regstr);
string intputstr = “Children eat lunch at an orphanage being used by the U.N. children‘s agency UNICEF for Haitian children separated from parents after last month’s earthquake”;
Match mat = reg.Match(intputstr);
Print(mat);
}
static void Print(Match match)
{
if (match.Value != "")
{
Console.WriteLine("匹配值:{0},匹配位置:{1}", match.Value, match.Index);
Print(match .NextMatch());
}
}
14、泛型
(1)使用泛型類型可以最大限度地重用代碼、保護類型的安全以及提高性能。
(2)泛型最常見的用途是創建集合類。
(3).NET Framework 類庫在 System.Collections.Generic 命名空間中包含幾個新的泛型集合類。應盡可能地使用這些類來代替普通的類,如 System.Collections 命名空間中的 ArrayList。
(4)您可以創建自己的泛型接口、泛型類、泛型方法、泛型事件和泛型委托。
(5)可以對泛型類進行約束以訪問特定數據類型的方法。
(6)關于泛型數據類型中使用的類型的信息可在運行時通過使用反射獲取。
類型參數命名準則:
(1)務必使用描述性名稱命名泛型類型參數
(2)考慮使用T作為具有單個字母類型參數的類型的類型參數名
(3)務必將T作為描述性類型參數名的前綴
(4)考慮在參數名中指示對此類型參數的約束
泛型方法:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintType<int>(5);
PrintType<bool>(true);
PrintType<string>("泛型真偉大");
PrintType(1.2); //省略類型參數,編譯器會自動推導出是double類型,這里要注意,編譯器是根據參數的類型推導出類型參數的,如果方法沒有參數,編譯器是無法推導出來的。
}
static void PrintType<T>(T i)
{
Console.WriteLine("類型:{0,-20} 值:{1}",i.GetType (),i);
}
說明:此時的泛型方法,有點類似于方法重載中參數類型不同,個數相同的情況,如果用泛型實現,大大減少了代碼。
15、泛型約束:在定義泛型類時,可以對客戶端代碼能夠在實例化類時用于類型參數的類型種類施加限制。如果客戶端代碼嘗試使用某個約束所不允許的類型來實例化類,則會產生編譯時錯誤。約束是用where上下文關鍵字指定的。
下面是幾種約束的類型:
(1)T:結構 類型參數必須是值類型。可以指定除以外的任何值類型。
(2)T:類 類型參數必須是引用類型;這一點也適用于任何類、接口、委托或數組類型。
(3)T:new() 類型參數必須是引用類型;這一點也適用于任何類、接口、委托或數組類型。
(4)T:<基類名> 類型參數必須是指定的基類或派生自指定的基類。
(5)T:<接口名稱> 類型參數必須是指定的接口或實現指定的接口。可以指定多個接口約束。約束接口也可以是泛型的。
(6)T:U 為 T 提供的類型參數必須是為 U 提供的參數或派生自為 U 提供的參數。這稱為裸類型約束。
例1:
T:結構
類型參數必須是值類型。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintType<int>(5); //正確的寫法
PrintType<string>(“泛型真偉大”); //錯誤的寫法
}
static void PrintType<T>(T i) where T: struct
{
Console.WriteLine("類型:{0,-20} 值:{1}",i.GetType (),i);
}
例2:
T:類
類型參數必須是引用類型;這一點也適用于任何類、接口、委托或數組類型。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintType<int>(5); //錯誤的寫法
PrintType<string>(“泛型真偉大”); //正確的寫法
}
static void PrintType<T>(T i) where T: class
{
Console.WriteLine("類型:{0,-20} 值:{1}",i.GetType (),i);
}
例3:
T:new()
類型參數必須具有無參數的公共構造函數。當與其他約束一起使用時,new() 約束必須最后指定。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintType<Demo>(new Demo());
}
static void PrintType<T>(T i) where T: new()
{
Console.WriteLine("類型:{0,-20} 值:{1}",i.GetType (),i);
}
}
class Demo
{
}
例4:
T:<基類名>
類型參數必須是指定的基類或派生自指定的基類。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintType<Demo>(new Demo1()); //正確
PrintType<Demo>(new Demo()); //正確
PrintType<Demo1>(new Demo1()); //正確
PrintType<Demo2>(new Demo2()); //錯誤
}
static void PrintType<T>(T i) where T:Demo
{
Console.WriteLine("類型:{0,-20} 值:{1}",i.GetType (),i);
}
}
class Demo
{}
class Demo1 : Demo
{}
class Demo2
{}
例5:
T:<接口名稱>
類型參數必須是指定的接口或實現指定的接口。可以指定多個接口約束。約束接口也可以是泛型的。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintType<IDemo>(new Demo()); //正確
PrintType<Demo>(new Demo()); //正確
}
static void PrintType<T>(T i) where T : IDemo
{
Console.WriteLine("類型:{0,-20} 值:{1}", i.GetType(), i);
}
}
interface IDemo
{ }
class Demo : IDemo
{ }
例6:
T:U
為 T 提供的類型參數必須是為 U 提供的參數或派生自為 U 提供的參數。這稱為裸類型約束。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintType<IDemo,Demo>(new Demo()); //錯誤
PrintType<Demo,IDemo>(new Demo()); //正確
PrintType<Demo, Demo>(new Demo()); //正確
}
static void PrintType<T,U>(T i) where T : U
{
Console.WriteLine("類型:{0,-20} 值:{1}", i.GetType(), i);
}
}
interface IDemo
{ }
class Demo : IDemo
{ }
也可以對同一類型參數應用多個約束,并且約束自身可以是泛型類型
如下所示:
static void PrintType<T>(T i) where T : class ,new ()
{
Console.WriteLine("類型:{0,-20} 值:{1}", i.GetType(), i);
}
16、泛型類:泛型類封裝不是特定于具體數據類型的操作。泛型類最常用于集合,如鏈接列表、哈希表、堆棧、隊列、樹等。像從集合中添加和移除項這樣的操作都以大體上相同的方式執行,與所存儲數據的類型無關。一般情況下,創建泛型類的過程為:從一個現有的具體類開始,逐一將每個類型更改為類型參數,直至達到通用化和可用性的最佳平衡。
創建自己的泛型類時應注意:
(1)將哪些類型通用化為類型參數。
(2)通常,能夠參數化的類型越多,代碼就會變得越靈活,重用性就越好。但是,太多的通用化會使其他開發人員難以閱讀或理解代碼。
(3)如果存在約束,應對類型參數應用什么約束。一條有用的規則是,應用盡可能最多的約束,但仍使您能夠處理必須處理的類型。例如,如果您知道您的泛型類僅用于引用類型,則應用類約束。這可以防止您的類被意外地用于值類型,并允許您對 T 使用 as 運算符以及檢查空值。
(4)是否將泛型行為分解為基類和子類。由于泛型類可以作為基類使用,此處適用的設計注意事項與非泛型類相同。
(5)是否實現一個或多個泛型接口。
17、default:此關鍵字對于引用類型會返回 null,對于數值類型會返回零。對于結構,此關鍵字將返回初始化為零或 null 的每個結構成員,具體取決于這些結構是值類型還是引用類型
18、程序:定義一個自己的泛型類
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections;
namespace Day1302
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyList<int> list = new MyList<int>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
list.remove(3);
foreach(int i in list)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
}
}
class MyList<T> : IEnumerable
{
T[] t = new T[0];
int count;
public int Count
{
get
{
return count;
}
}
public T this[int index]
{
get
{
if (index > count)
{
throw new Exception("超出索引!");
}
else
{
return t[index];
}
}
set
{
if (index < count)
{
t[index] = value;
}
else
{
throw new Exception("超出索引!");
}
}
}
public MyList()
{ }
public MyList(int capacipy)
{
t=new T[capacipy];
}
public int Capacipy
{
get
{
return t.Length;
}
set
{
if (value < count)
{
throw new Exception("容量小于元素個數!");
}
else
{
T[] t1=new T[value];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
t1[i]=t[i];
}
t1 = t;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 添加
/// </summary>
/// <param name="t2"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int add(T t2)
{
if (t.Length == 0)
{
t = new T[4];
t[0] = t2;
count++;
return 0;
}
else if (count < t.Length)
{
t[count] = t2;
count++;
return count - 1;
}
else
{
T[] t3=new T[t.Length*2];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
t3[i] = t[i];
}
t3[count] = t2;
count++;
t = t3;
return count - 1;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 移除元素
/// </summary>
/// <param name="t2"></param>
public void remove(T t2)
{
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
if (t[i].Equals(t2))
{
index = i;
}
}
if (index != -1)
{
for (int i = index; i < count-1; i++)
{
t[i] = t[i + 1];
}
t[count-1]=default(T);
count--;
}
}
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
yield return t[i];
}
}
}
}
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。